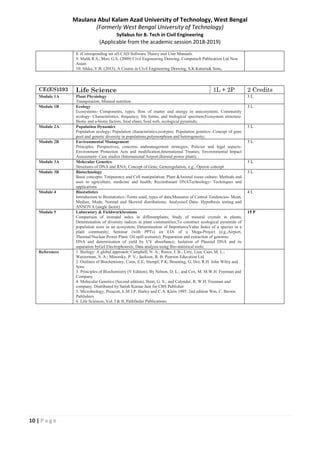
This document outlines the syllabus for the Biology course CE(BS)301 for the B. Tech in Civil Engineering program at Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology. The course is divided into 9 modules that cover topics such as classification of life forms, genetics, biomolecules, enzymes, information transfer, macromolecular analysis, metabolism, and microbiology. The modules aim to convey fundamental biological concepts and their importance to engineering, such as how biological observations led to scientific discoveries, the universality of the genetic code, and that life relies on the same basic biomolecules and energy transactions as physical systems. The document also provides references for further reading.