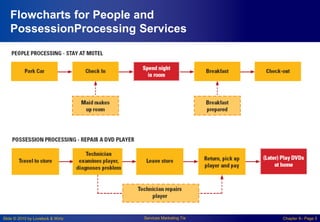
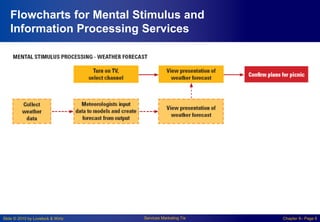
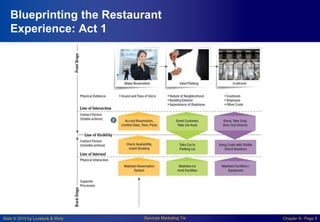
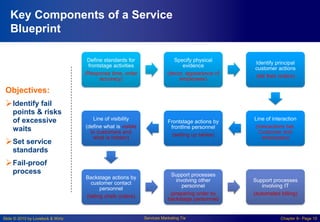
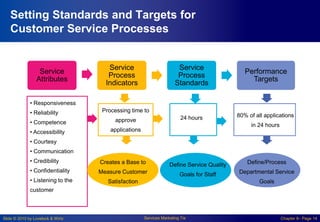
Chapter 8 focuses on designing and managing service processes through flowcharting customer service, blueprinting services, and process redesign. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer involvement, setting service standards, and evaluating performance to enhance productivity and reduce service failures. Key components include identifying fail points, defining standards, and considering customer participation in service delivery.