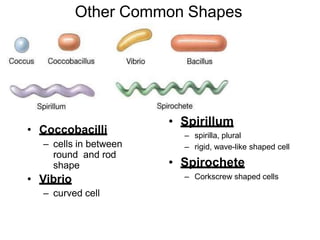
1. Bacteria come in three basic shapes: coccus (spherical), bacillus (rod-shaped), and spirillum (spiral-shaped). They vary in size from 0.5-5 μm.
2. Cocci can be arranged as diplococci, streptococci, staphylococci, sarcinae, or tetracocci depending on how their cells divide and group together. Bacilli similarly arrange as single cells, diplobacilli, streptobacilli, or palisades.
3. Bacterial structures include the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, chromosome, plasmids, capsule/slime layer, endospore, pilus