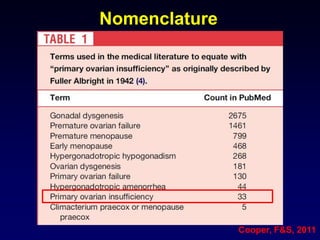
This document discusses premature ovarian failure (POI), including its definition, causes, incidence, clinical features, evaluation, and genetic factors. Some key points include:
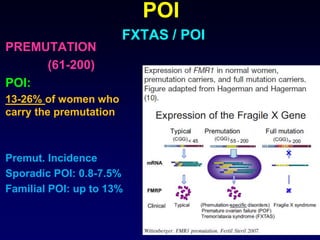
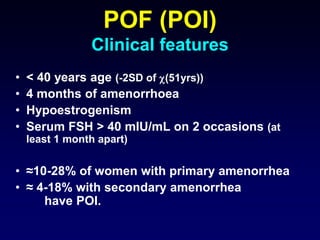
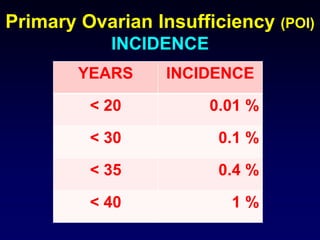
- POI is defined as ovarian failure before age 40 years with elevated FSH levels.
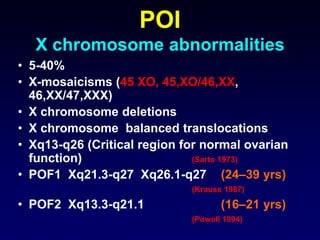
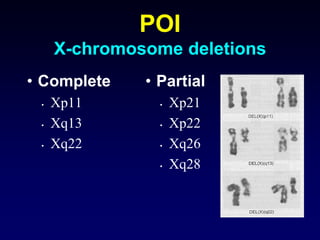
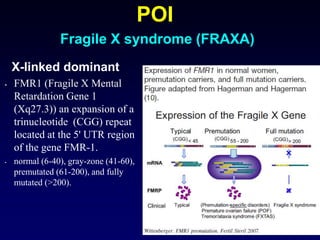
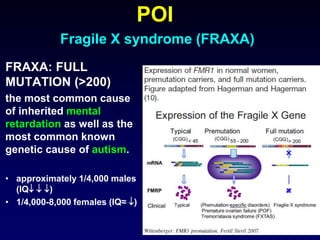
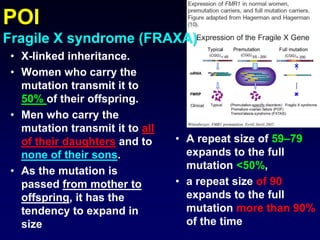
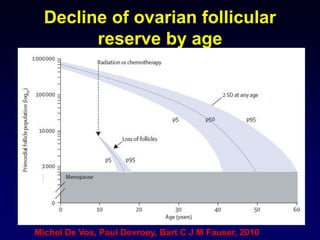
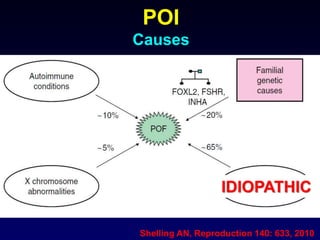
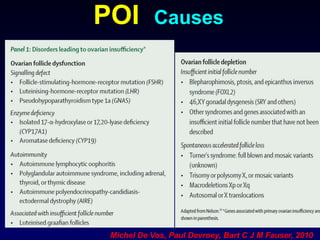
- Causes include genetic factors like fragile X syndrome, galactosemia, or chromosomal abnormalities. Other causes are premature follicle loss, autoimmunity, or unknown/idiopathic factors.
- Evaluation involves assessing family history, testing hormone levels, and obtaining a karyotype to check for genetic abnormalities in some cases. Further genetic testing may be considered if an underlying condition is suspected.










![Early menopause
Family history
• 129 early menopause cases (<46 years old)
• Overall 129 (37.5%) of the early menopause
cases reported a family history of
menopause before age 46 years in a mother,
sister, aunt, or grandmother compared to 31
(9.0%) of controls yielding an odds ratio
(OR) of 6.1 (95% [CI] of 3.9 to 9.4) after
adjustment for smoking history, education,
parity, and body mass index.
Cramer DW, 1995](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/senturklmemaswebinarpof20160127-210315082435/85/Senturk-lm-emas-webinar-pof_20160127-19-320.jpg)