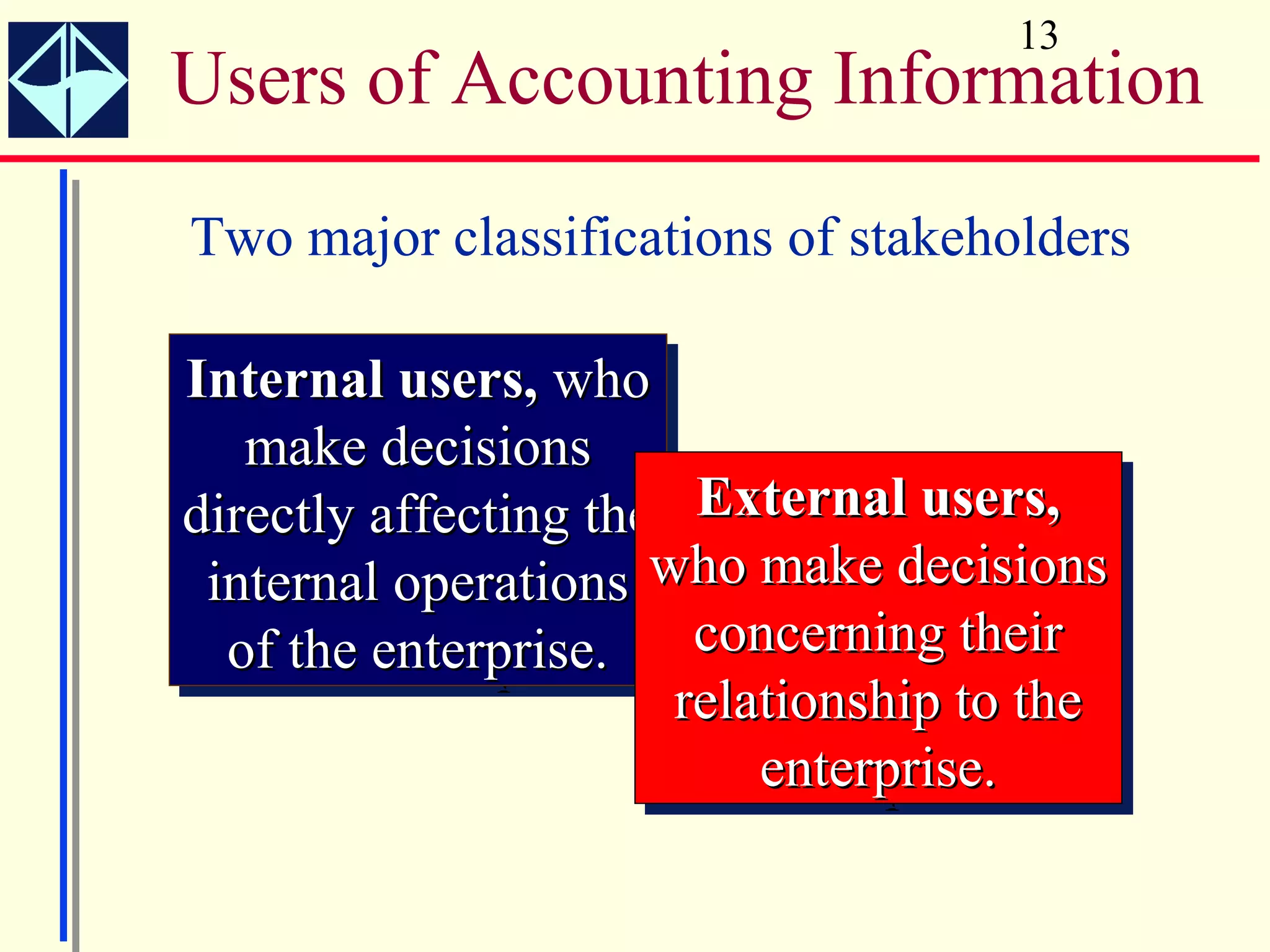
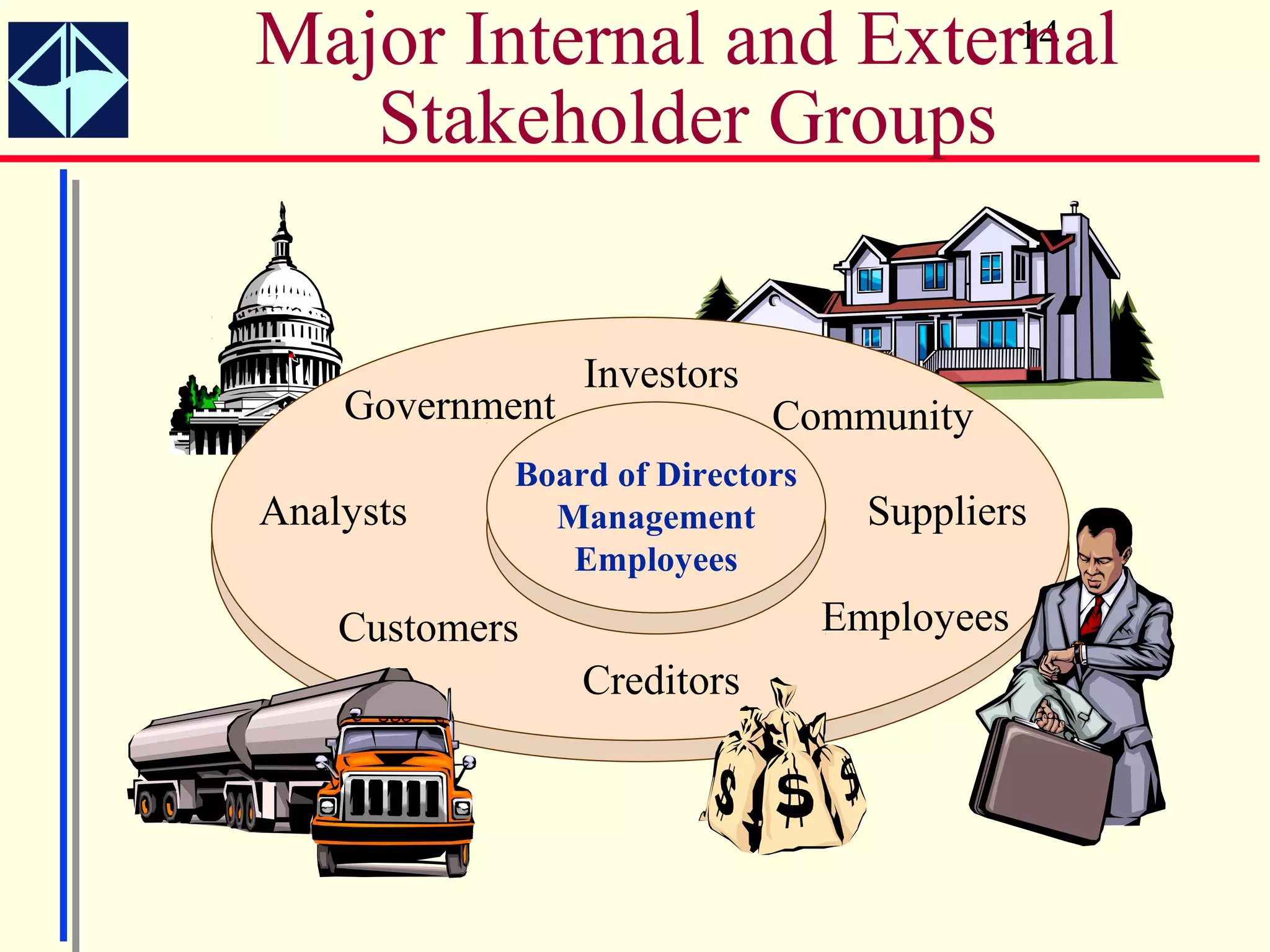
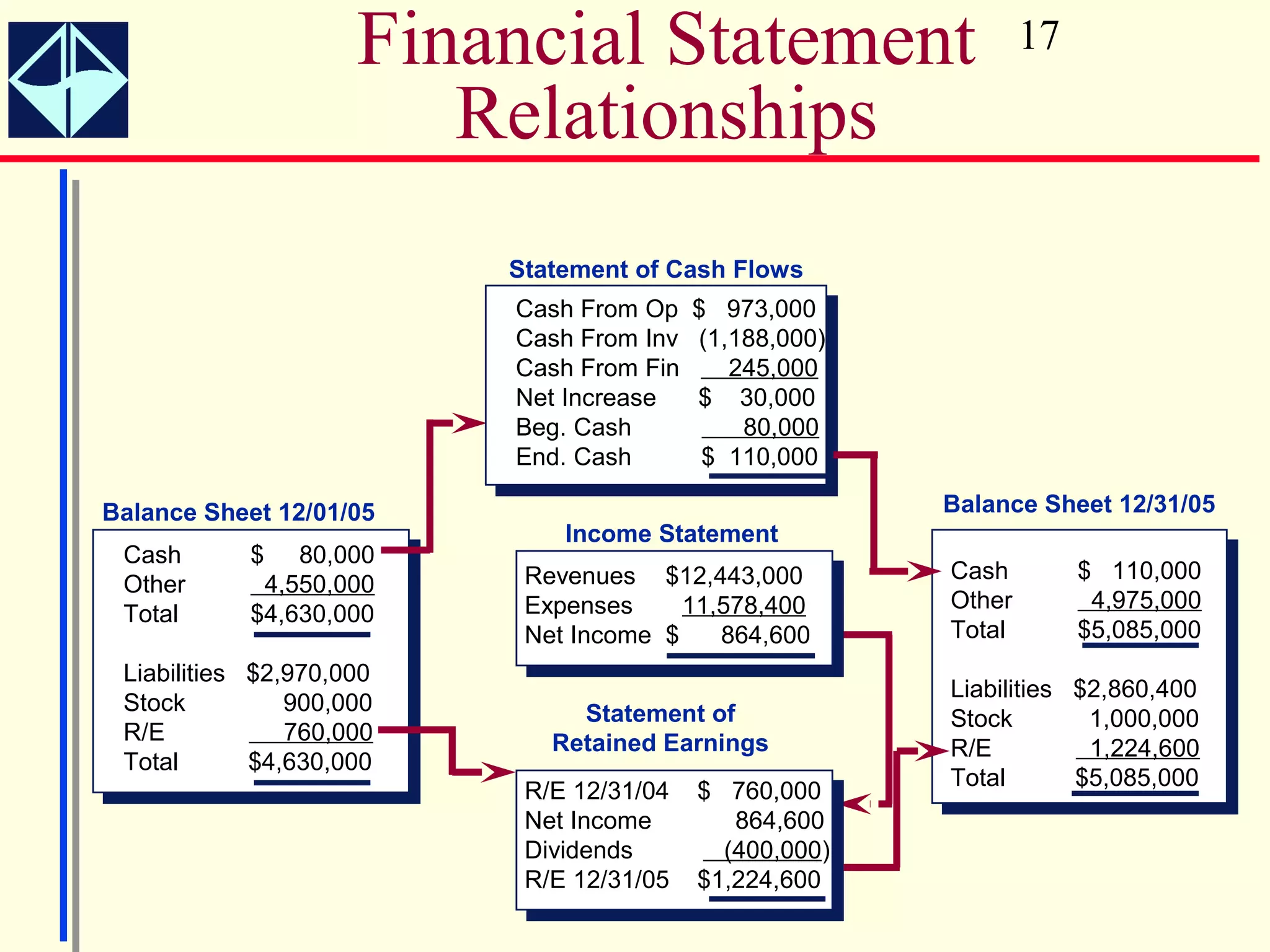
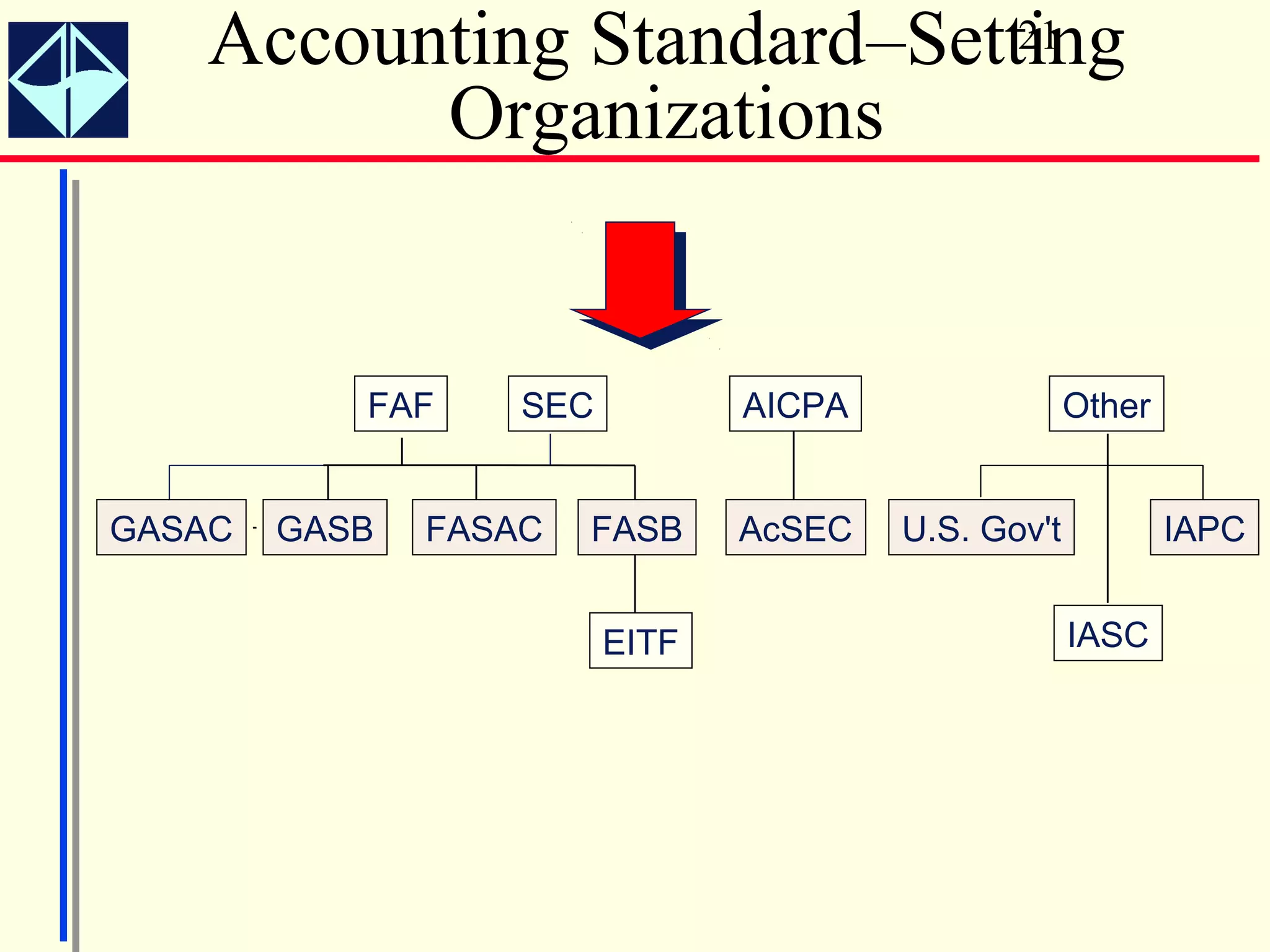
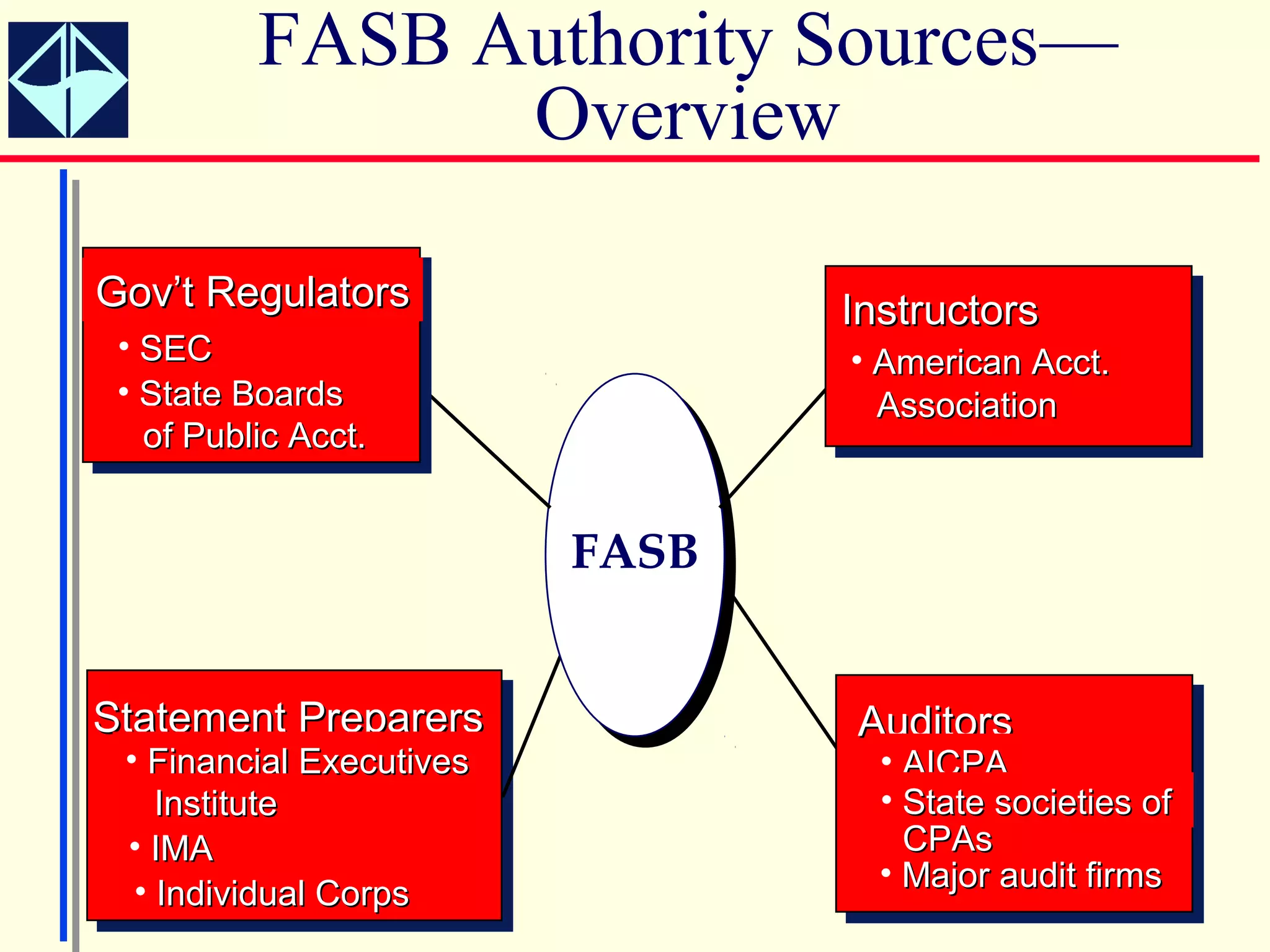
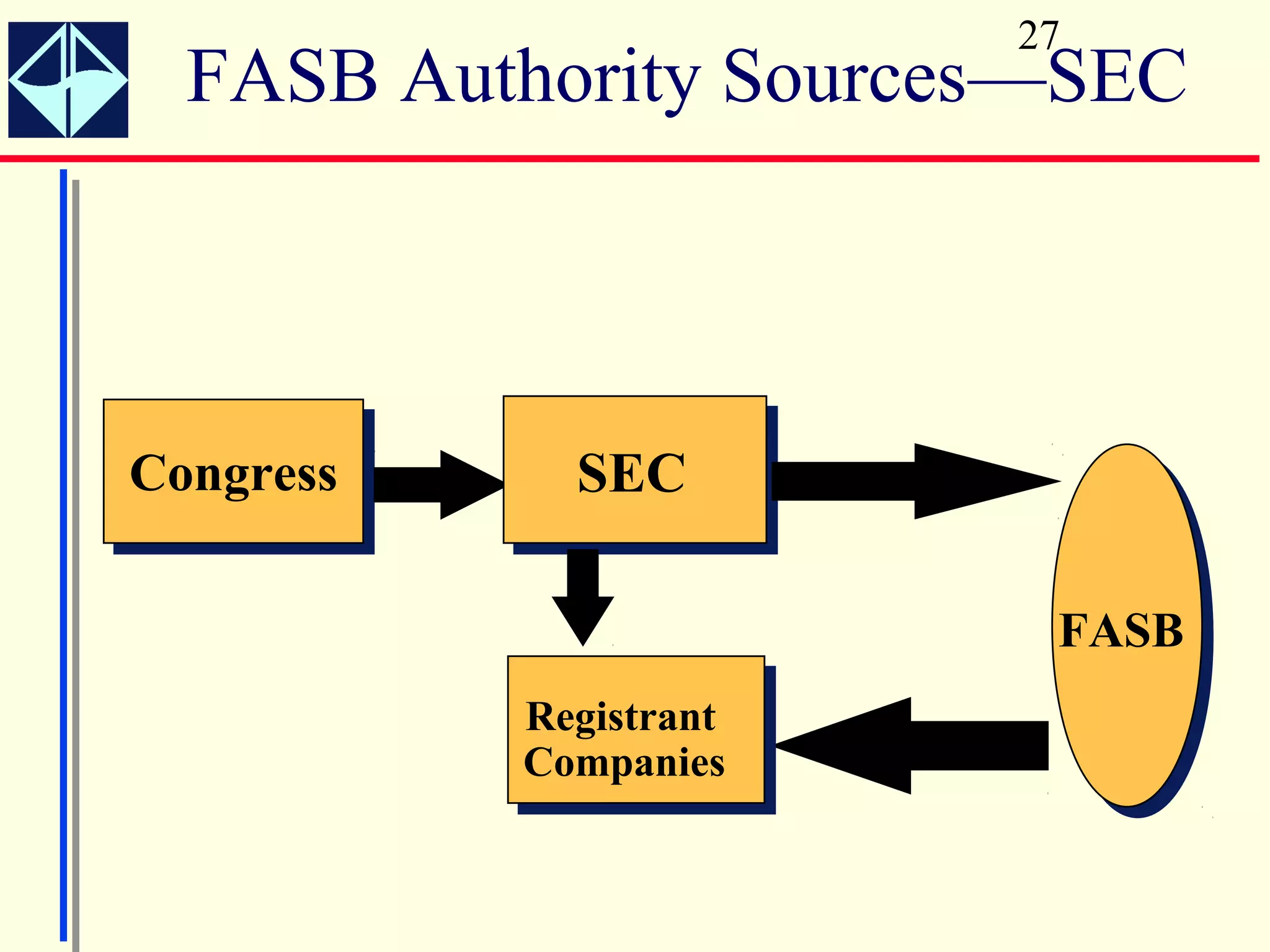
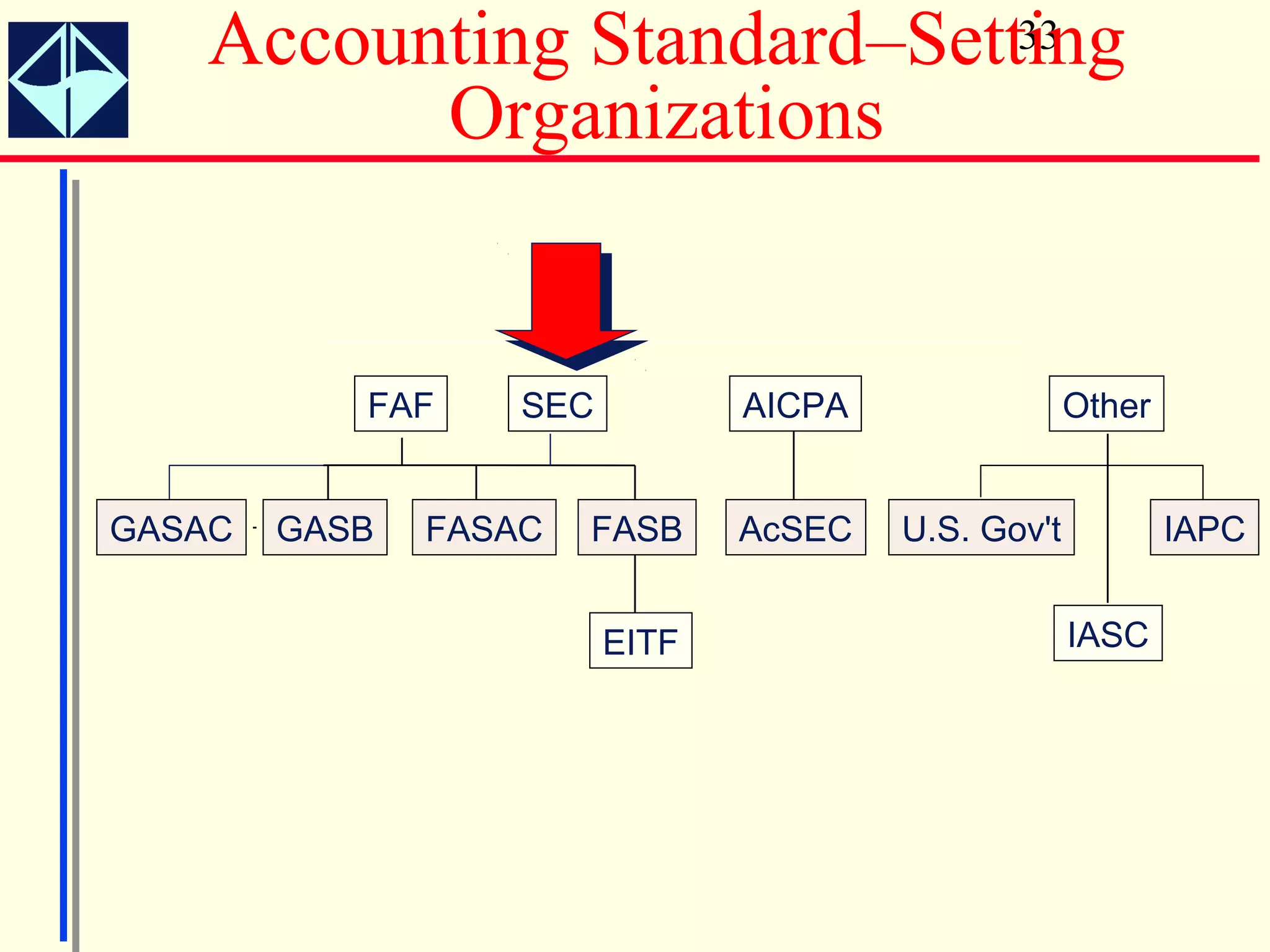
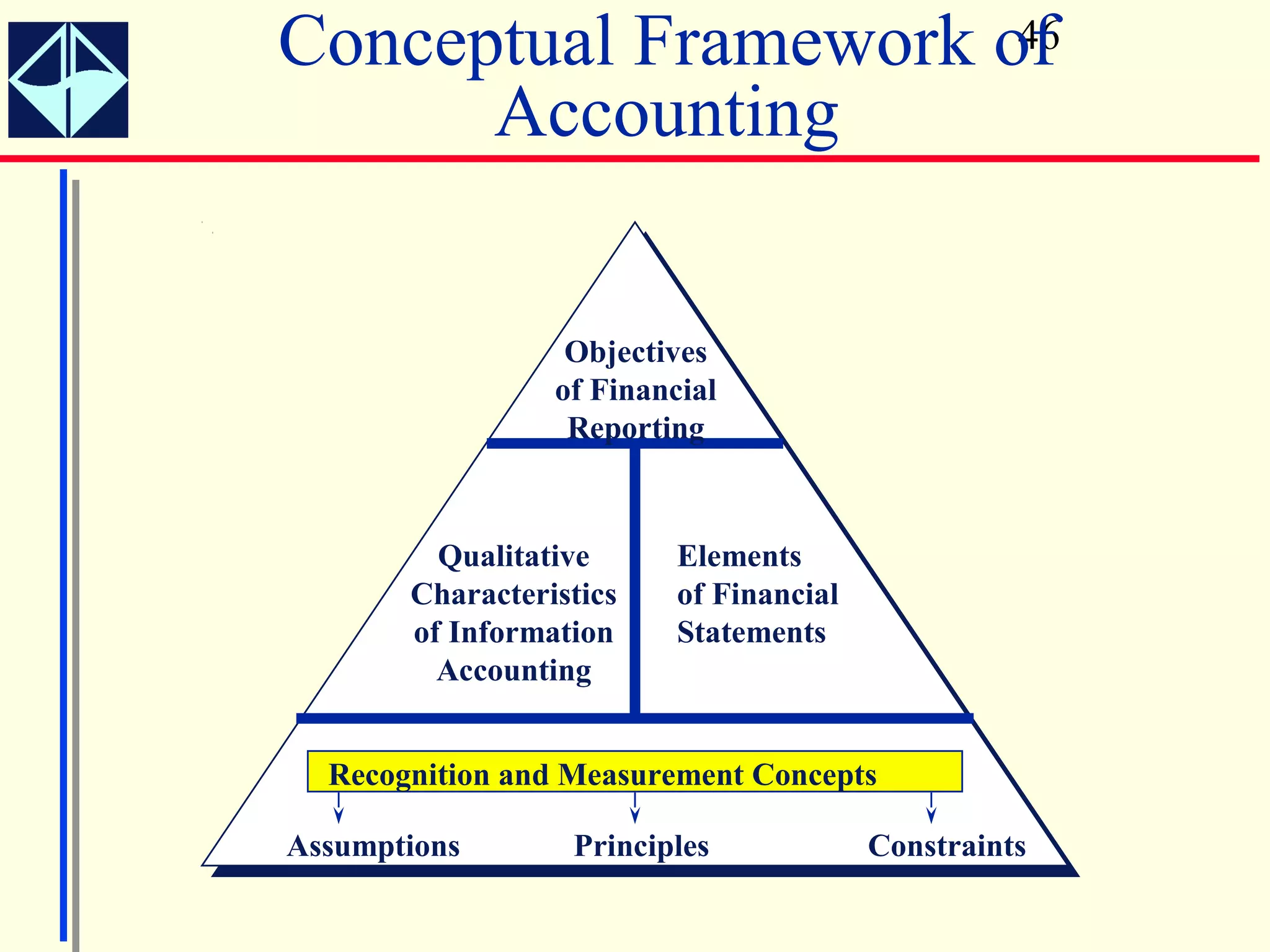
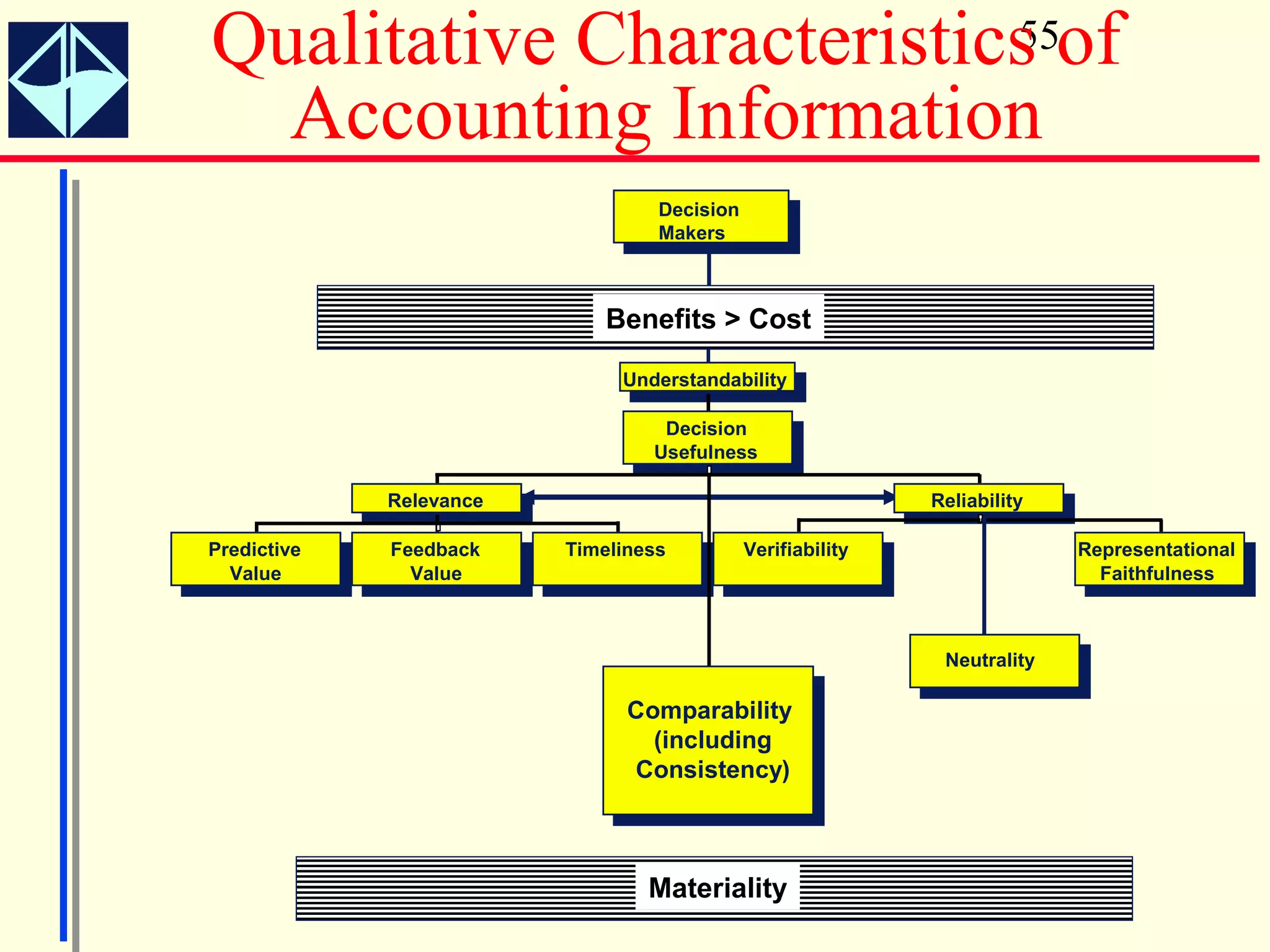
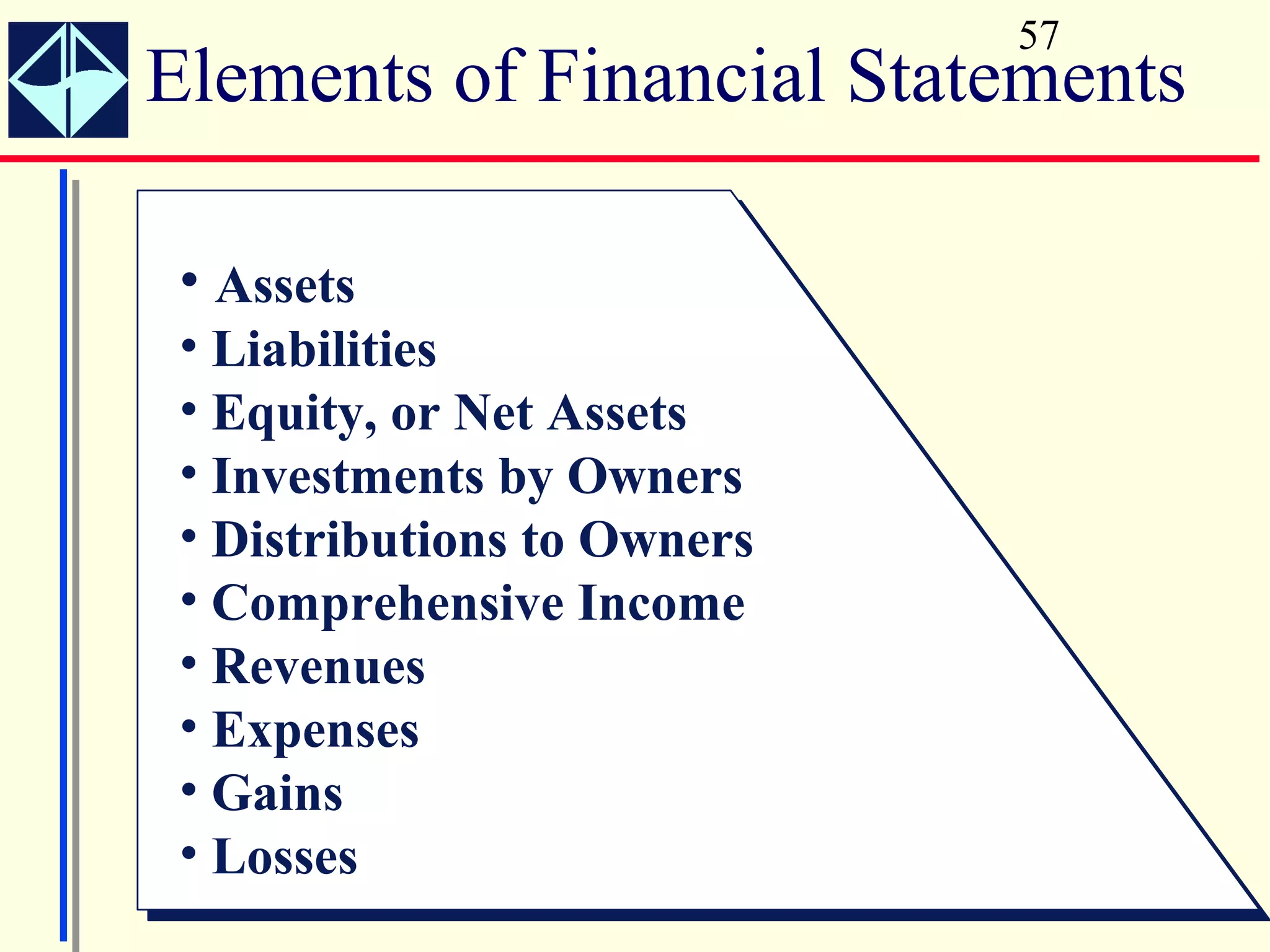
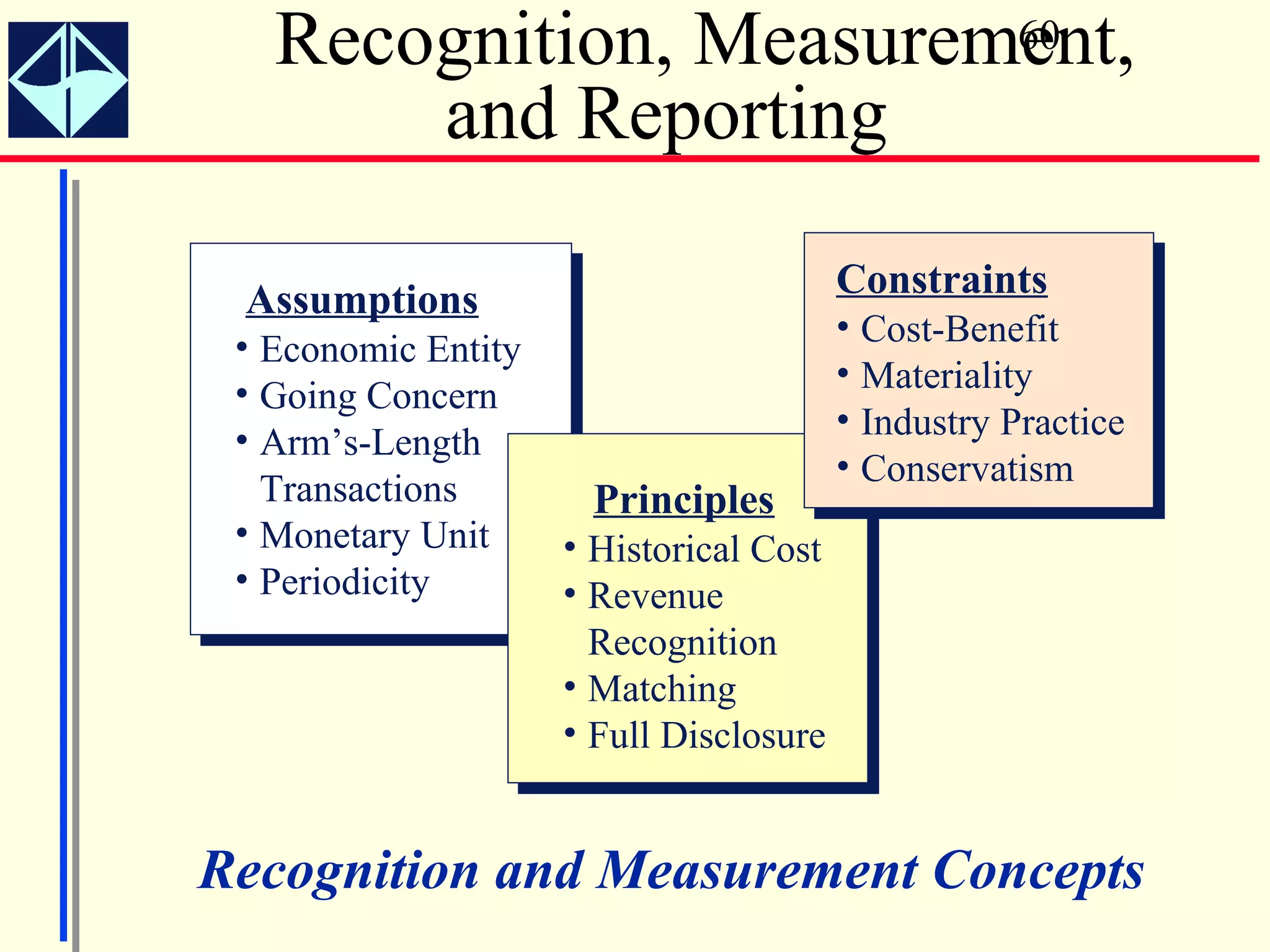
The document summarizes key concepts from Intermediate Accounting, 15th Edition by K. Fred Skousen, Earl K. Stice, and James D. Stice. It discusses the purpose of financial reporting, accounting standards organizations like the FASB and SEC, the conceptual framework of accounting, and objectives of financial reporting like usefulness, understandability, assessing future cash flows, and evaluating economic resources.