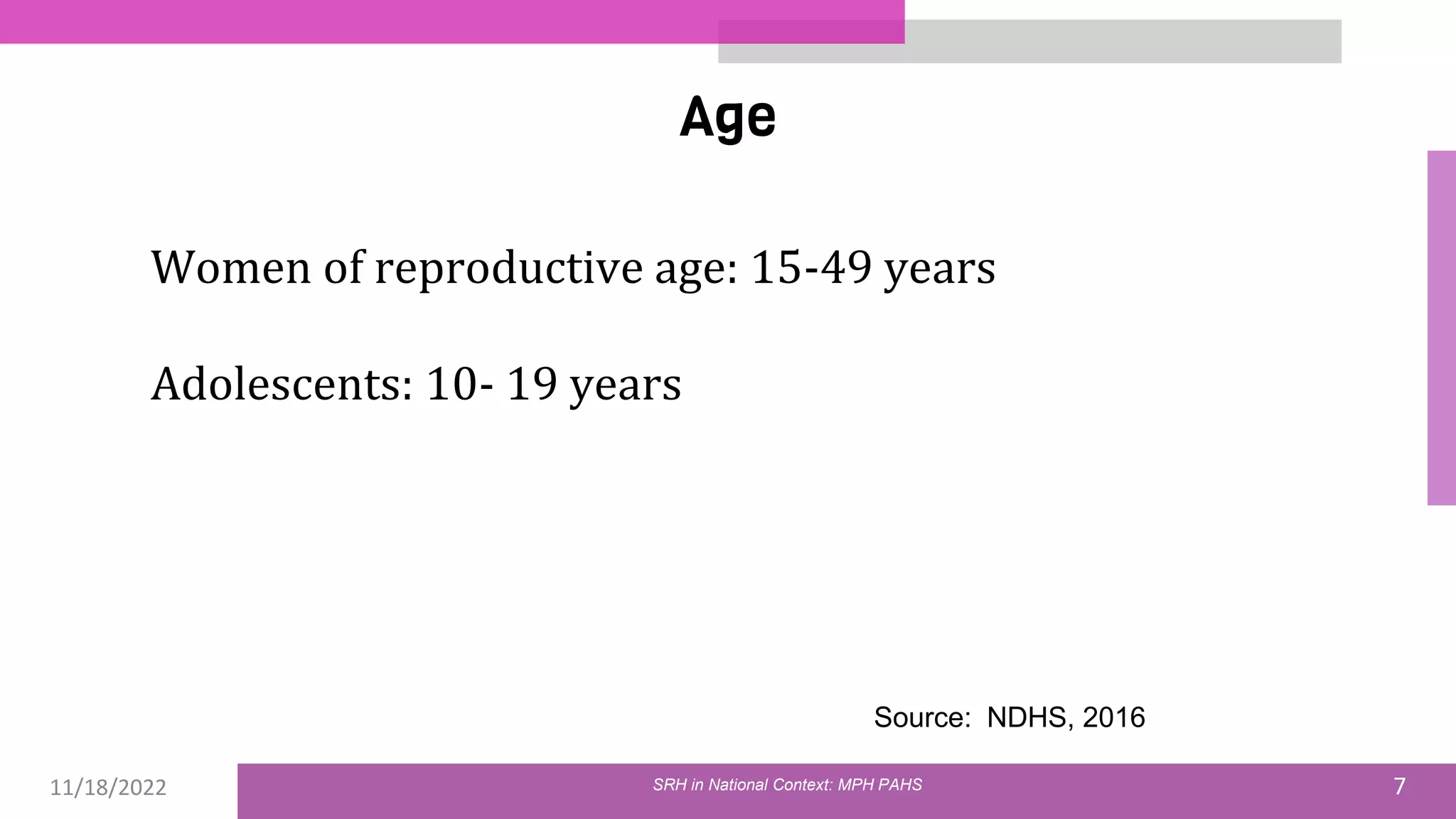
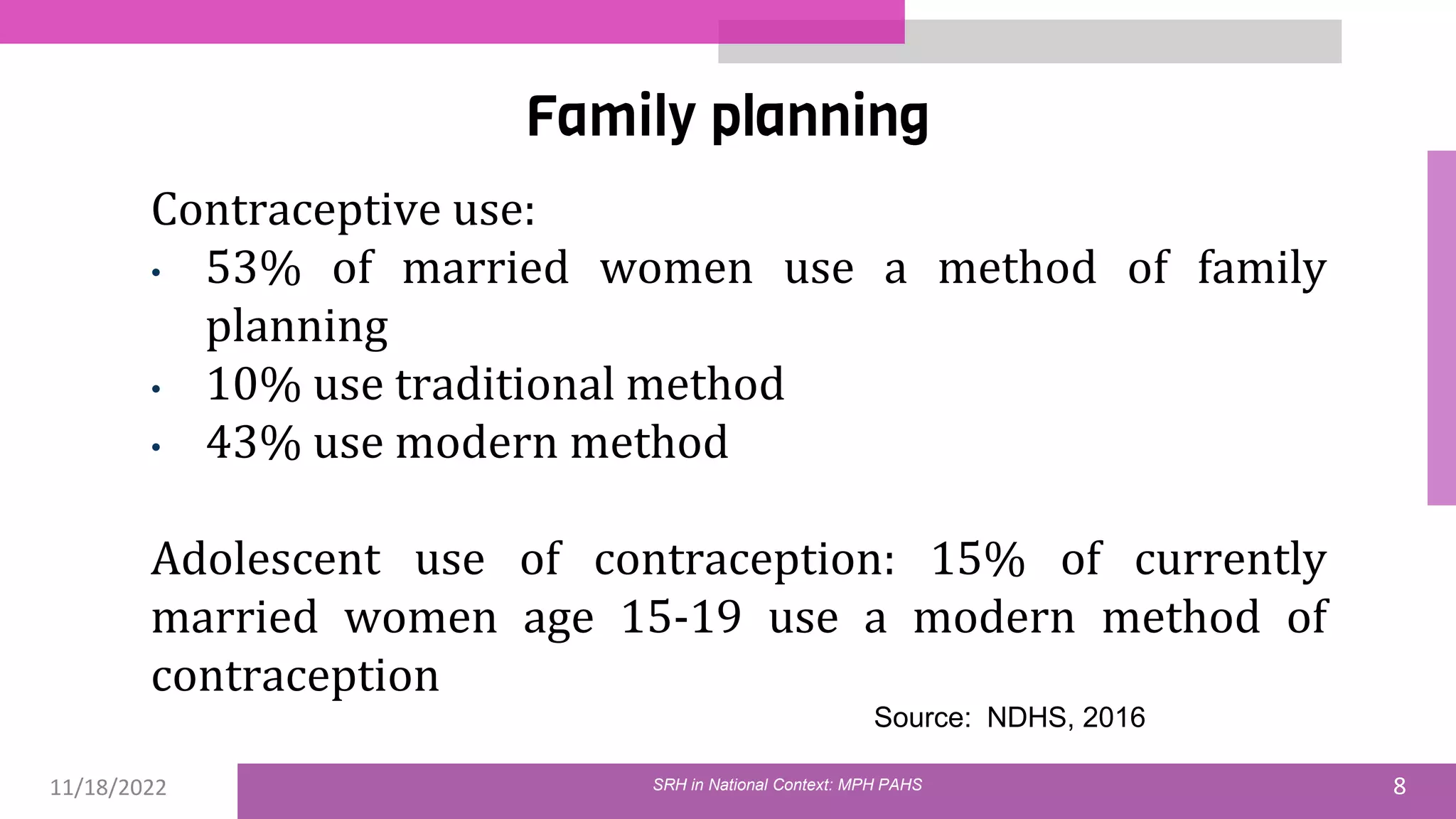
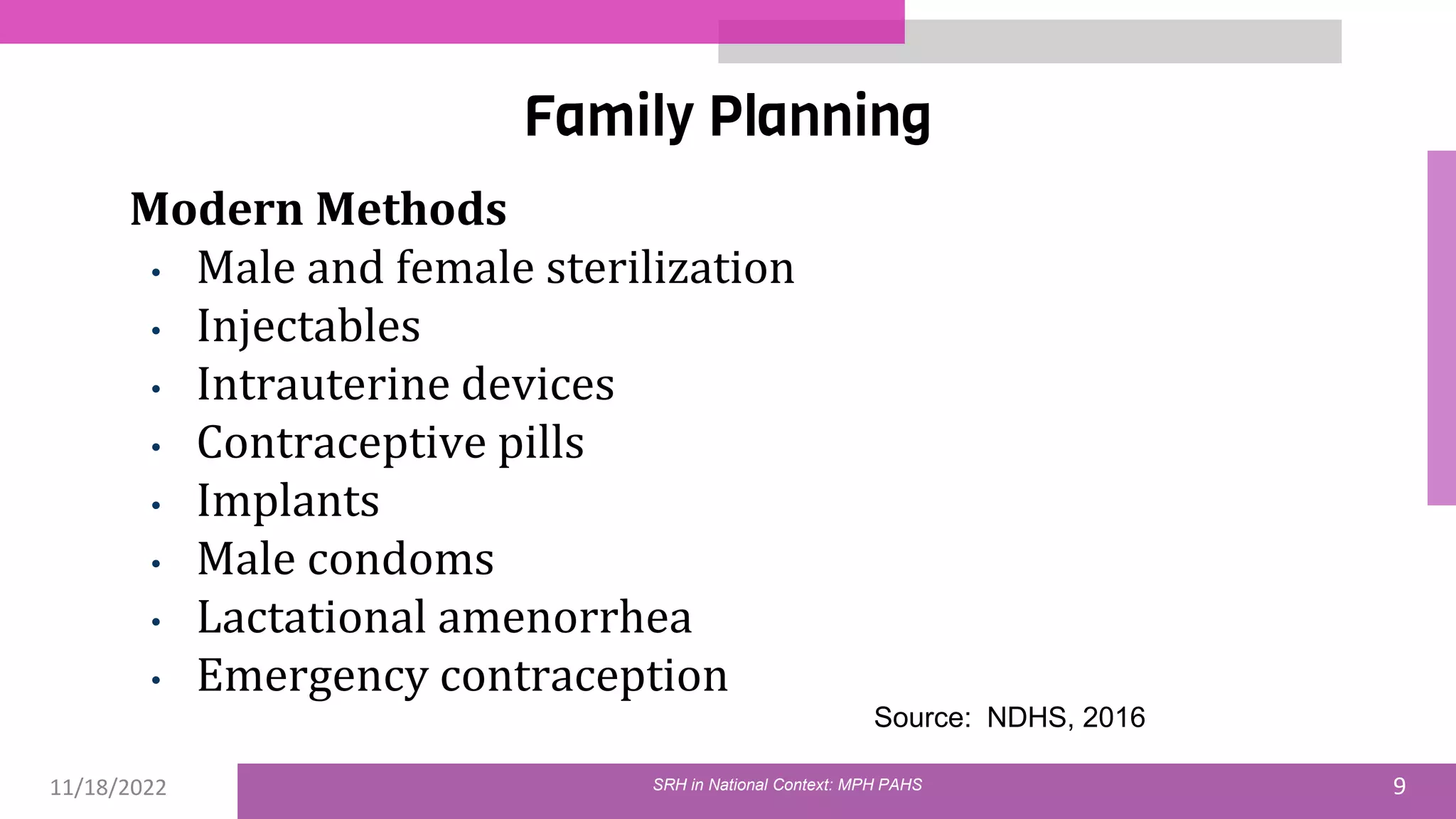
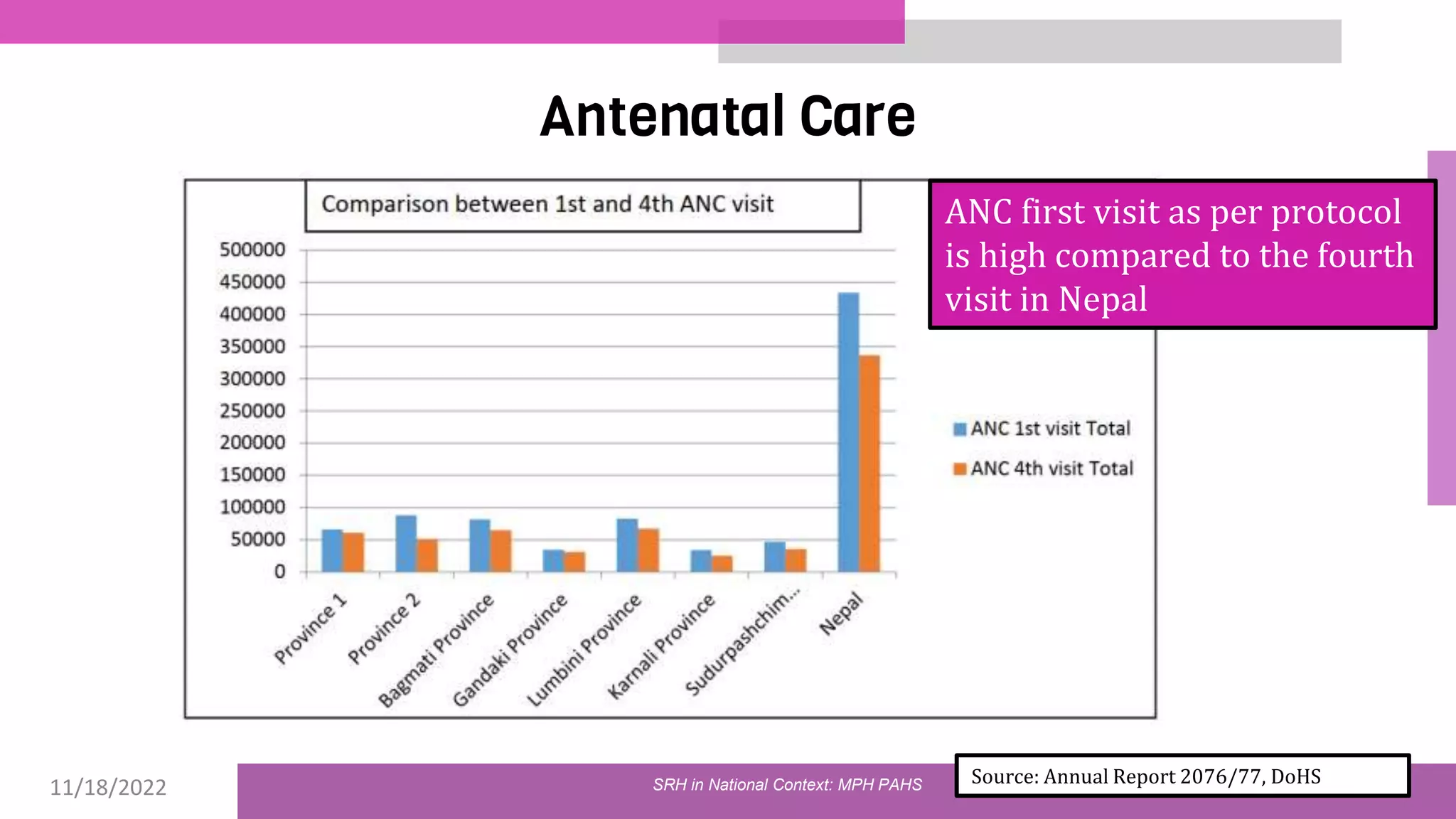
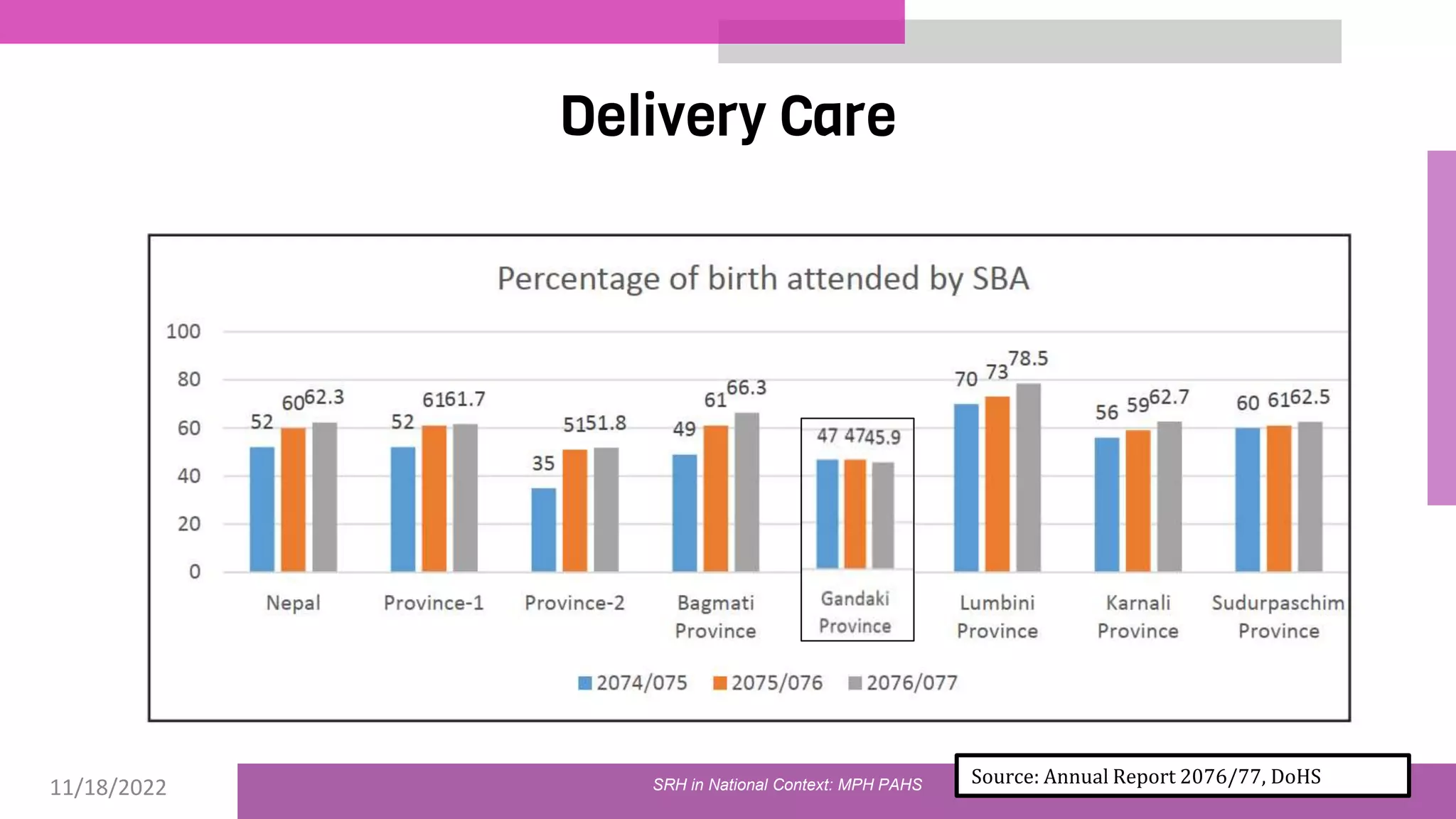
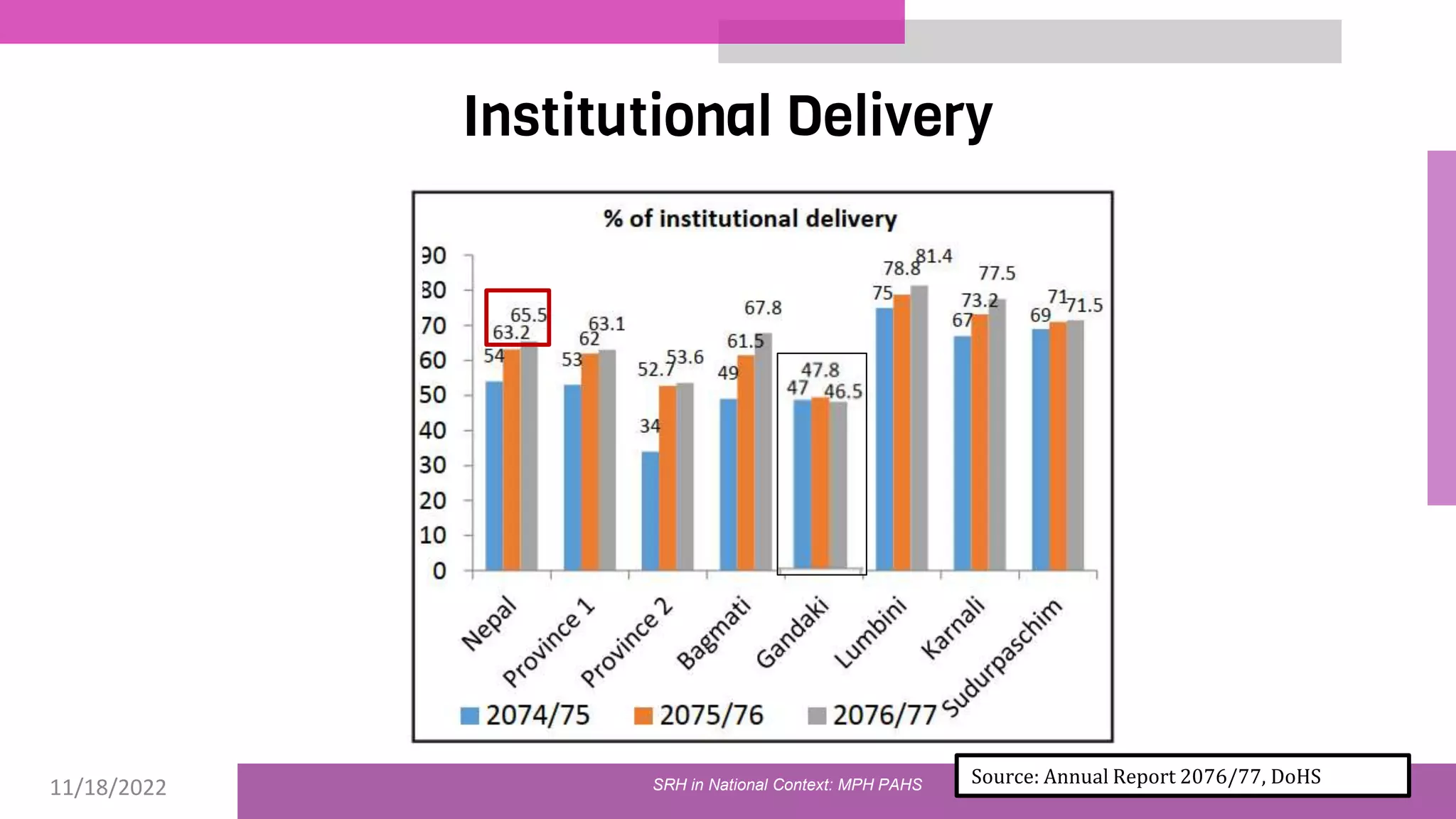
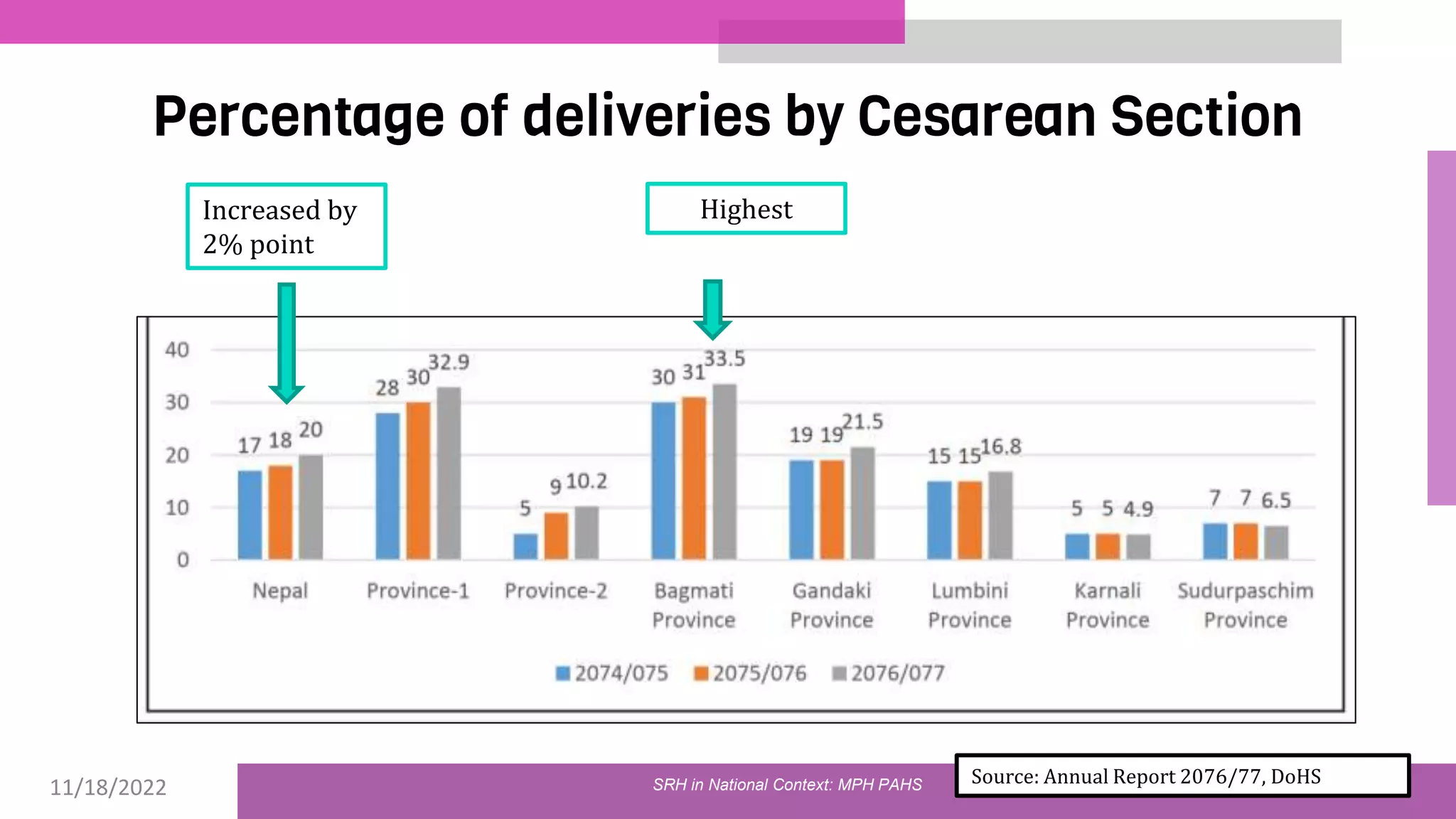
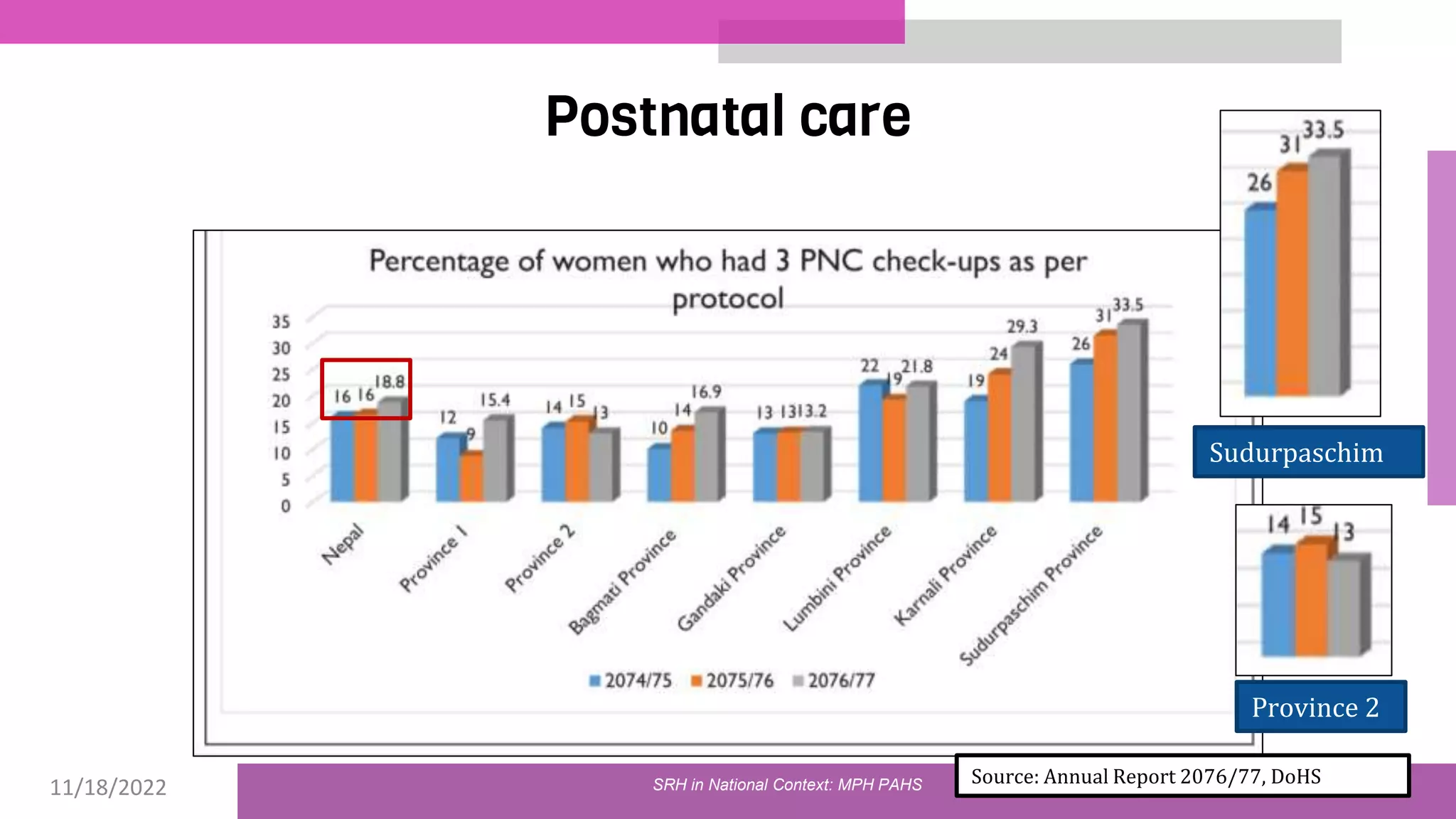
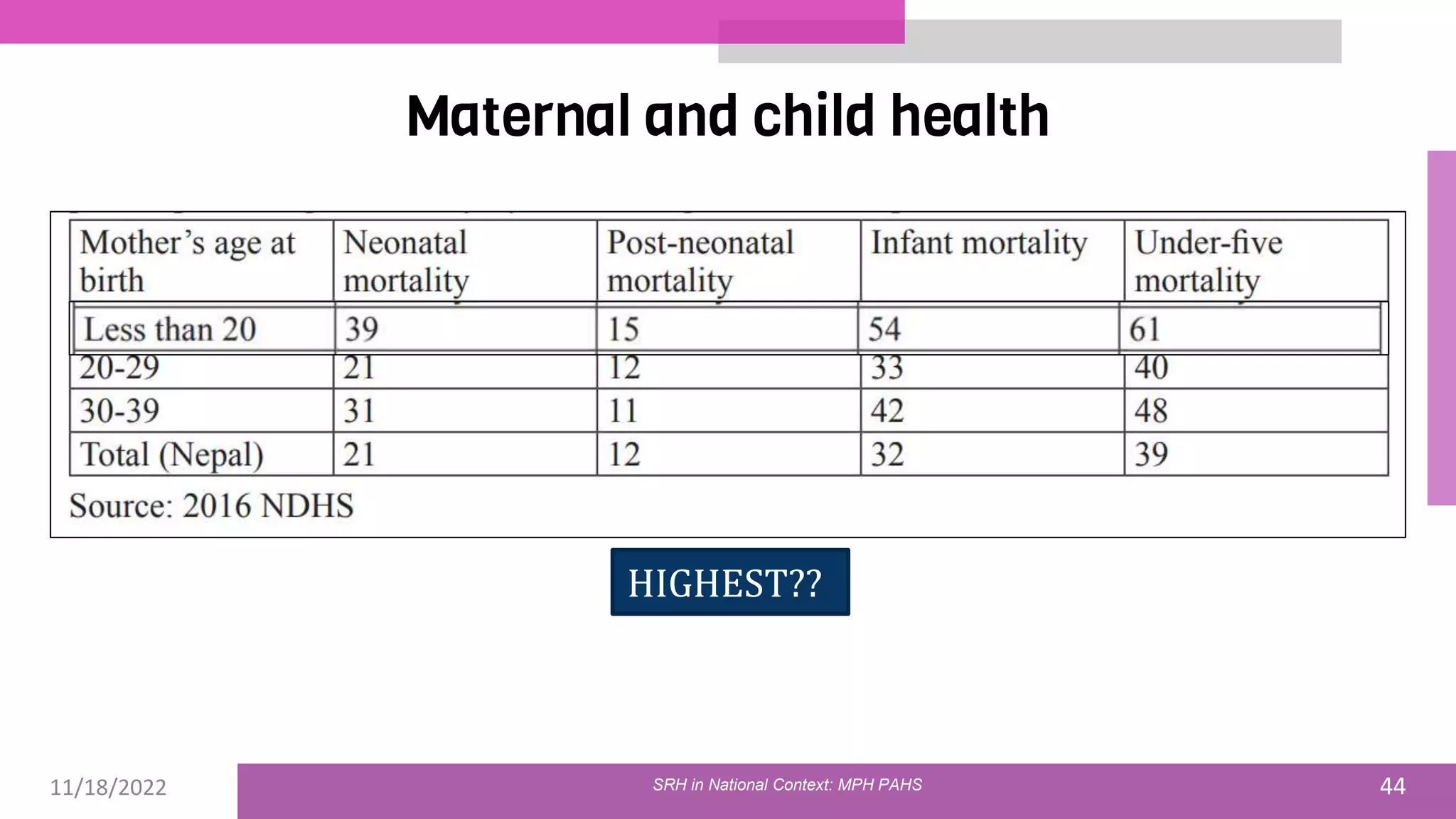
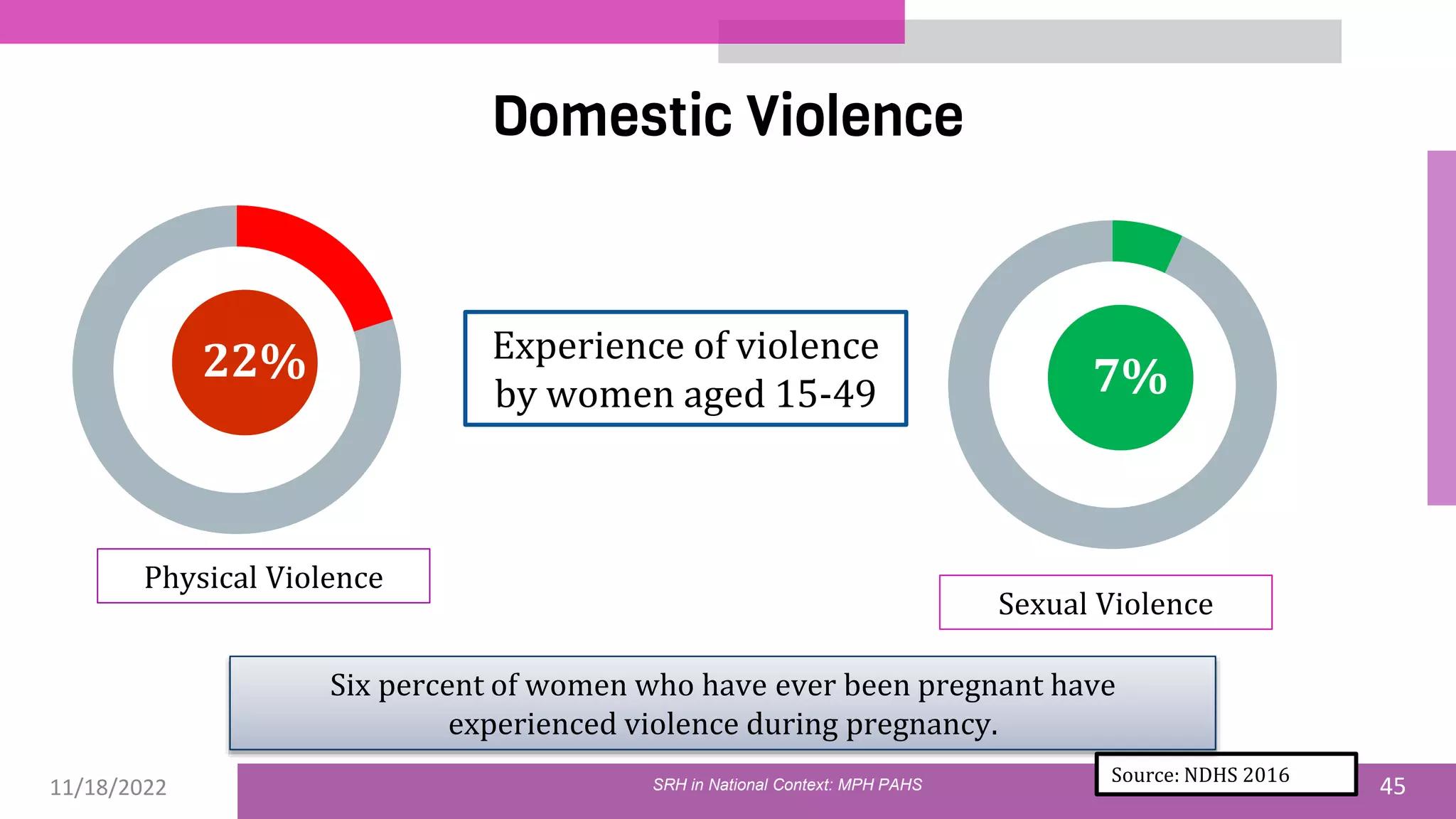
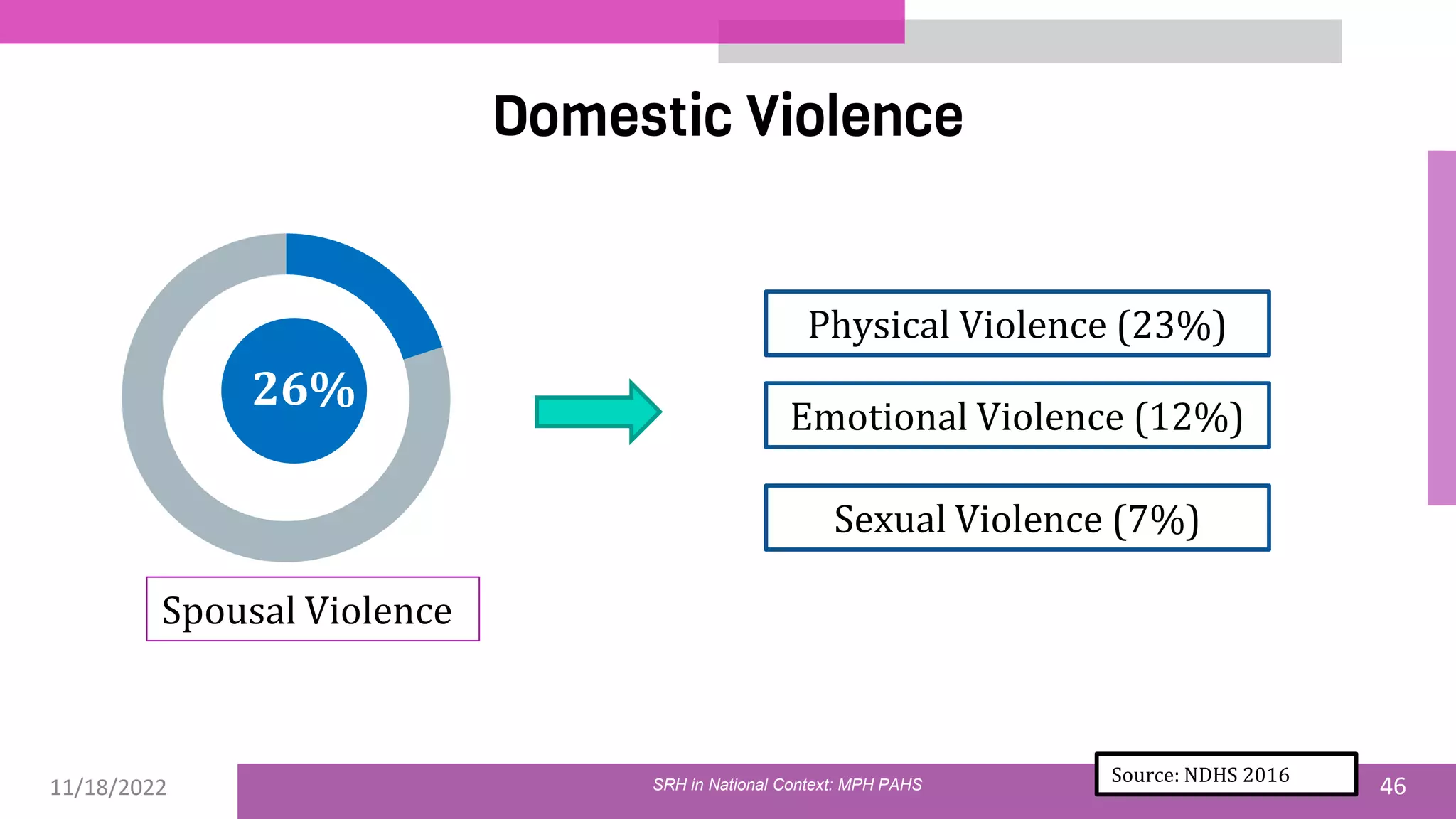
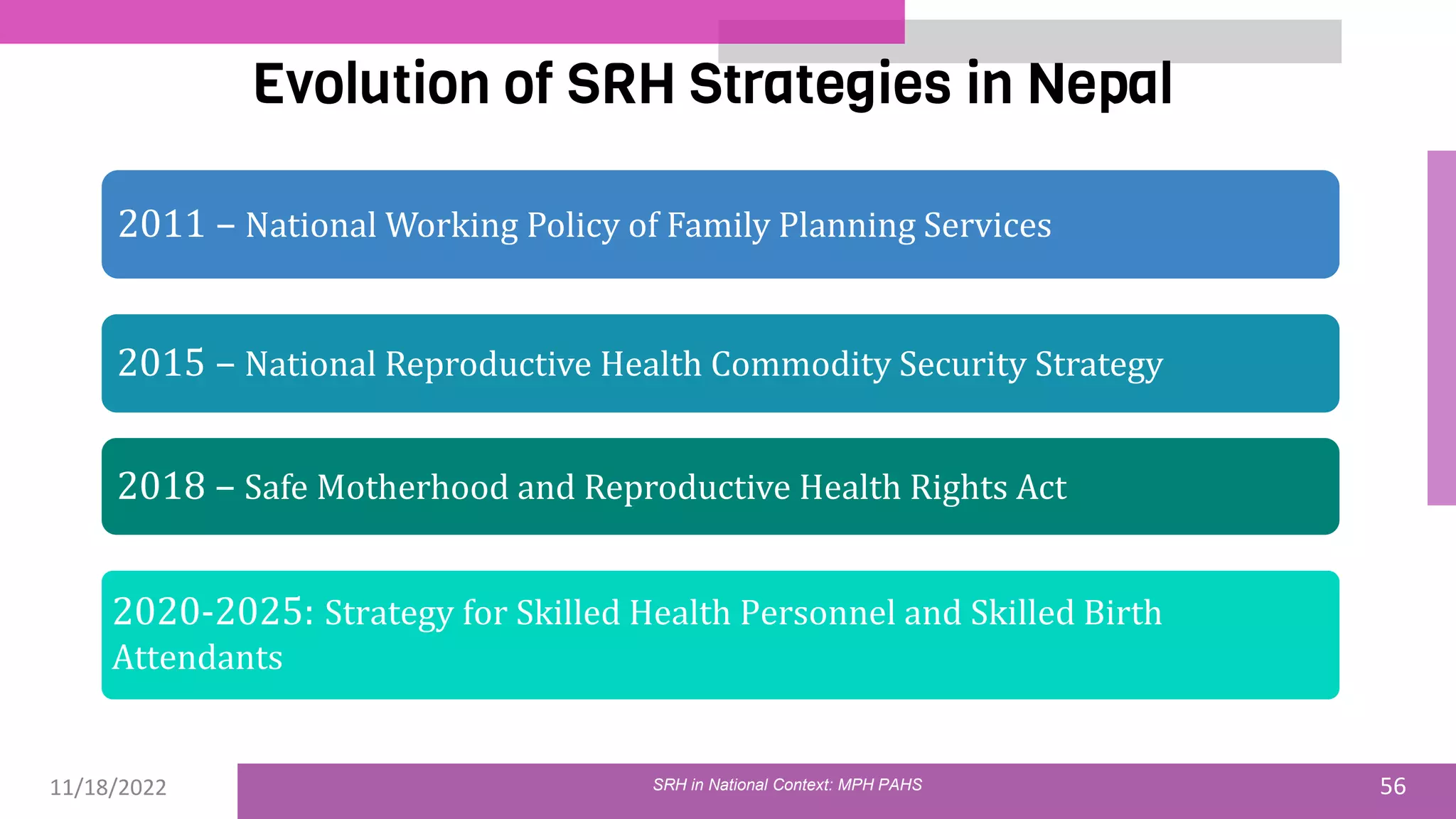
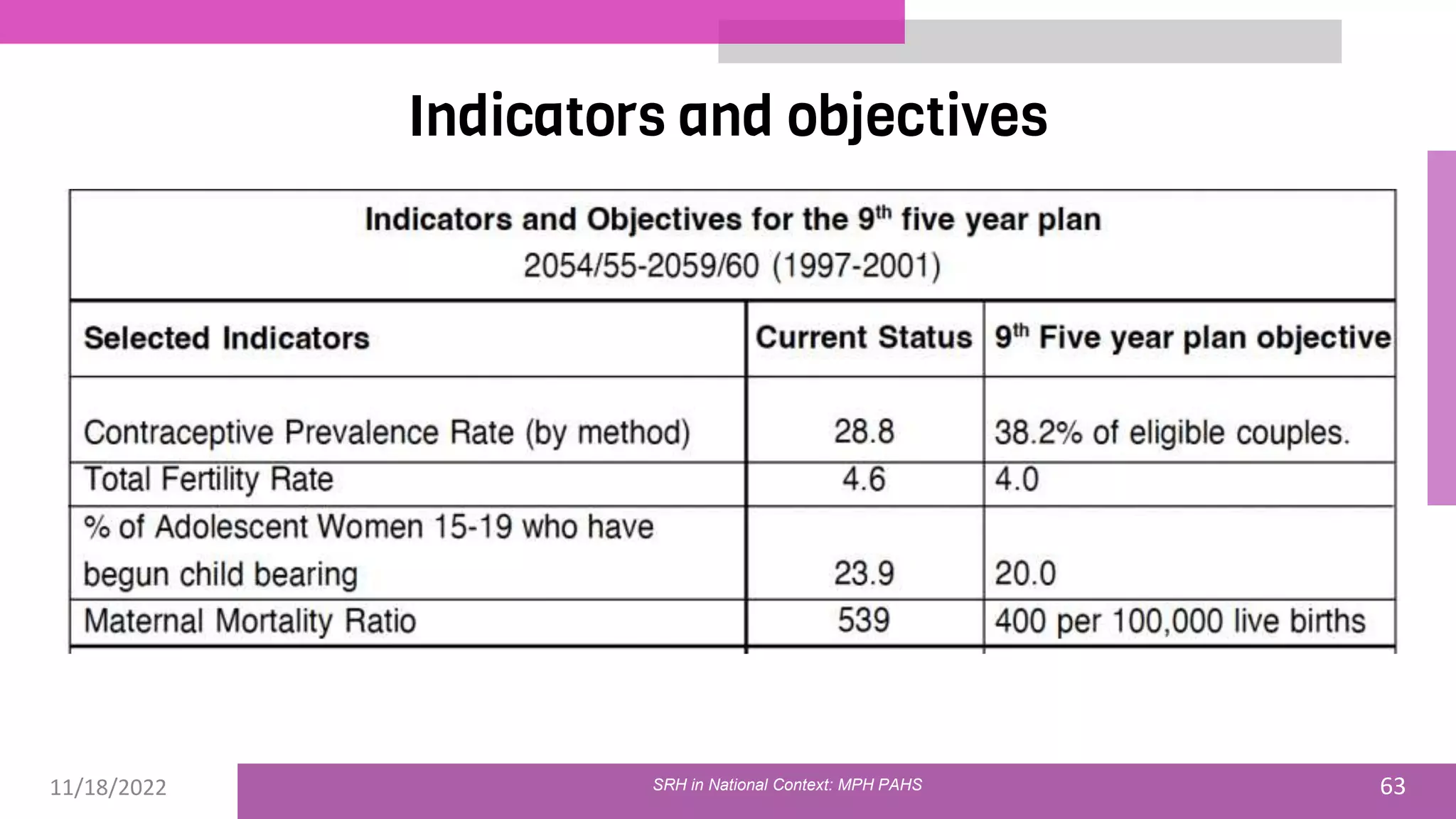
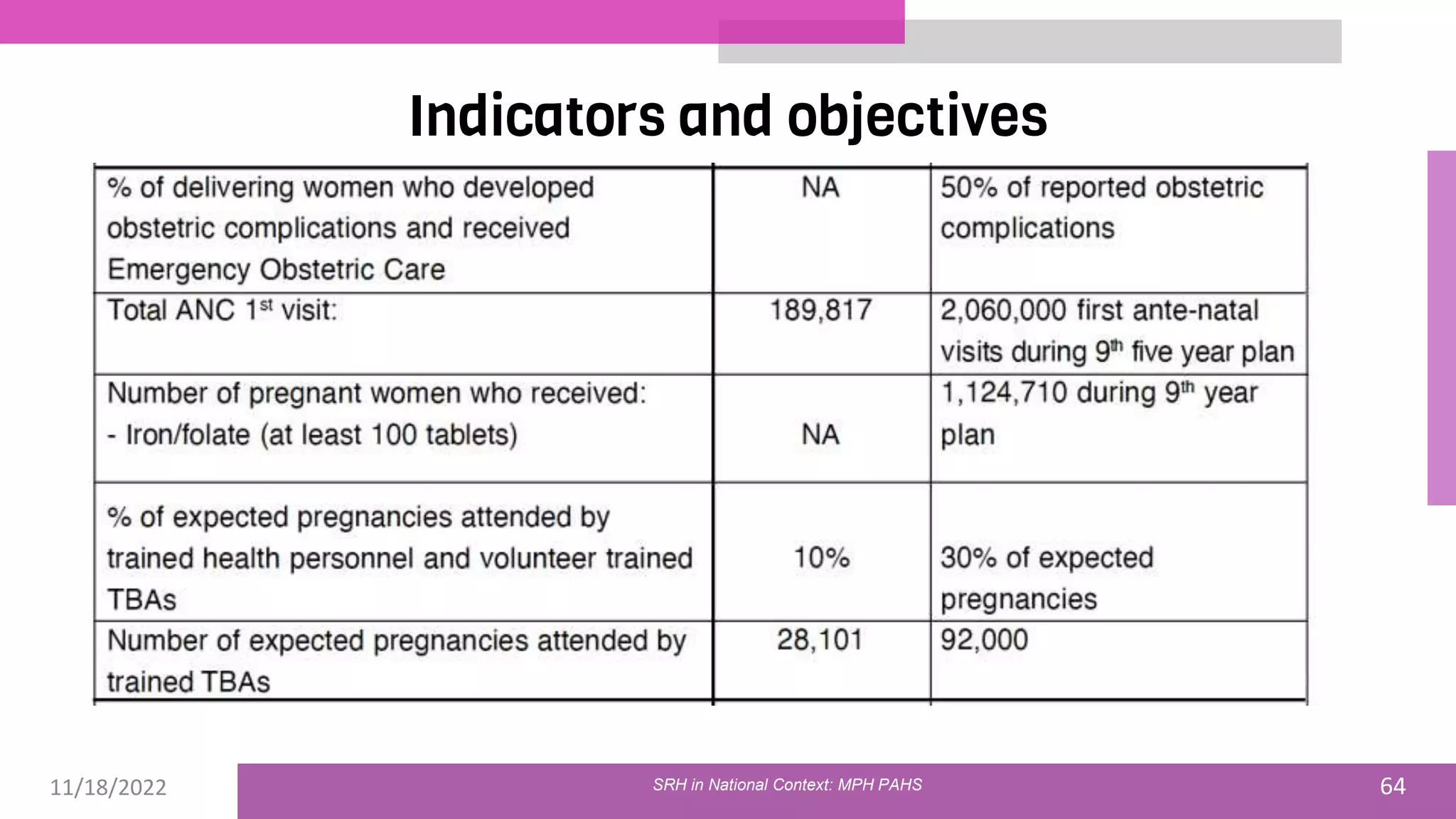
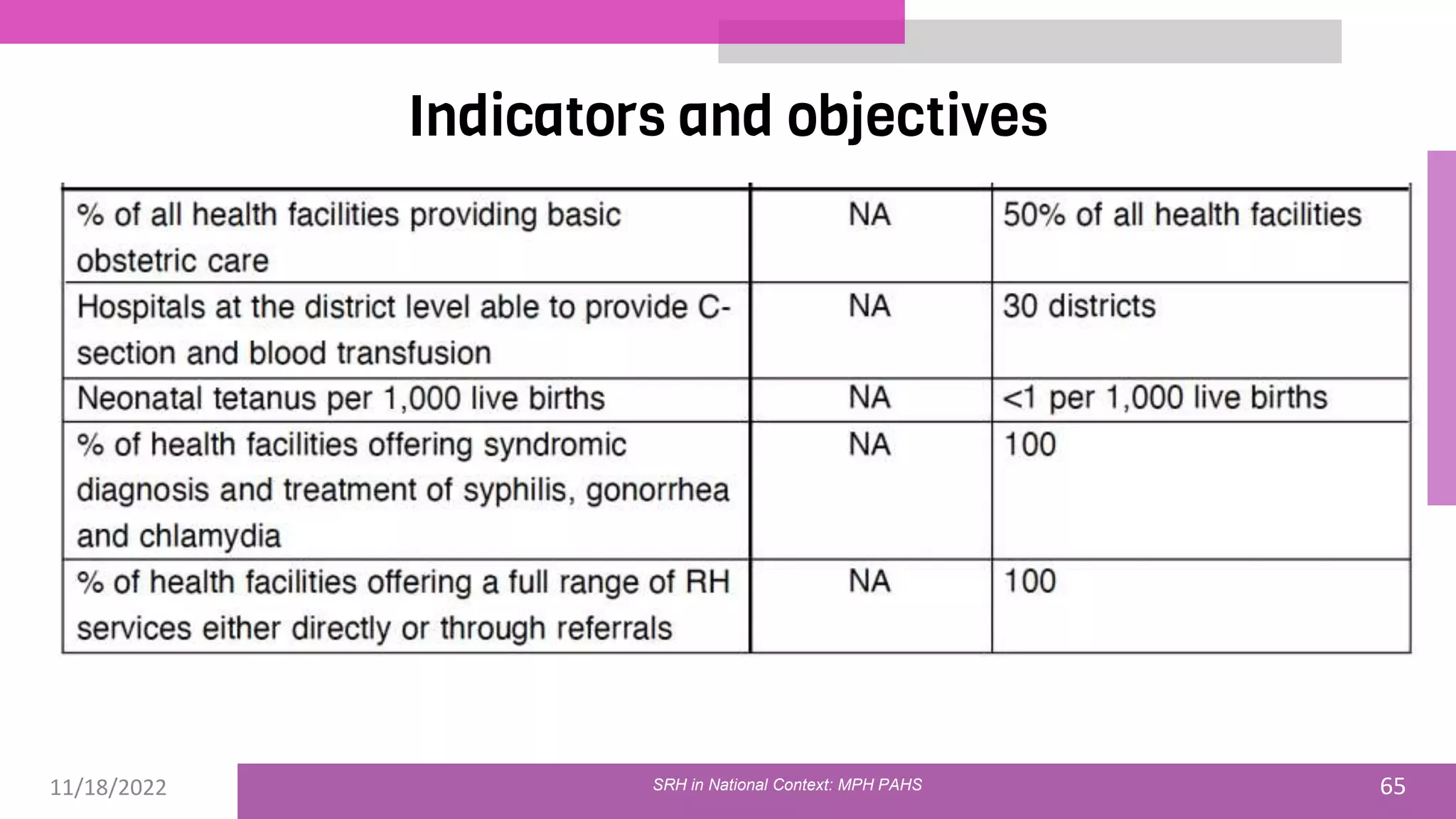
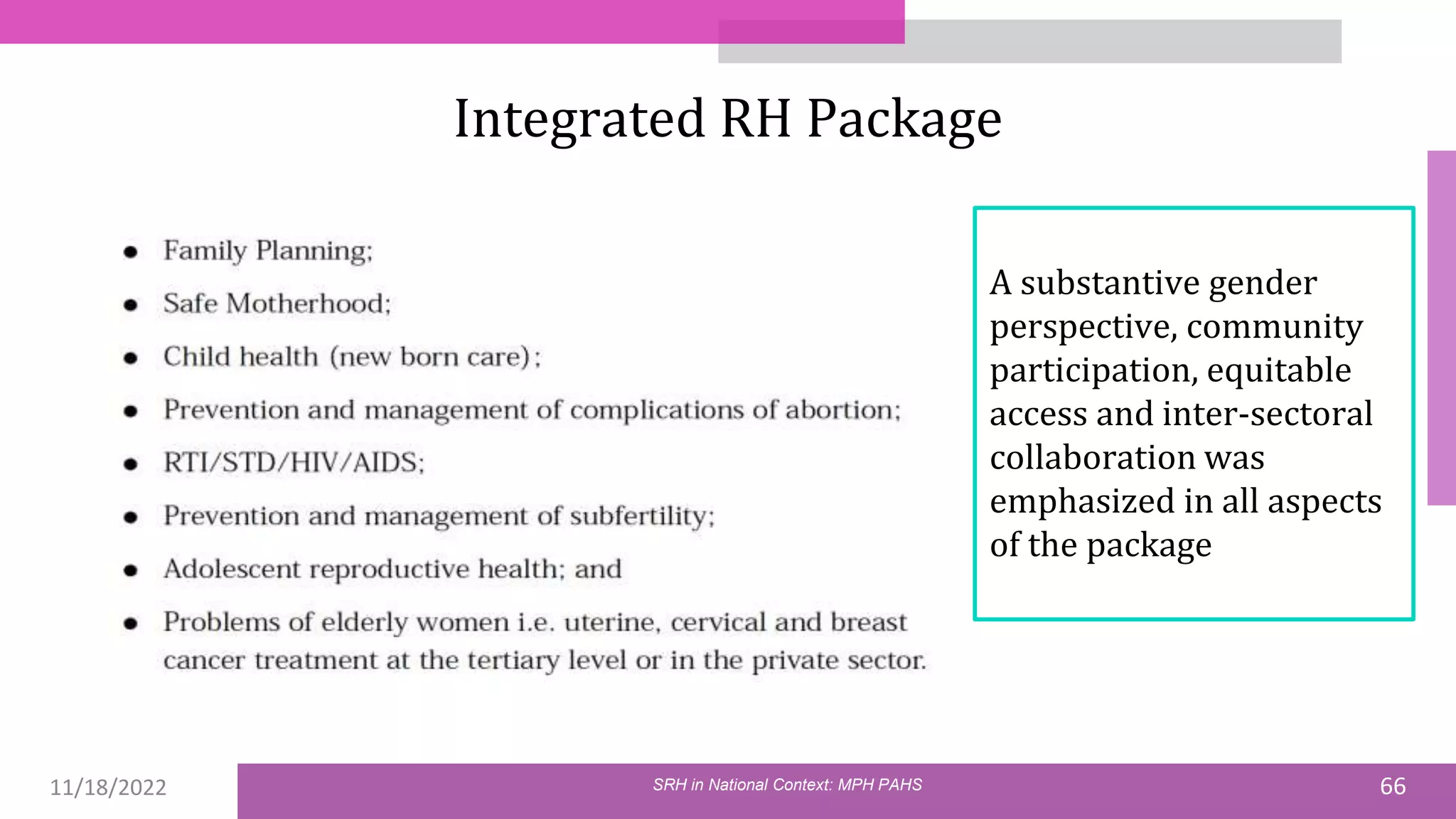
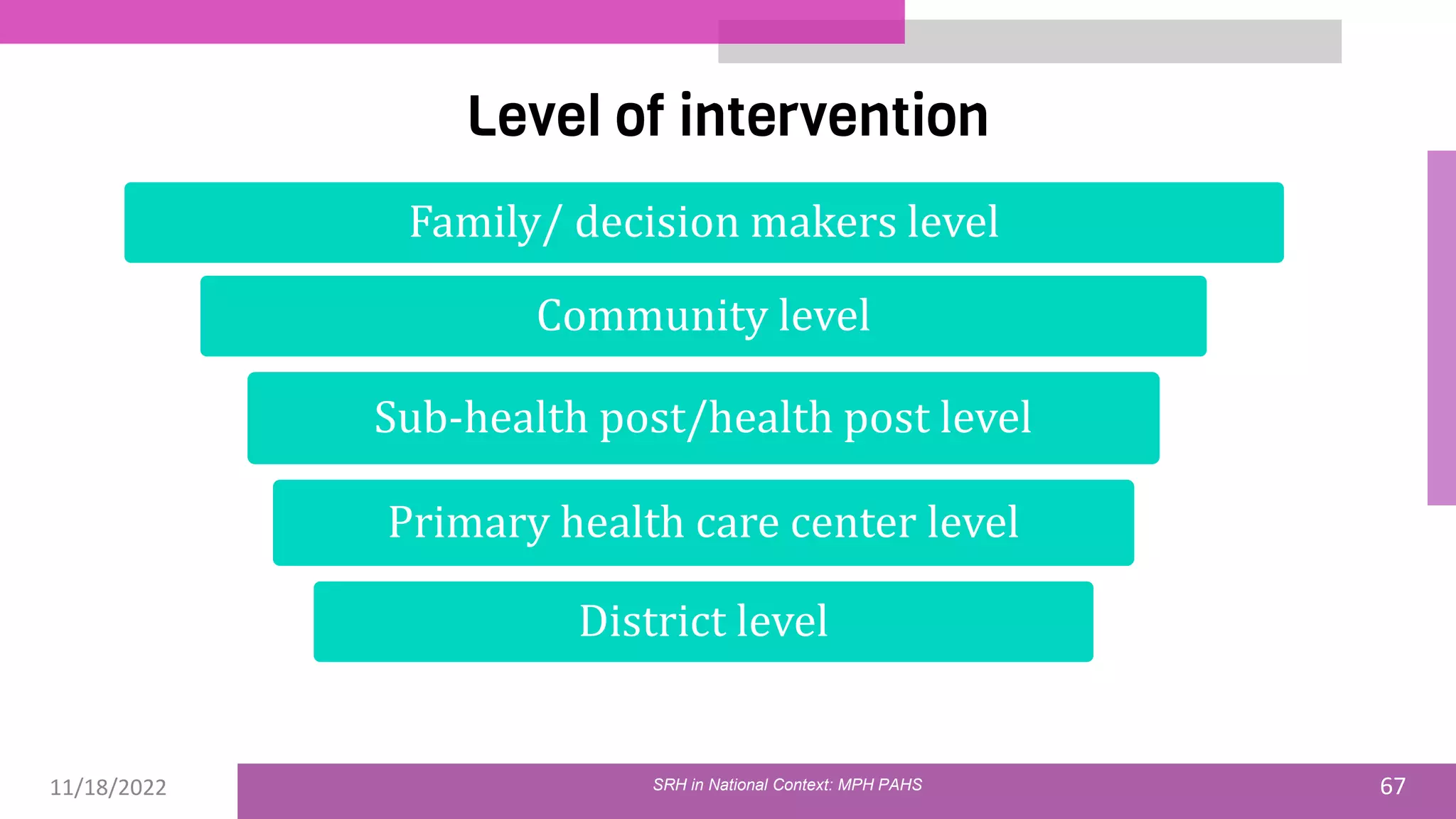
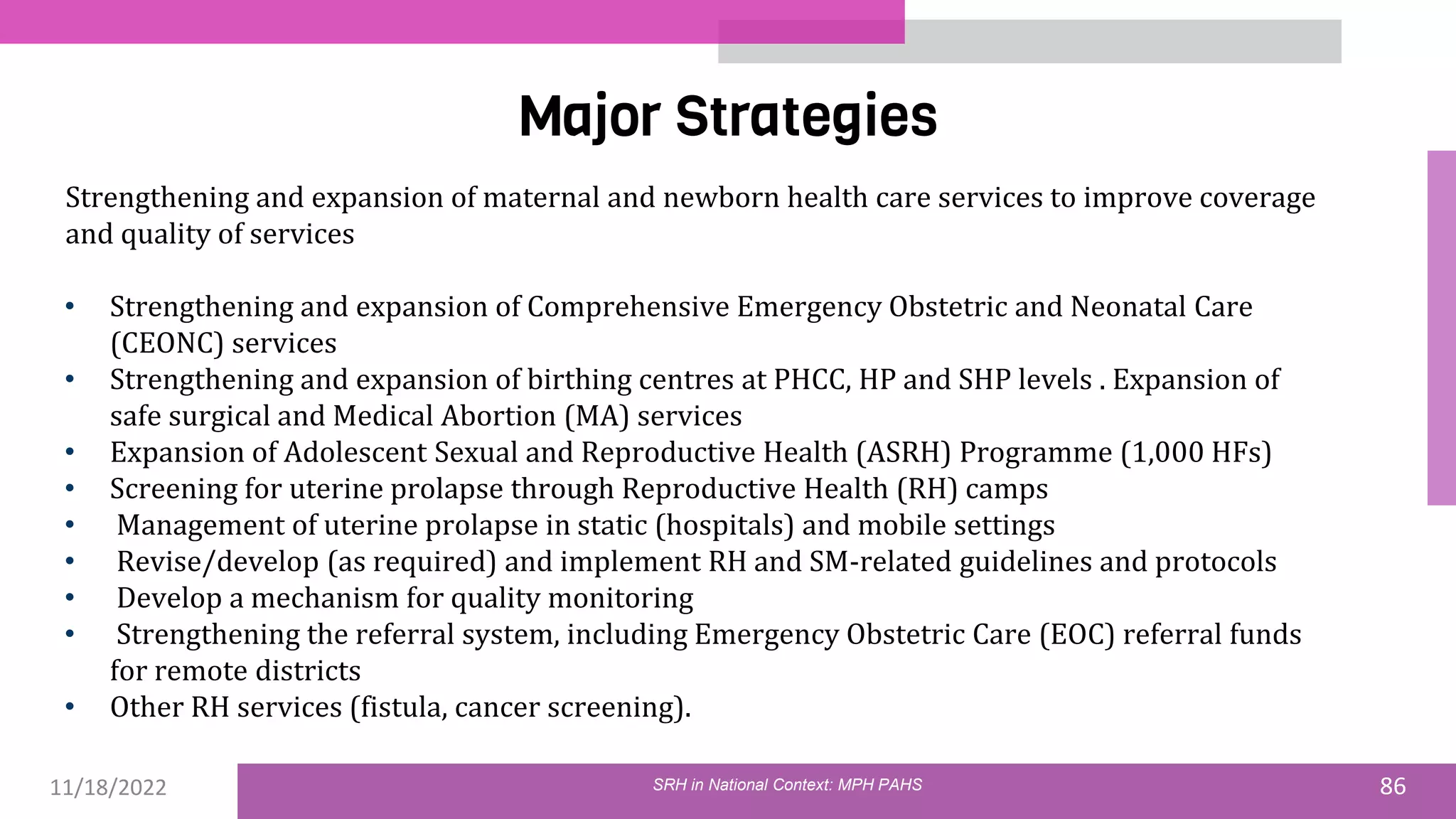
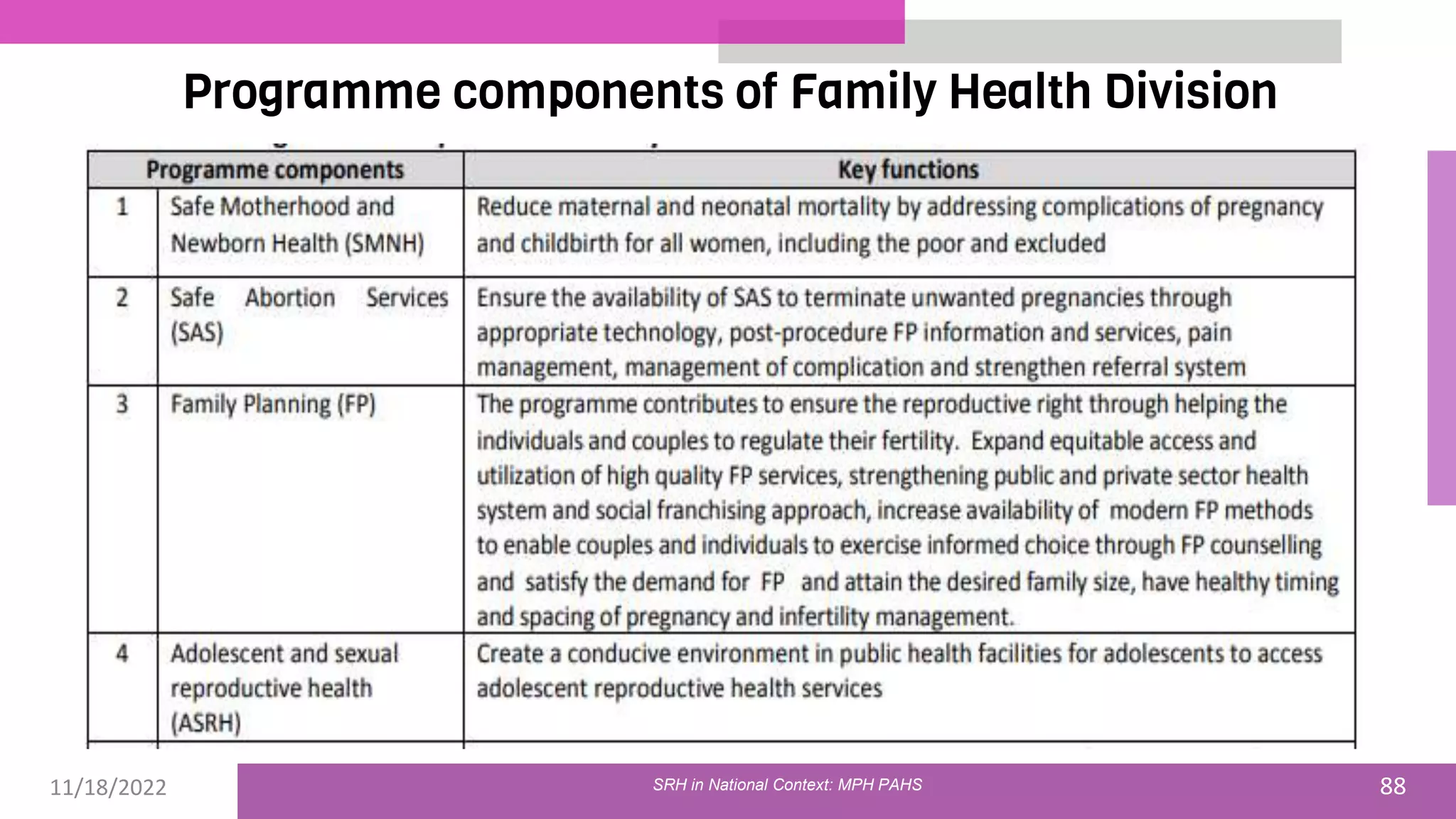
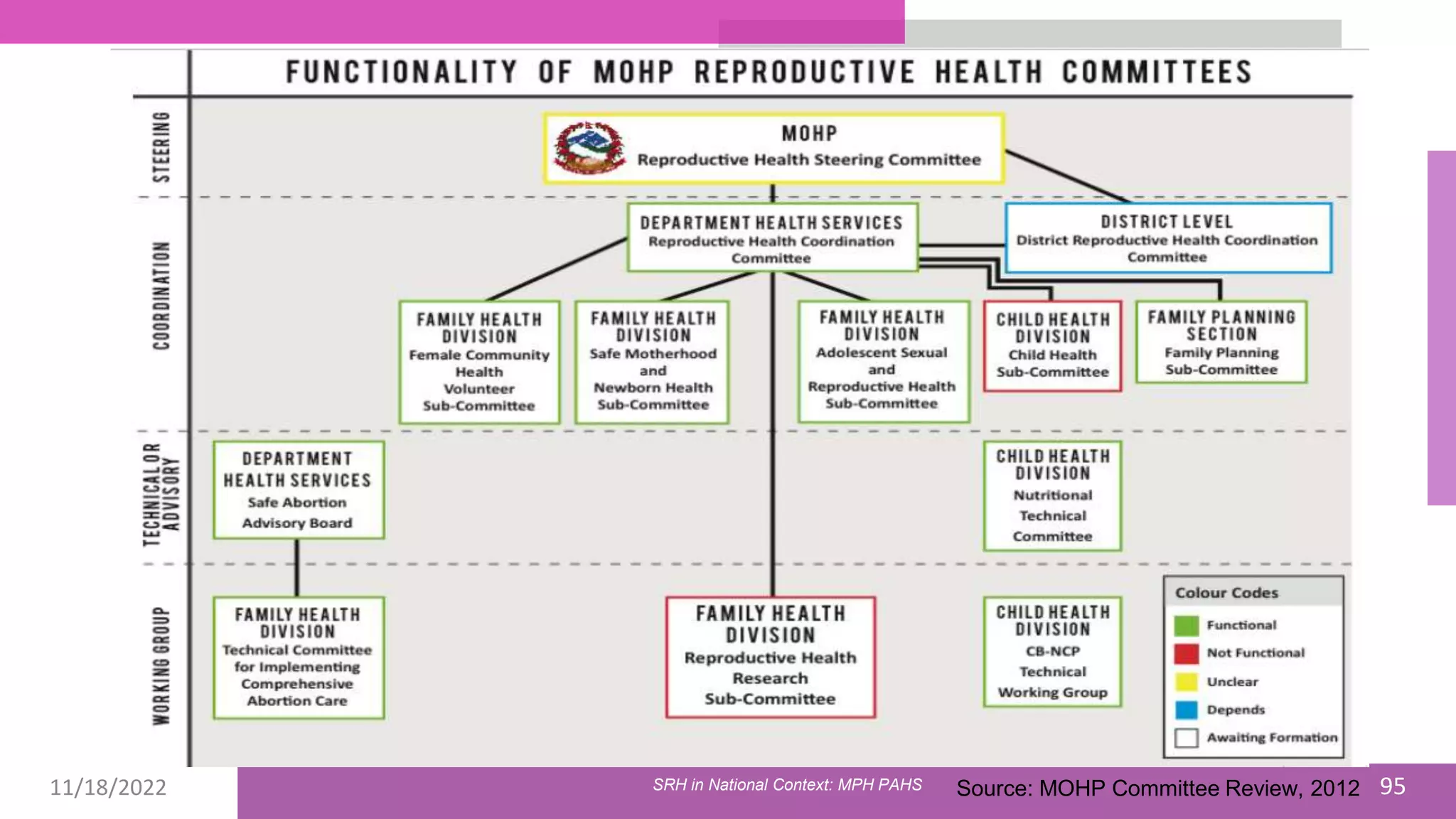
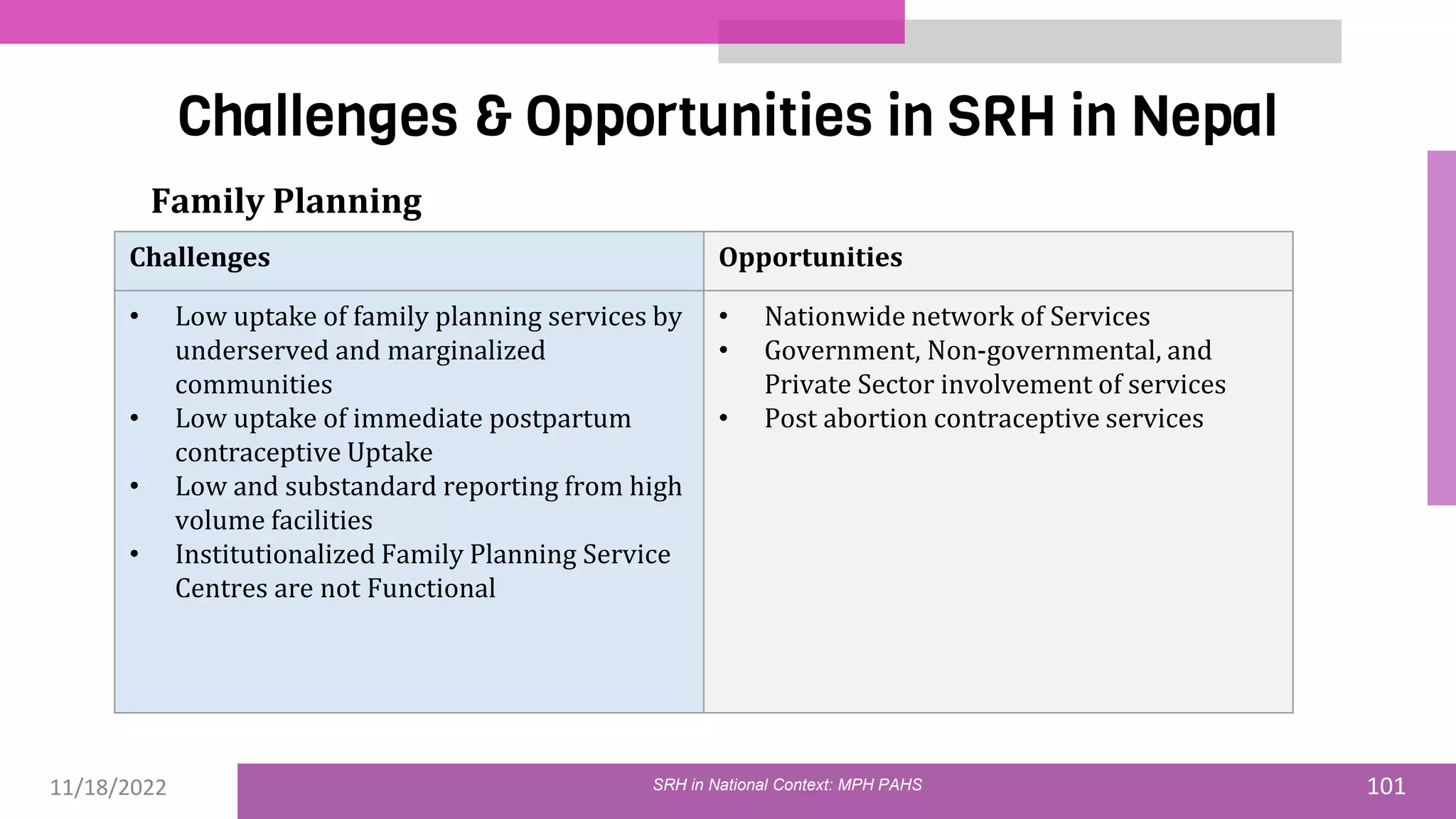
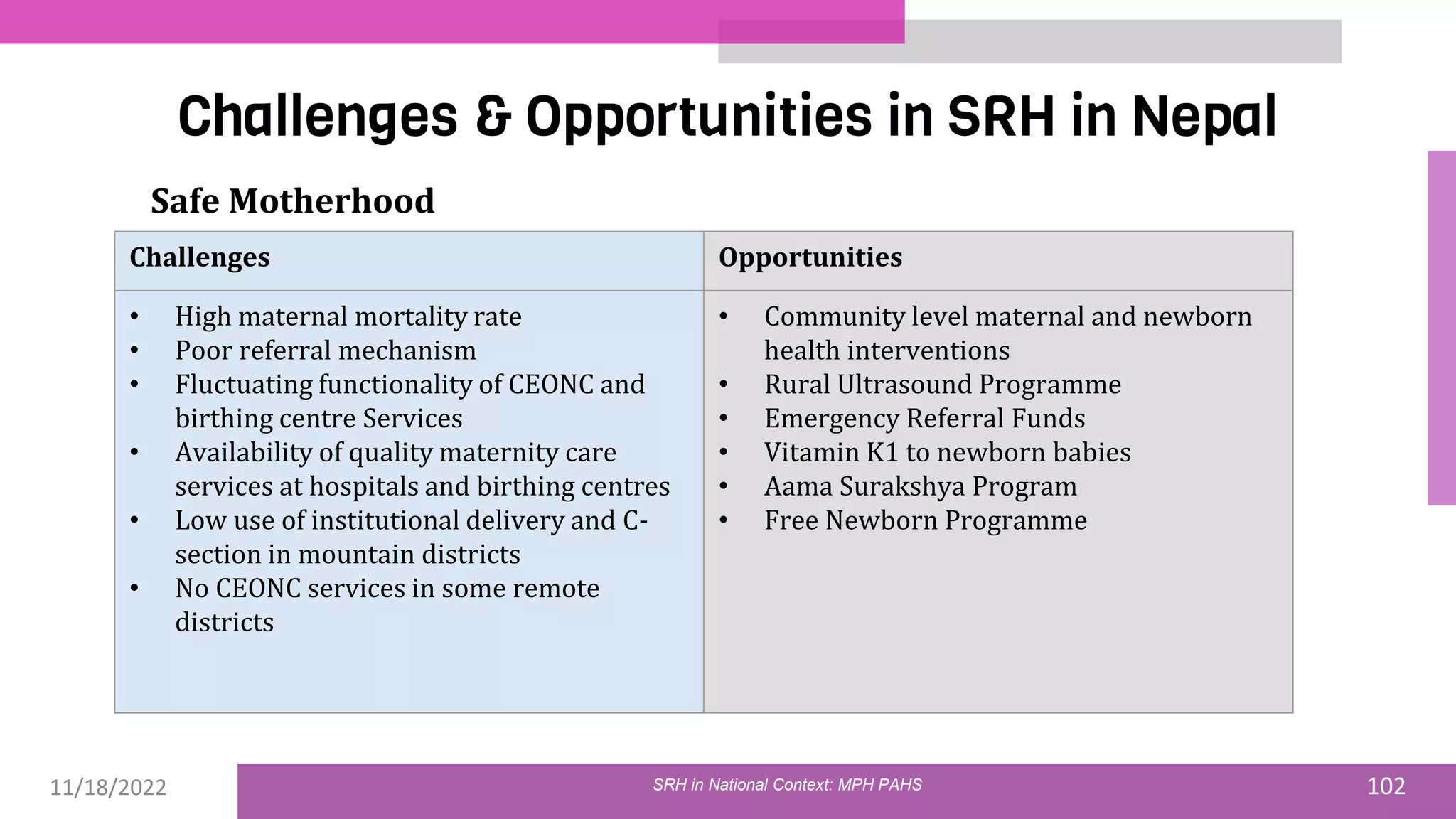
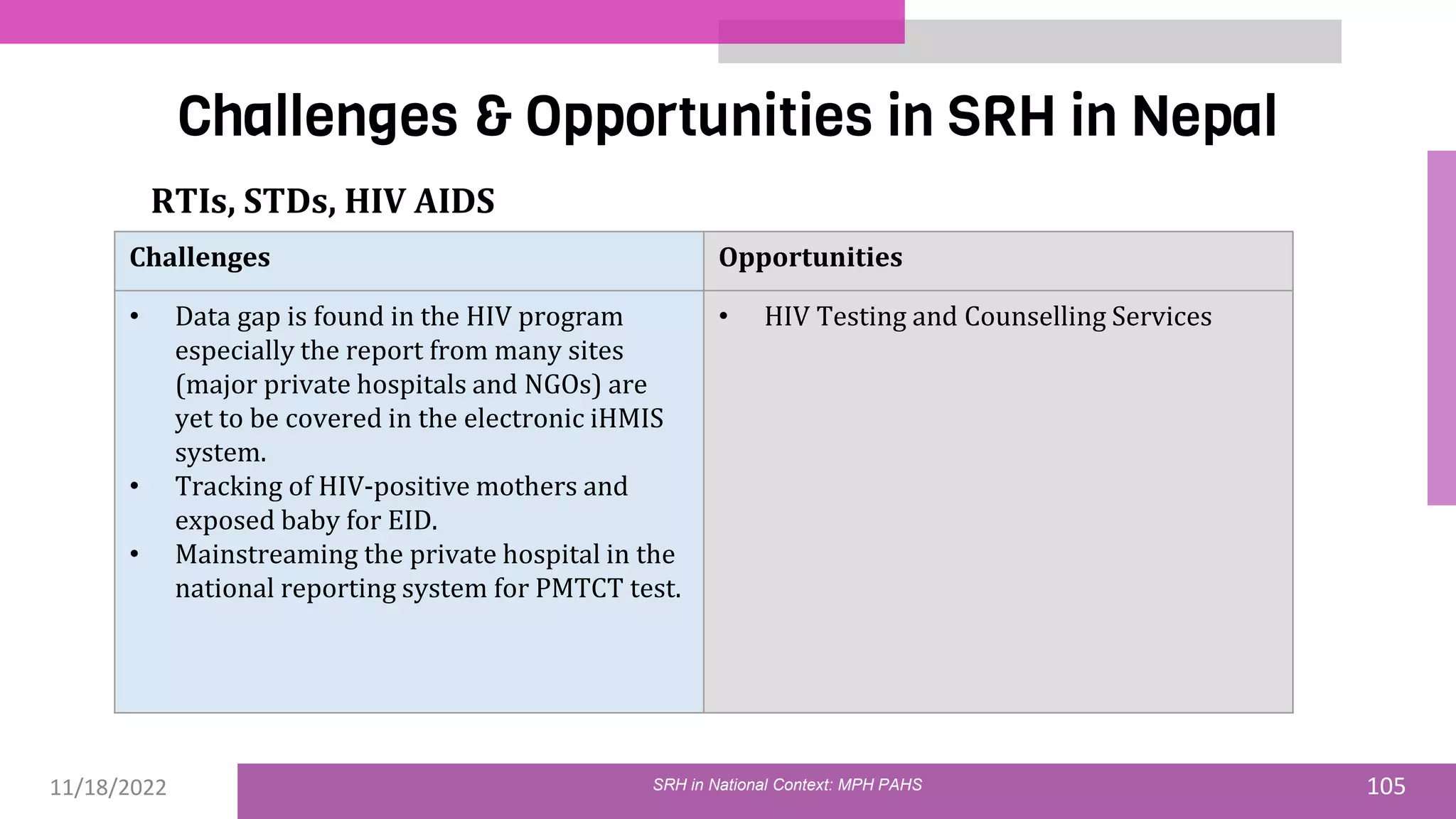
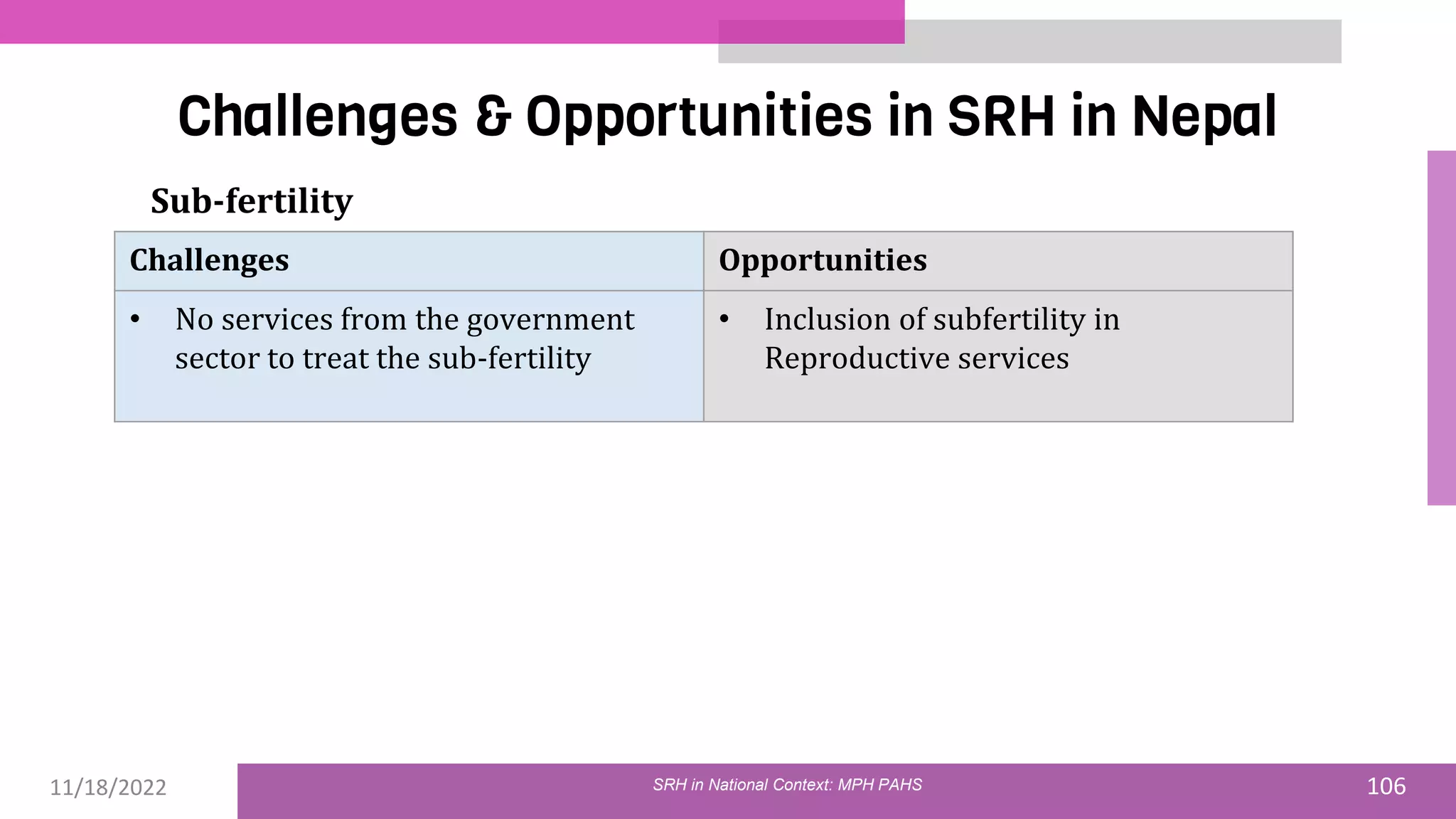
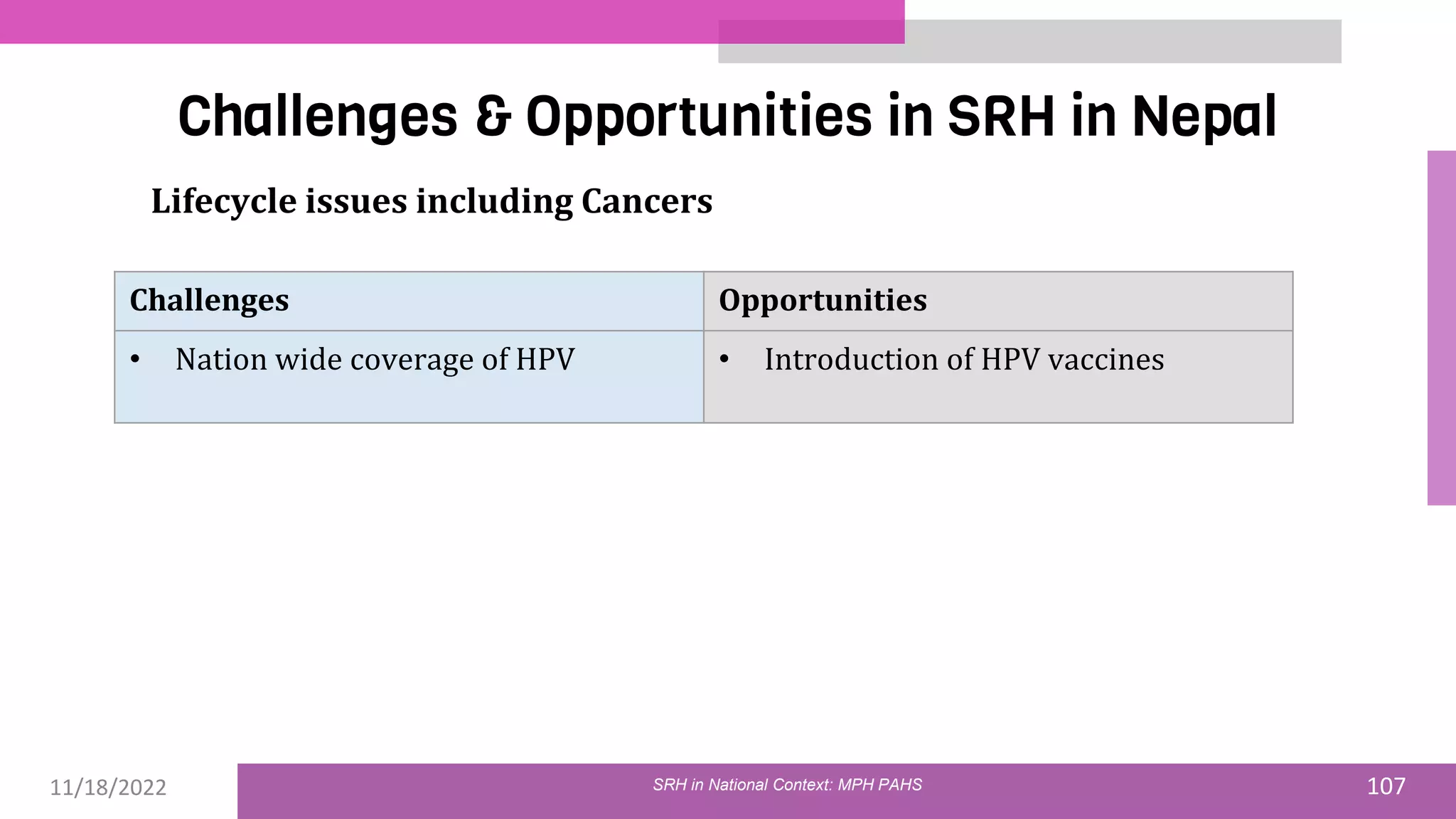
The document discusses the state of sexual and reproductive health (SRH) in Nepal, highlighting its definition, current situation, and the evolution of SRH strategies in the country. It includes statistical data on family planning, contraceptive use, teenage childbearing, and the legal framework surrounding abortion and maternal health care. The document also outlines the challenges and opportunities within the context of Nepal's SRH policies and programs.






















































![11/18/2022 110
References
SRH in National Context: MPH PAHS
• DoHS, Annual Report 2077/78
• MoHP, New Era, NDHS 2016
• National Reproductive Health Strategy, 2054
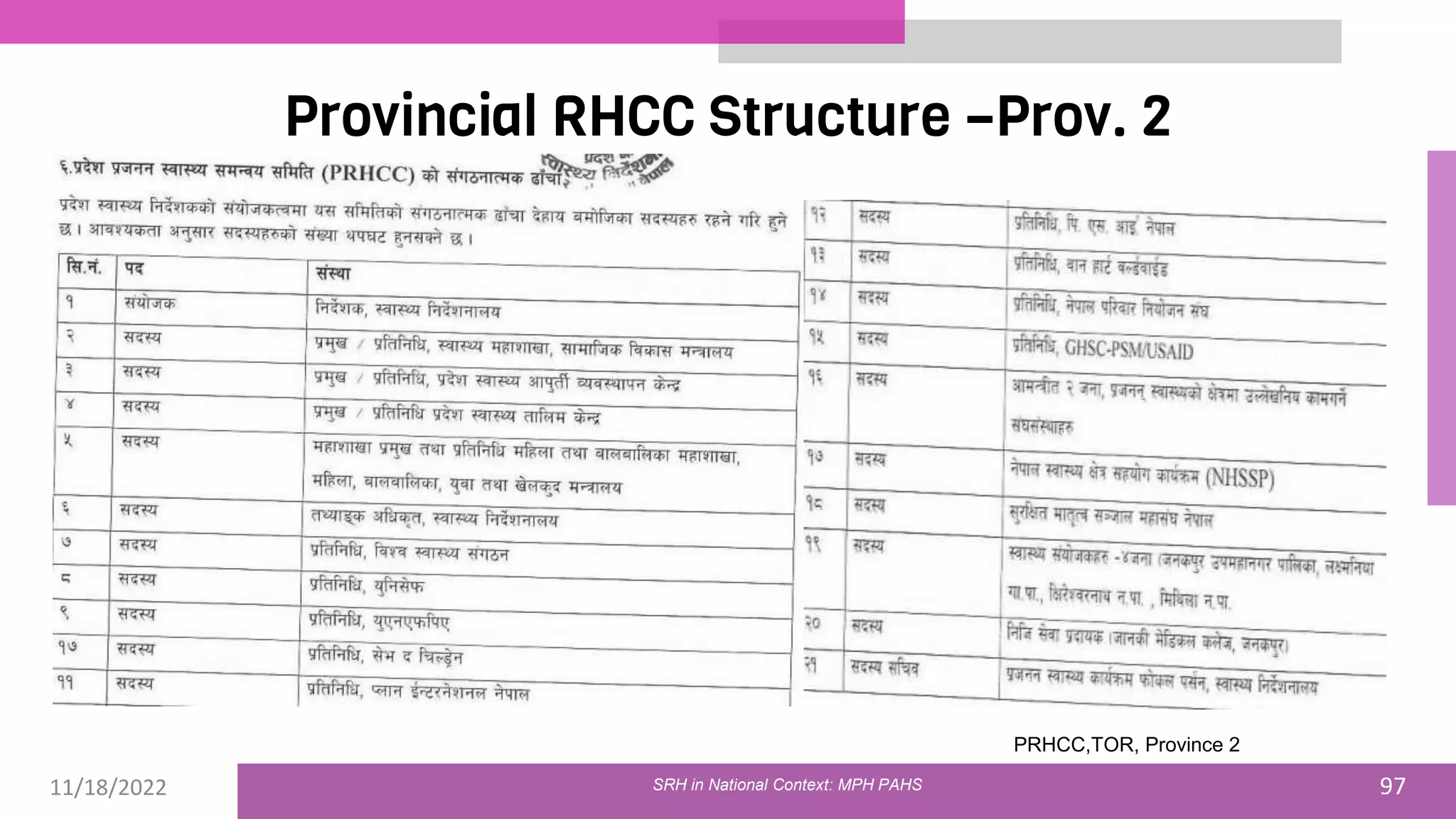
• Provincial Reproductive Health Coordination Committee ToR
[Internet].Available from https://mosd.p2.gov.np/post/provincial-
reproductive-health-coordination-committee-tor
• NHSSP Review of MOHP Committees-Summary Report.2012. [Internet]
Available from
http://www.nhssp.org.np/NHSSP_Archives/health_policy/MoHP_commi
ttees_review_2012.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group1srhcontextinnepalfinaltechnical1-221118161030-2e129f31/75/Sexual-and-Reproductive-Health-in-Context-of-Nepal-110-2048.jpg)

