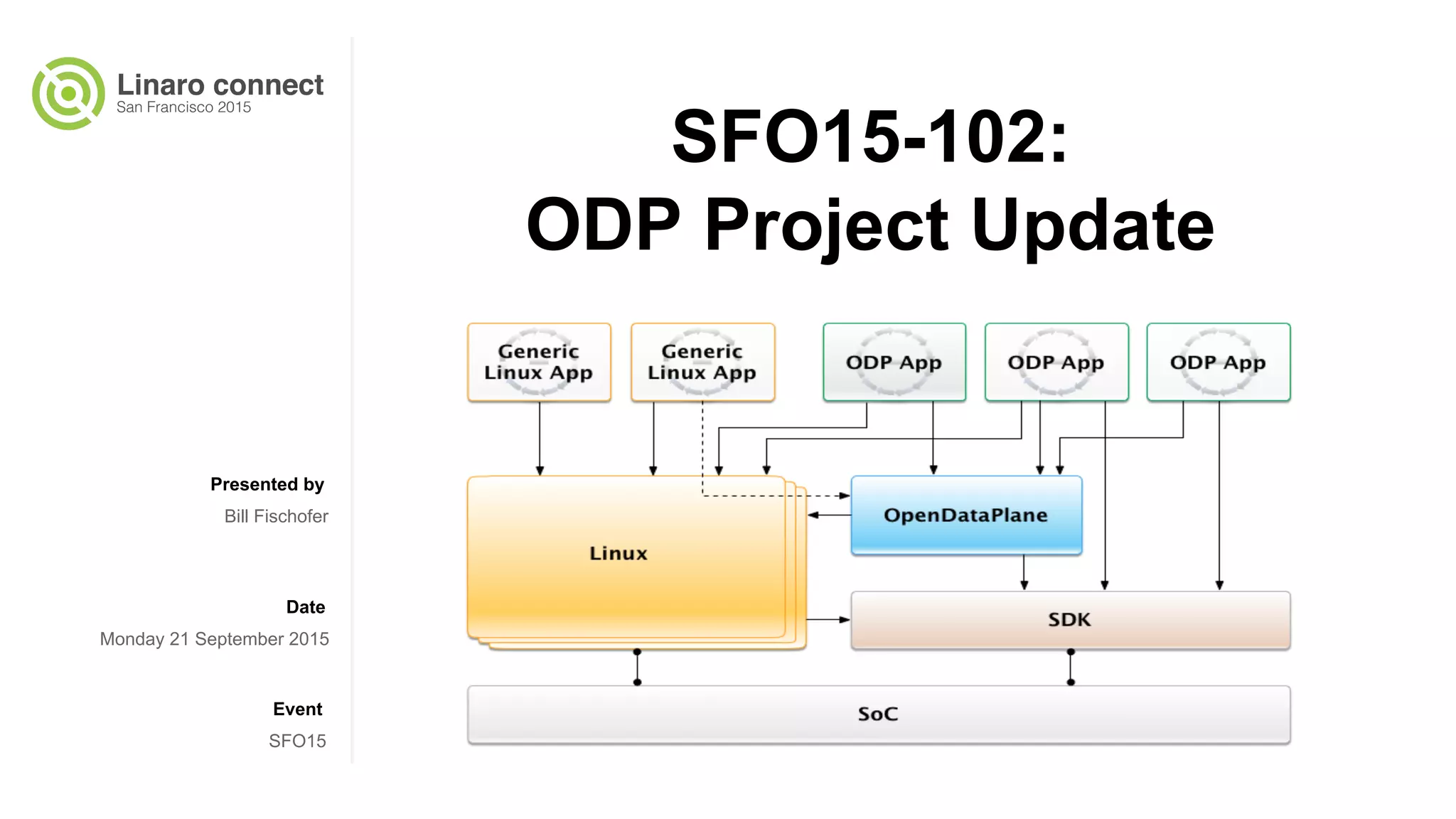
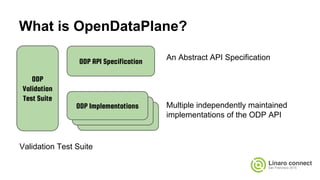
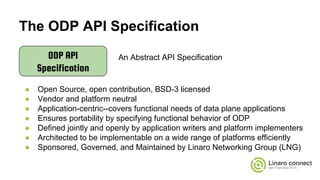
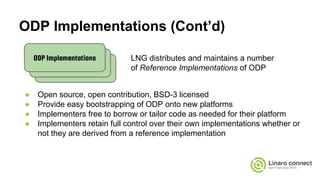
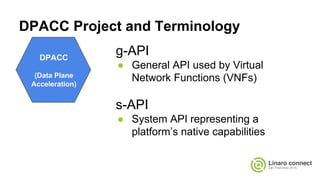
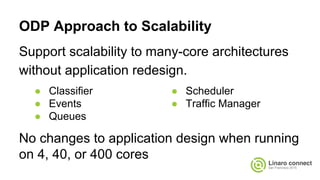
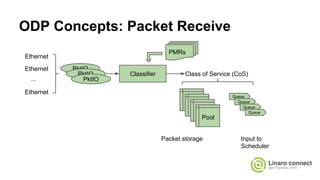
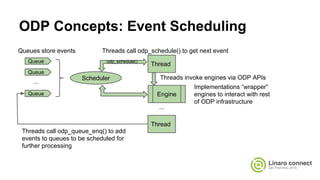
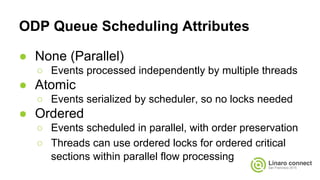
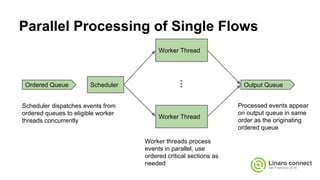
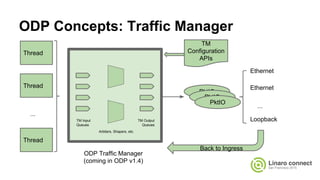
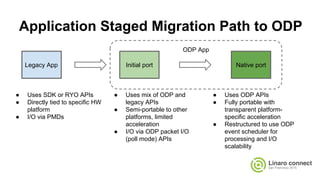
The document provides an update on the OpenDataPlane (ODP) project, including its overview, current status, and future plans. It discusses key developments and changes to the ODP API across various version releases, highlighting the project's focus on portability, scalability, and leveraging platform-specific features. Additionally, the document outlines upcoming ODP releases and their functionalities, while also addressing collaboration with other projects like OPNFV.