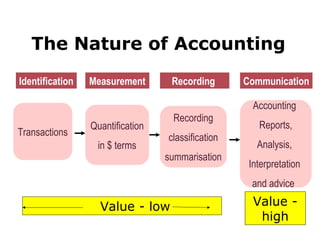
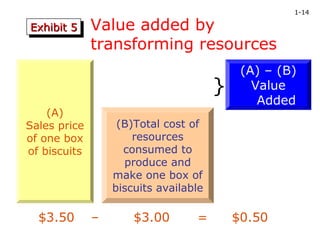
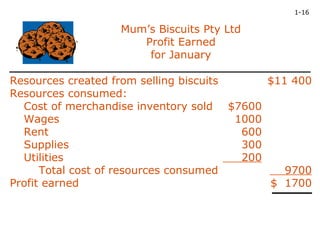
Accounting provides essential information for organizations to make decisions and measure performance. It identifies, measures, records, and communicates financial information. The accounting process allows organizations to determine value created through transformations of resources and profits earned. However, accounting relies on assumptions and constraints that could impact profit calculations if invalid. Management selection of accounting policies can affect financial statements and influence economic consequences and stakeholder perceptions.