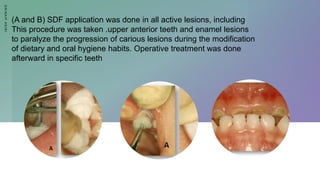
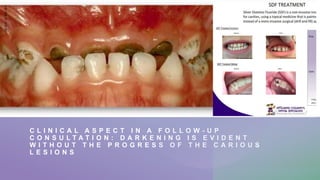
SDF is a solution containing silver diamine fluoride that is used to treat dental caries. It has several advantages as a treatment for caries, including being painless and effective at stopping the progression of lesions. Potential disadvantages include tooth staining. SDF is generally applied using a simple technique and has indications for use in patients with early childhood caries, disabilities, or those who are not cooperative for traditional restorative treatments. The staining can be addressed using other restorative materials immediately following SDF application.




![ W h a t i s S D F - S i l v e r D i a m i n e F l u o r i d e
❓
• SDF is made of:
• silver: helps kill bacteria
• water: provides a liquid base for the mixture
• fluoride: helps your teeth rebuild the materials
• ammonia: helps the solution remain concentrated so that it’s maximally
effective against cavity resonance
SDF is a 38% silver diamine fluoride ,SDF (AgF[NH3]2) is a colorless solution
with alkaline pH (pH 8–10). Its main components are silver, fluoride and
ammonia. Basically, the silver is an antimicrobial agent, the ammonia
stabilizes the solution, while the fluoride aids remineralization..
D
R
/
N
A
I
F
A
S
I
R
I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sdf-210120072152/85/silver-diamine-fluoride-SDF-Pediatric-dentistry-5-320.jpg)