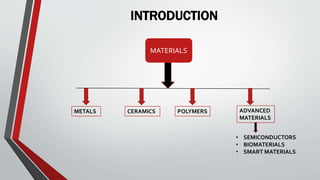
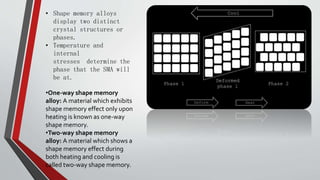
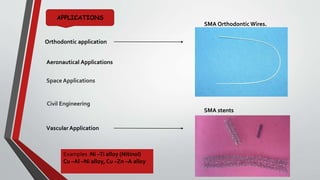
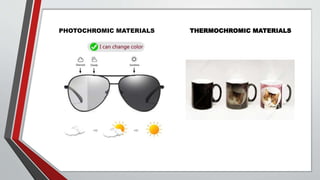
This document discusses smart materials, which are materials that can sense and respond to environmental stimuli in predetermined ways. It defines smart materials and provides examples of types, including piezoelectric materials, shape memory alloys, shape memory polymers, ferrofluids, and photochromic and thermochromic materials. Piezoelectric materials generate electric currents when mechanically stressed and can be used for power generation or sensors. Shape memory alloys remember their original shape and can return to it after deformation at low temperatures. The document outlines several applications for smart materials and also notes some limitations, such as response times, toxicity, stability, and cost.