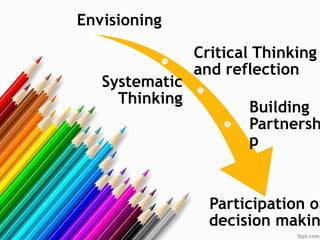
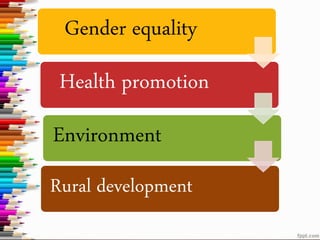
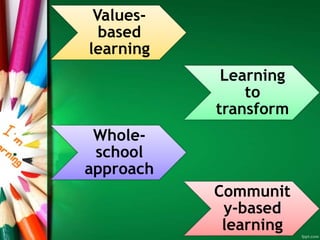
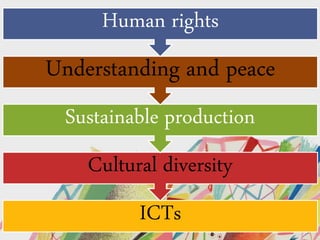
The document discusses Education for Sustainable Development (ESD). It aims to open awareness of globalization, nurture problem-solving skills, and provide education for all as a human right. ESD has three components - environment, economic, and social. It affects sustainability through an educated citizenry for implementation, decision-making, and improving quality of life. The UN Decade of ESD from 2005-2014 aimed to integrate sustainability principles into education worldwide.