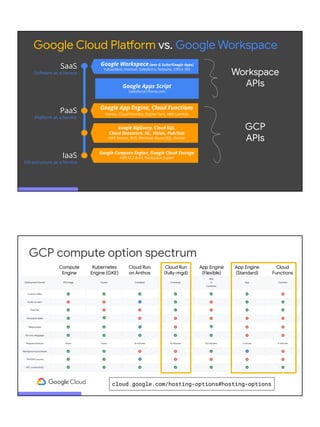
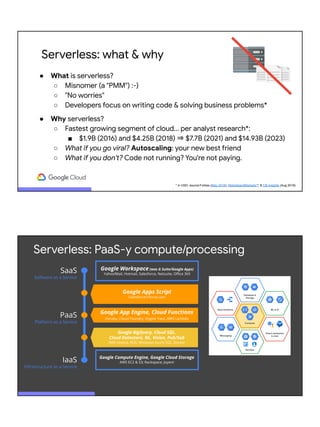
The document discusses serverless computing on Google Cloud, highlighting the speaker's extensive background and mission to facilitate developer success using Google’s cloud offerings. It outlines various serverless platforms such as App Engine, Cloud Functions, and Cloud Run, detailing their advantages, use cases, and best practices for development. Emphasis is placed on optimizing performance, architecture, and the importance of choosing the right tool for specific tasks in cloud development.







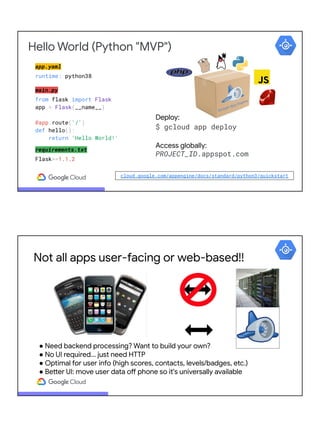


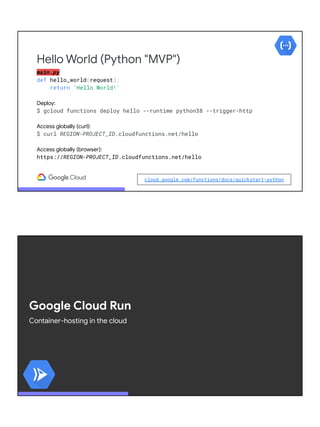

![Hello World (Python "MVP")
Dockerfile
FROM python:3-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
CMD ["python", "main.py"]
.dockerignore
Dockerfile
README.md
*.pyc
*.pyo
.git/
__pycache__
Build (think docker build and docker push) then deploy (think docker run):
$ gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/PROJ_ID/IMG_NAME
$ gcloud run deploy SVC_NAME --image gcr.io/PROJ_ID/IMG_NAME
OR… Build and Deploy (1-line combination of above commands):
$ gcloud run deploy SVC_NAME --source .
Access globally:
SVC_NAME-HASH-REG_ABBR.a.run.app
Docker &
Dockerfile
OPTIONAL!!
● Build containers easily & securely without creating/managing Dockerfiles
● Open source, open standard; based on CNCF Buildpacks spec v3
● Used by GCF Functions Framework to deploy locally-developed functions
● Supports most common development tools
○ Go 1.10+
○ Node.js 10+
○ Python 3.7+
○ Java 8 & 11
○ .NET Core 3.1+
● Blog posts
○ cloud.google.com/blog/products/containers-kubernetes/google-cloud-now-supports-buildpacks and
cloud.google.com/blog/products/serverless/build-and-deploy-an-app-to-cloud-run-with-a-single-command
Deploy to Cloud Run with Buildpacks
github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/buildpacks
$ ls
index.js package.json
$ gcloud run deploy myapp --source .
$ ls
app.py requirements.txt
$ gcloud run deploy myapp --source .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverless76-211014042646/85/Serverless-computing-with-Google-Cloud-17-320.jpg)
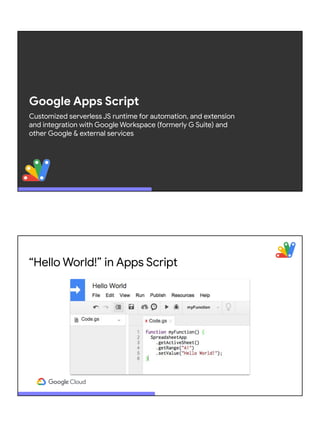
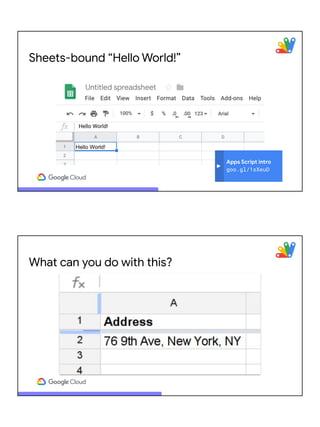
![Accessing maps from
spreadsheets?!?
goo.gl/oAzBN9
This… with help from Google Maps & Gmail
function sendMap() {
var sheet = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSheet();
var address = sheet.getRange("A2").getValue();
var map = Maps.newStaticMap().addMarker(address);
GmailApp.sendEmail('friend@example.com', 'Map',
'See below.', {attachments:[map]});
}
JS
g.co/codelabs/apps-script-intro](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverless76-211014042646/85/Serverless-computing-with-Google-Cloud-20-320.jpg)





![BPs: Local development/testing
● App Engine — local or framework devserver
○ Local devserver (Gen1 or Gen2) and local unit testing (Gen1)
○ Testing and deploying your application: running locally (Gen2)
● Cloud Functions — Functions Framework
○ Functions Framework (local dev/testing; bundle function for Cloud Run)
○ Cloud Functions local development
○ Cloud Functions testing overview
○ Codelab: Local development with Cloud Functions (Node.js) using VSC
● Cloud Run — run Docker containers locally
○ Testing a Cloud Run service locally
○ Tutorial: Local troubleshooting of a Cloud Run service
BPs: Local testing Cloud emulators
● Cloud Datastore
○ Datastore emulator (non-App Engine or App Engine [Gen2])
○ App Engine Datastore emulator (Gen1 [or Gen2]; migrate to above)
● Firebase/Cloud Firestore
○ Firebase Emulator Suite (multiple product emulators; unit testing video)
○ Cloud Firestore emulator (w/in Firebase Emulator Suite; ex: React Native)
○ Cloud Storage emulator (w/in Firebase Emulator Suite; ex: React Native)
● Other Google Cloud emulators
○ Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Spanner, Cloud BigTable
● Others: Google Cloud Java test tools; BigQuery test kit (non-Google)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverless76-211014042646/85/Serverless-computing-with-Google-Cloud-27-320.jpg)


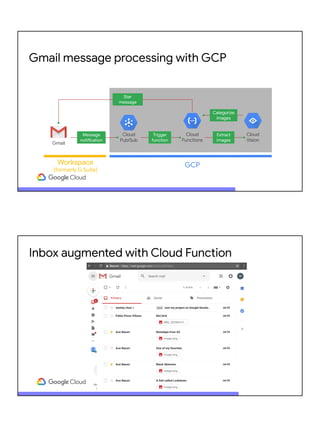

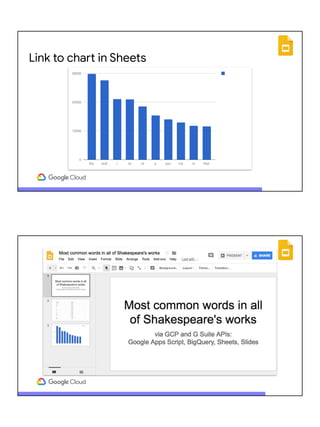
![Supercharge Workspace (G Suite) with GCP
Workspace (G Suite) GCP
BigQuery
Apps Script
Slides Sheets
Application
request
Big data
analytics
App summary
● Leverage GCP and build the "final mile" with Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)
● Driven by Google Apps Script
● Google BigQuery for data analysis
● Google Sheets for visualization
● Google Slides for presentable results
● "Glued" together w/Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) serverless
● Build this app (codelab): g.co/codelabs/bigquery-sheets-slides
● Video and blog post: bit.ly/2OcptaG
● Application source code: github.com/googlecodelabs/bigquery-sheets-slides
● Presented at Google Cloud NEXT (Jul 2018 [DEV229] & Apr 2019 [DEV212])
● cloud.withgoogle.com/next18/sf/sessions/session/156878
● cloud.withgoogle.com/next/sf/sessions?session=DEV212](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverless76-211014042646/85/Serverless-computing-with-Google-Cloud-35-320.jpg)
![06
Summary
Online resources &
references
Cost of Google Cloud serverless tools
● What is free in Google Cloud overall?
○ Free Trial (credit card required; expires)
■ $300USD credit good for first 90 days
○ Always Free tier (credit card required; no expiration; subject to change)
■ Independent of Free Trial & education grants (more below)
■ Some GCP products free up to usage limits
○ Learn about both programs at cloud.google.com/free
● Serverless Always Free tier (daily or monthly quotas)
○ App Engine (28 [or 9] hours, 1GB storage & 1GB egress) per day
○ Cloud Run (2M reqs, 350k GB-secs, 180k vCPU-secs, 1GB egress) per month
○ Cloud Functions (2M calls, 400k GB-secs, 200k vCPU-secs, 5GB egress) per month
● Higher education (teaching & research) grants
○ cloud.google.com/edu (credit card NOT required; expires)
○ Provides "free" usage for coursework and initial research
$$ FREE $$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverless76-211014042646/85/Serverless-computing-with-Google-Cloud-36-320.jpg)
![Cloud/serverless session summary
● Why go cloud?
○ Cloud computing has taken the world by storm
○ You're behind if you're not already using it… it's not too late!
○ Help train the next generation cloud-ready workforce!
● Google Cloud and why serverless?
○ Many features: compute, storage, AI/ML, NW, data processing, etc.
○ Modernization more than moving VMs to the cloud
○ Serverless lets users focus on just their logic (apps or functions)
○ Interesting possibilities using all of Google Cloud (GCP + Workspace)
● Documentation
○ GCP: cloud.google.com/{docs,appengine,functions,run,vision,automl,translate,language,
speech,texttospeech,video-intelligence,firestore,bigquery,compute,storage,gpu,tpu}
○ G Suite: developers.google.com/{workspace,drive,calendar,docs,sheets,slides,apps-script}
● Introductory "codelabs" (free, online, self-paced, hands-on tutorials [Python])
○ App Engine: codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/cloud-app-engine-python
○ Cloud Functions: codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/cloud-starting-cloudfunctions
○ Cloud Run: codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/cloud-run-hello-python3
○ Apps Script: g.co/codelabs/apps-script-intro
● Others: gcplab.me (GCP) & codelabs.developers.google.com/?cat=googleworkspace (Workspace)
● Videos: youtube.com/GoogleCloudPlatform (GCP) and goo.gl/JpBQ40 (Workspace)
● Samples: github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform (GCP) and github.com/googleworkspace (Workspace)
● Know AWS/Azure? Compare w/GCP at cloud.google.com/docs/compare/{aws,azure}
● Google Cloud serverless products: cloud.google.com/serverless
Google Cloud references](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverless76-211014042646/85/Serverless-computing-with-Google-Cloud-37-320.jpg)
![Other Google APIs & platforms
● Google Workspace (G Suite) (code Gmail, Drive, Docs, Sheets, Slides!)
○ developers.google.com/gsuite
● Firebase (mobile development platform and RT DB plus ML-Kit)
○ firebase.google.com and firebase.google.com/docs/ml-kit
● Google Data Studio (data visualization, dashboards, etc.)
○ datastudio.google.com/overview
○ goo.gle/datastudio-course
● Actions on Google/Assistant/DialogFlow (voice apps)
○ developers.google.com/actions
● YouTube (Data, Analytics, and Livestreaming APIs)
○ developers.google.com/youtube
● Google Maps (Maps, Routes, and Places APIs)
○ developers.google.com/maps
● Flutter (native apps [Android, iOS, web] w/1 code base[!])
○ flutter.dev
Thank you! Questions?
Wesley Chun
@wescpy
Video: youtu.be/nOj8y_gjSWI?t=1170
Progress bars: goo.gl/69EJVw](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serverless76-211014042646/85/Serverless-computing-with-Google-Cloud-38-320.jpg)