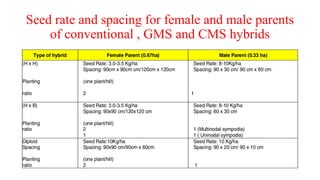
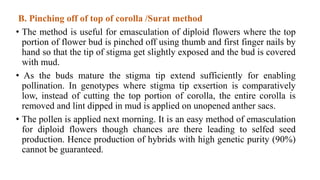
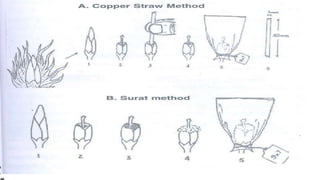
India is the pioneer in commercial cotton hybrid cultivation, which covers over 50% of cotton area and yields 50% higher productivity than varieties. Hybrids have wider adaptability, higher resistance to stresses, and better fiber quality. They can be developed faster than varieties. Hybrid seed production in India is done through conventional hand emasculation and pollination or non-conventional male sterility-based methods. Conventional hybrids require identifying male and female parents and emasculating female parents before pollination. Male sterility-based hybrids eliminate emasculation since female parents produce no pollen. Proper agronomic practices like isolation distances, fertilizer use, plant protection measures are required for high quality hybrid seed production