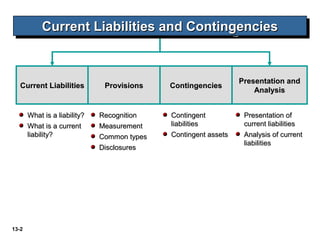
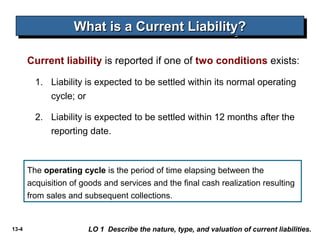
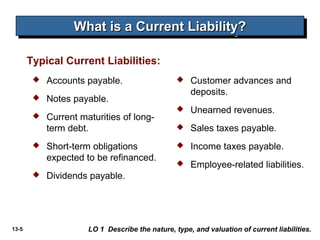
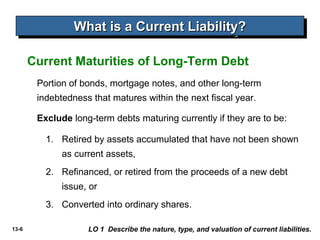
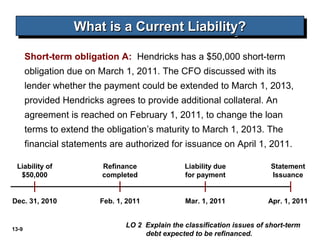
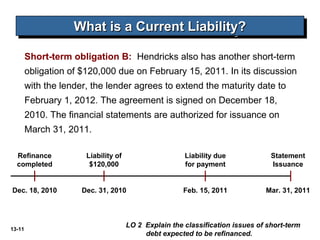
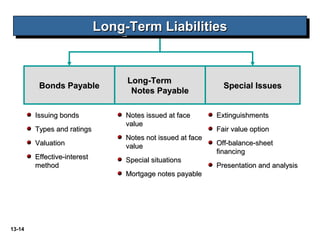
The document discusses current liabilities, provisions, and contingencies. It defines a liability and current liability, and lists common types of current liabilities such as accounts payable, notes payable, and income taxes payable. It also discusses classifying short-term debt as current or non-current depending on whether an agreement to refinance is completed before the reporting date for IFRS or before the financial statements are issued for US GAAP. The document also briefly discusses long-term liabilities such as bonds payable, notes payable, and off-balance sheet financing arrangements.