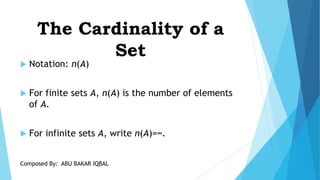
This document defines and provides examples of sets and different types of sets. It discusses the empty set, finite and infinite sets, the cardinality of a set, the universal set, equality and subsets of sets, and the power set. The document was composed by Abu Bakar Iqbal and covers basic concepts in mathematics related to sets.