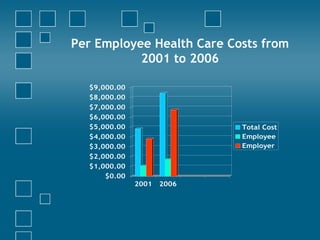
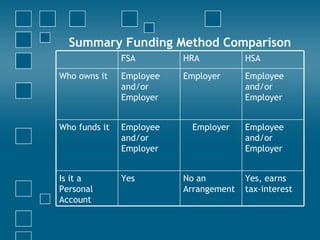
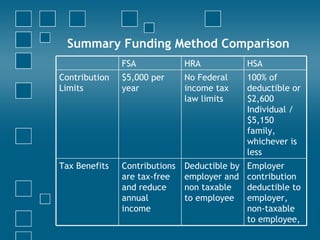
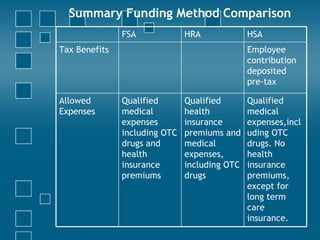
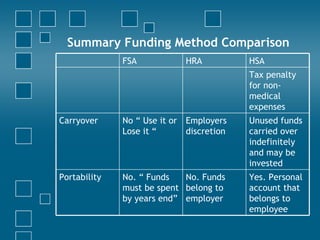
Consumer directed health care (CDHC) plans aim to make consumers more aware of healthcare costs through high deductible plans paired with tax-advantaged savings accounts. Three common account types are flexible spending accounts (FSA), health reimbursement accounts (HRA), and health savings accounts (HSA). FSAs have annual "use it or lose it" limits while HRAs and HSAs allow funds to roll over. HSAs offer the most tax benefits and are owned permanently by the employee, unlike HRAs owned by the employer. CDHC plans shift costs to consumers in hopes of curbing healthcare spending increases.