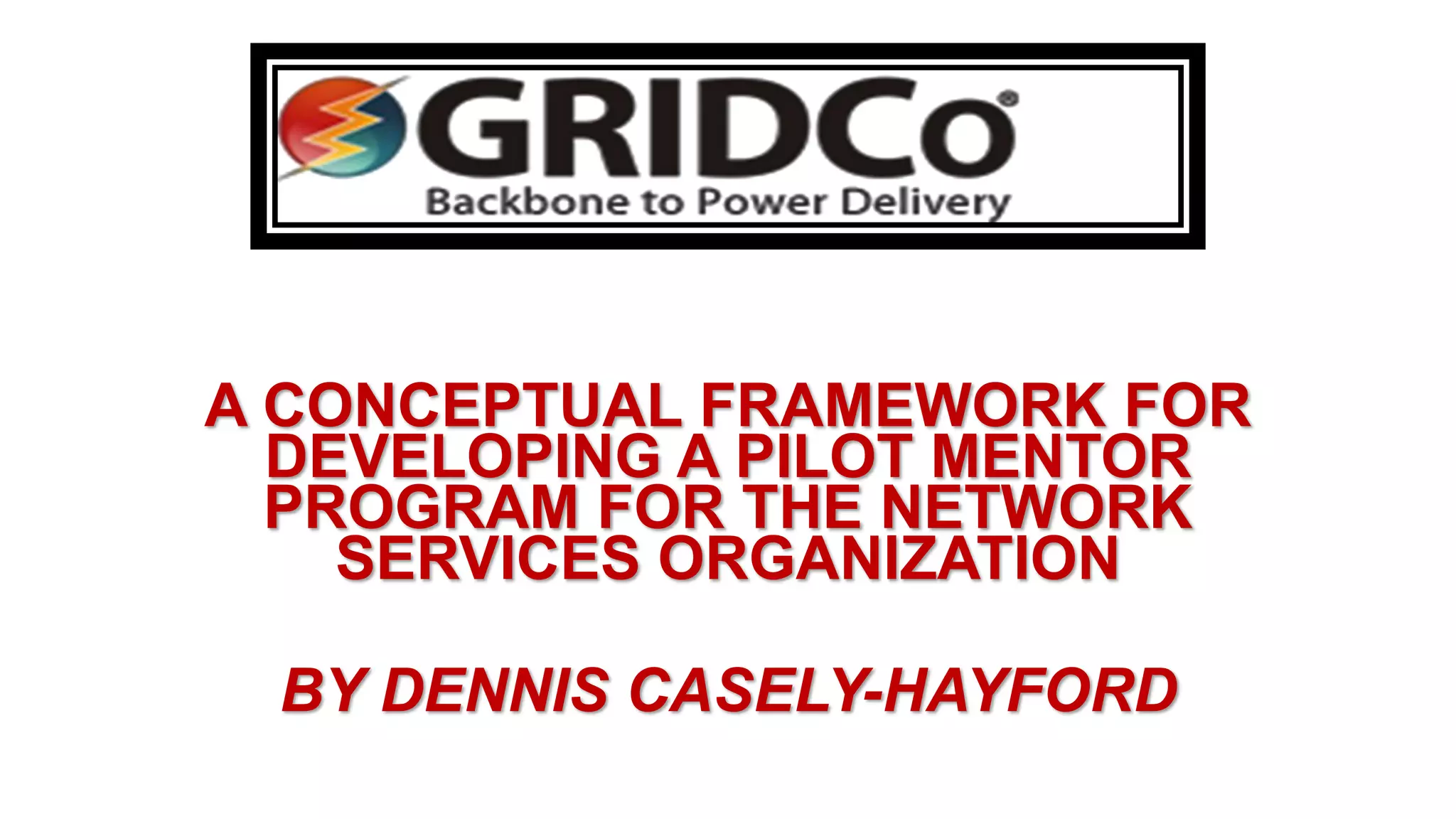
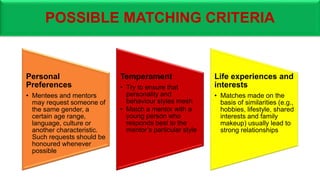
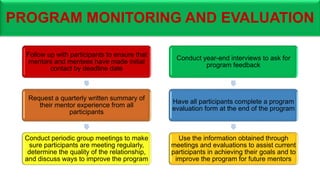
The document proposes a conceptual framework for a pilot mentor program at GRIDCo. The program would pair 20-25 new engineer and technician hires with mentors. The objectives are to assist mentees' professional development through coaching, challenging assignments, and exposure. Benefits include improving skills, motivation, and knowledge transfer. The framework defines mentor and mentee roles and responsibilities, and provides guidelines for recruitment, matching, meetings, and program management. The goal is to evaluate the pilot program before expanding it organization-wide.