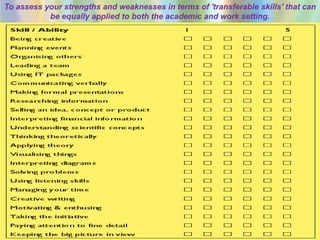
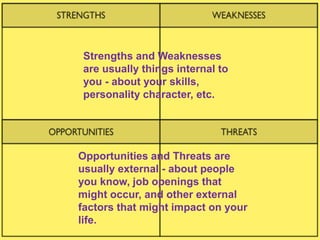
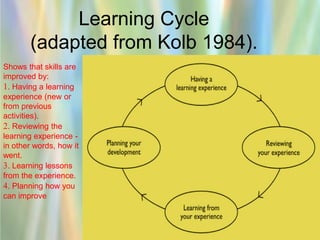
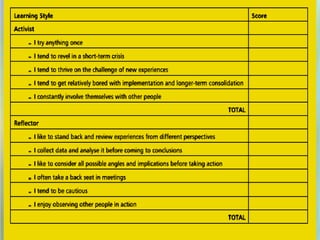
1) A skills audit involves gathering information about employees' capabilities for specific tasks or job roles. This allows organizations to understand strengths, weaknesses, and training needs.
2) Psychometric testing assesses abilities, personality, and interests in a structured way. These tests are commonly used in recruitment to help employers select candidates.
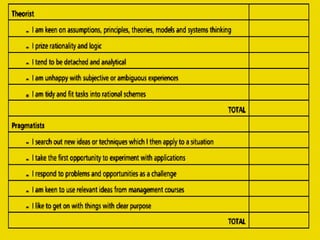
3) Identifying individual and organizational learning needs is important for optimizing performance. Methods include skills audits, gap analysis between current and required skills, and understanding individual learning styles.