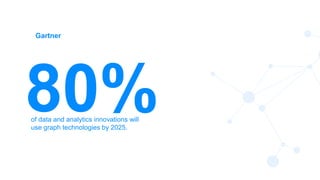
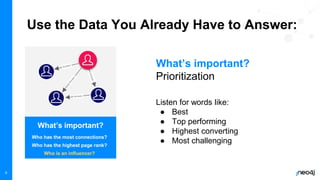
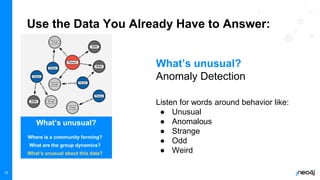
The document discusses the significance of graph data science in enhancing fraud detection, projecting that 80% of data innovations will utilize graph technologies by 2025. It details how traditional data approaches struggle with identifying relationships and anomalies, whereas graph algorithms significantly improve detection capabilities, exemplified by Banking Circle's 300% increase in fraud detection rates. Types of fraud addressed include credit card fraud, identity theft, and more, with next steps provided for further resources.