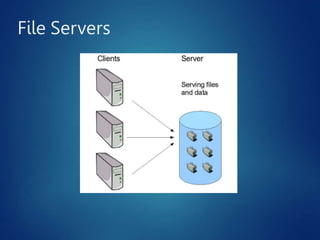
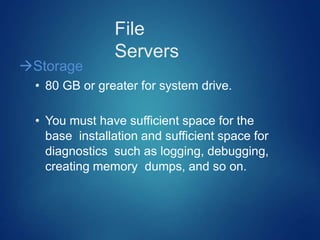
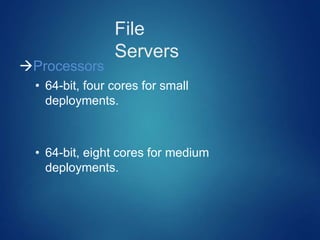
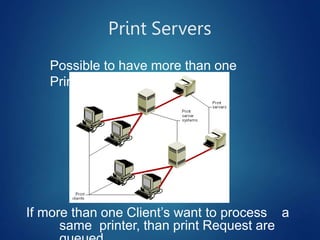
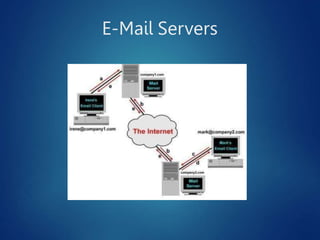
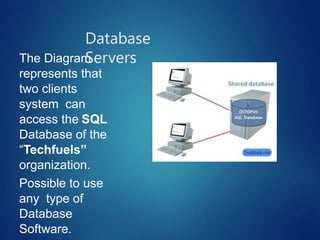
This document discusses different types of servers. It describes file servers, which store and share files across a network. Print servers manage shared printers. Email servers function like a virtual post office, storing and routing messages. Database servers provide database services and functionality to other programs and computers, with examples including Oracle, DB2, and SQL Server. Requirements for file servers include a minimum of 4GB RAM, 80GB storage, and 4-8 processor cores depending on deployment size.