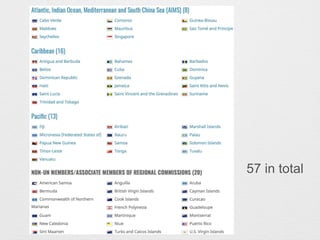
Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are maritime countries that face unique sustainable development challenges due to their small size, remoteness, and vulnerability to climate change impacts and natural disasters. The document outlines the history of international agreements focused on SIDS, including the 1994 Barbados Programme of Action, 2005 Mauritius Strategy, and 2014 Samoa Pathway, which identified priority areas and called for partnerships to support SIDS' sustainable development efforts. The Samoa Pathway established an ongoing partnership framework and dialogue to facilitate coordinated support for SIDS across 18 policy areas.