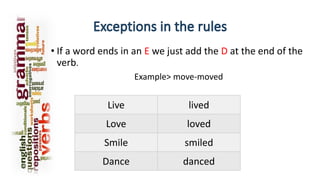
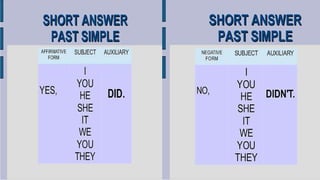
The simple past tense is used to talk about finished past events or states. It is formed by adding "-ed" to regular verbs or making other changes like doubling consonants. Some examples of its uses include talking about things that happened at a specific time in the past or with a frequency modifier. The grammatical structure is subject + verb in past form + complement. To make negatives, "didn't" or "did not" is used before the verb, except for forms of "to be" which use "wasn't/were not". Questions are formed by using "did" before the subject and verb.