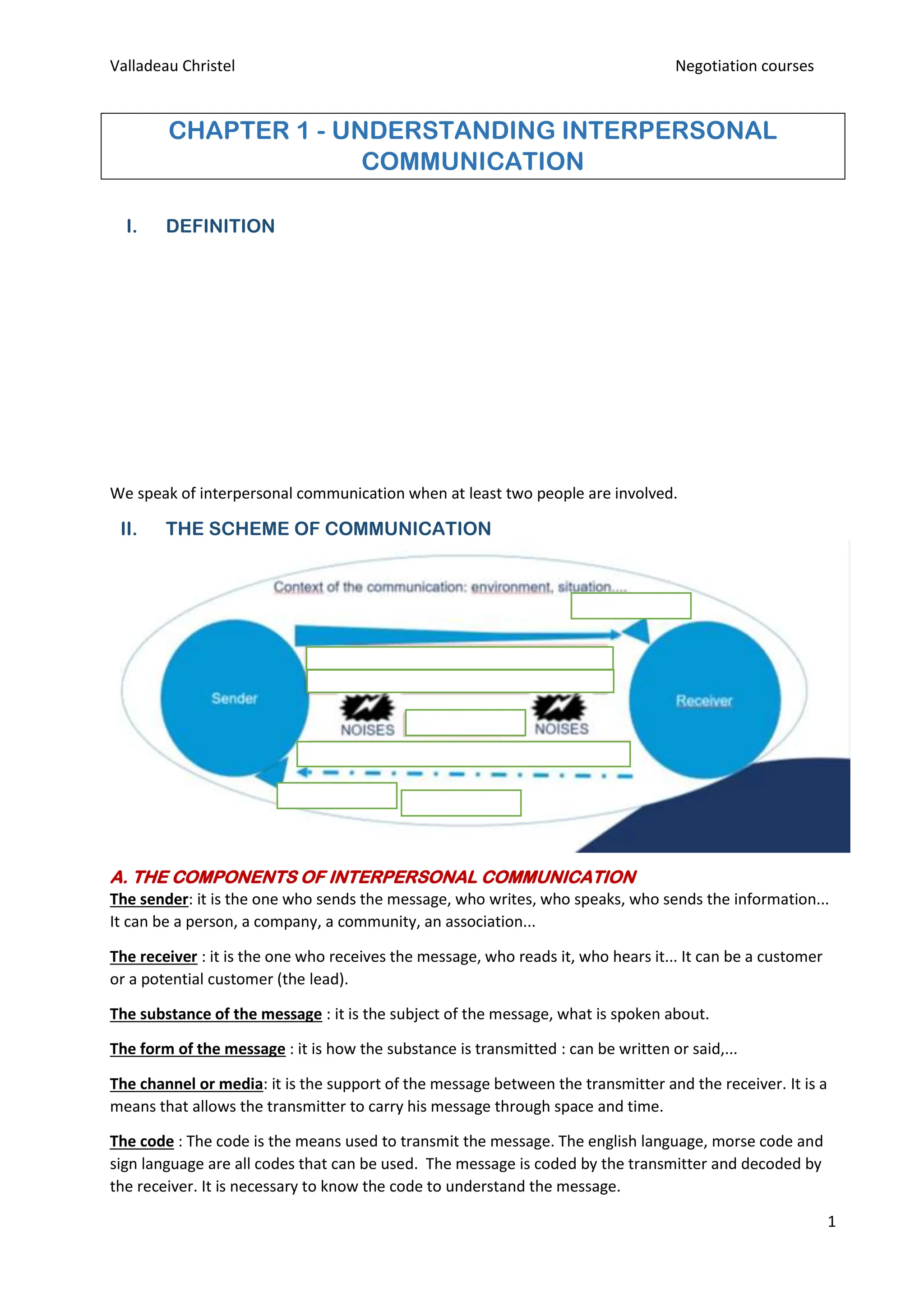
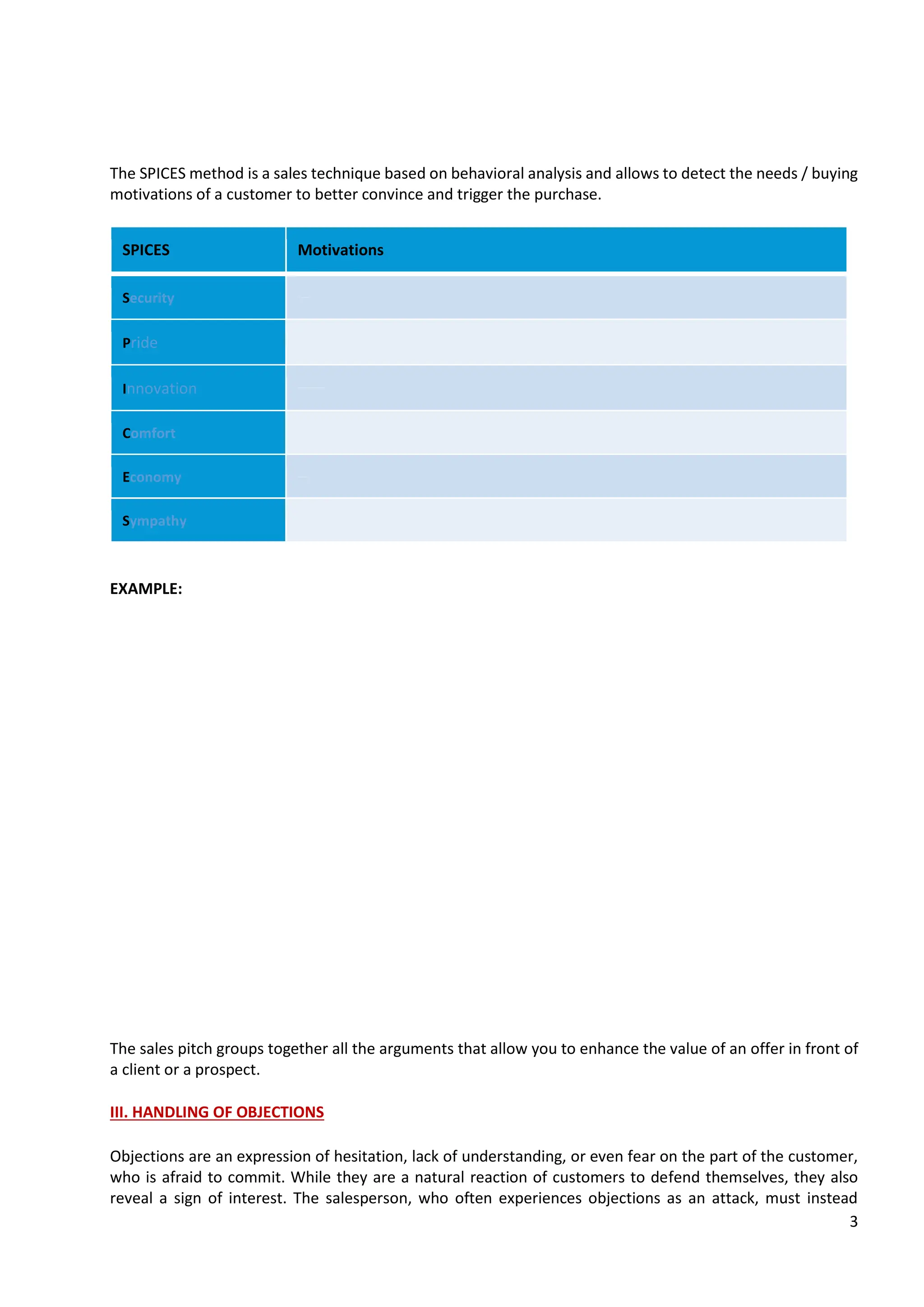
The document discusses the fundamentals of interpersonal communication, emphasizing the roles of senders and receivers, the substance and form of messages, the importance of context, and the various filters that affect communication. It outlines types of communication, including verbal and non-verbal, highlighting the necessity for congruence between speech and body language. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of understanding personality traits and employing effective communication techniques to enhance interpersonal interactions.