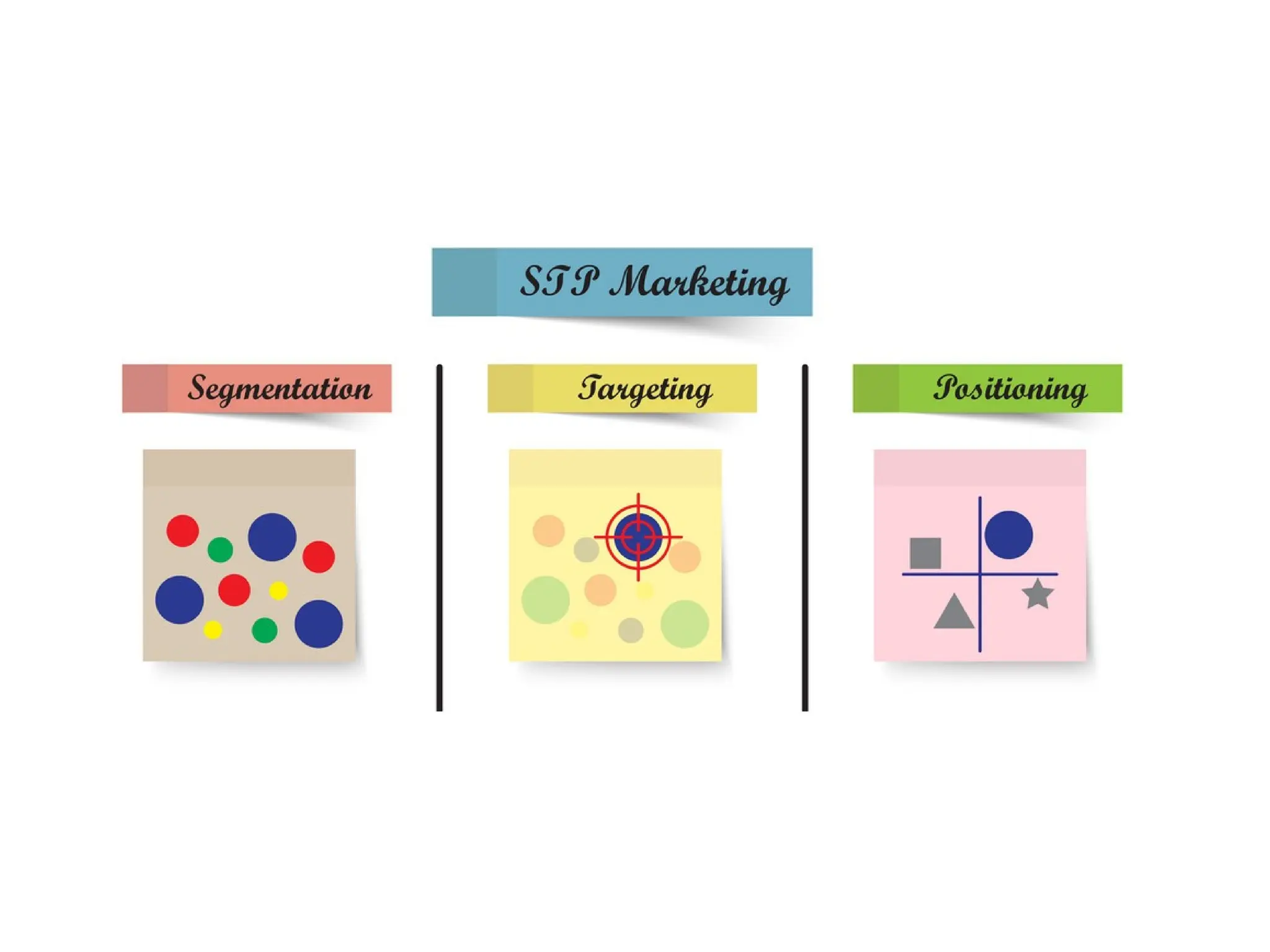
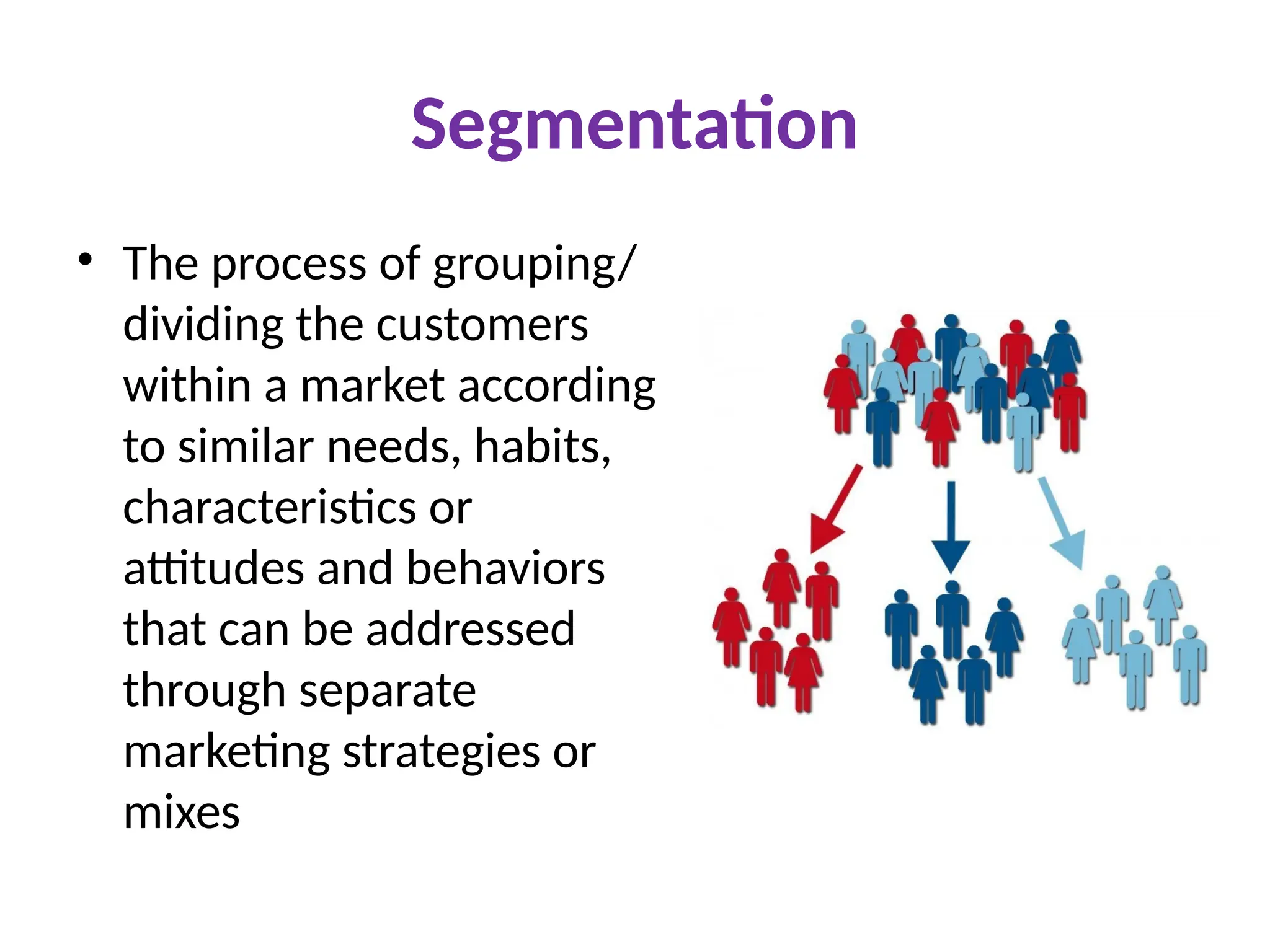
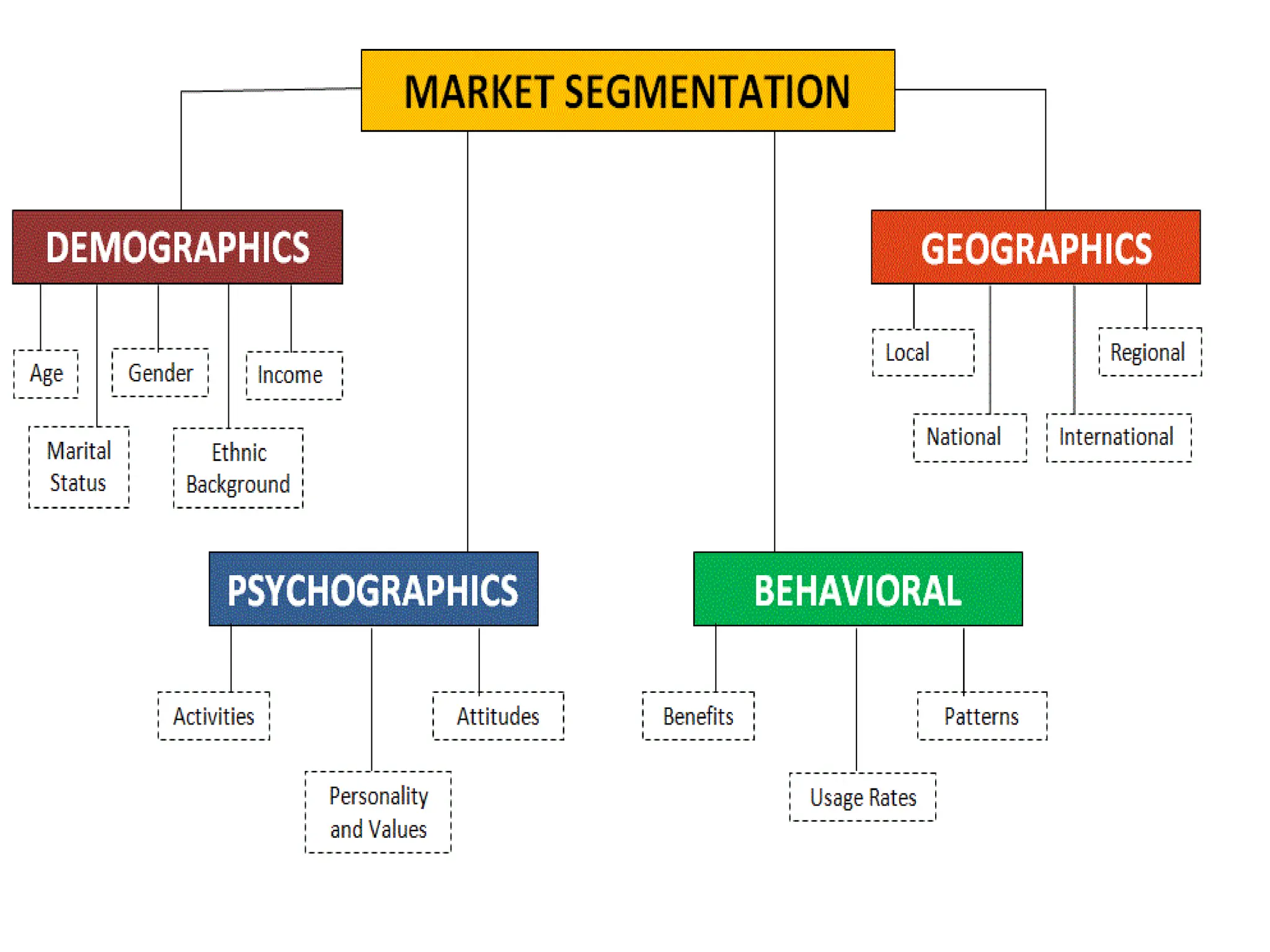
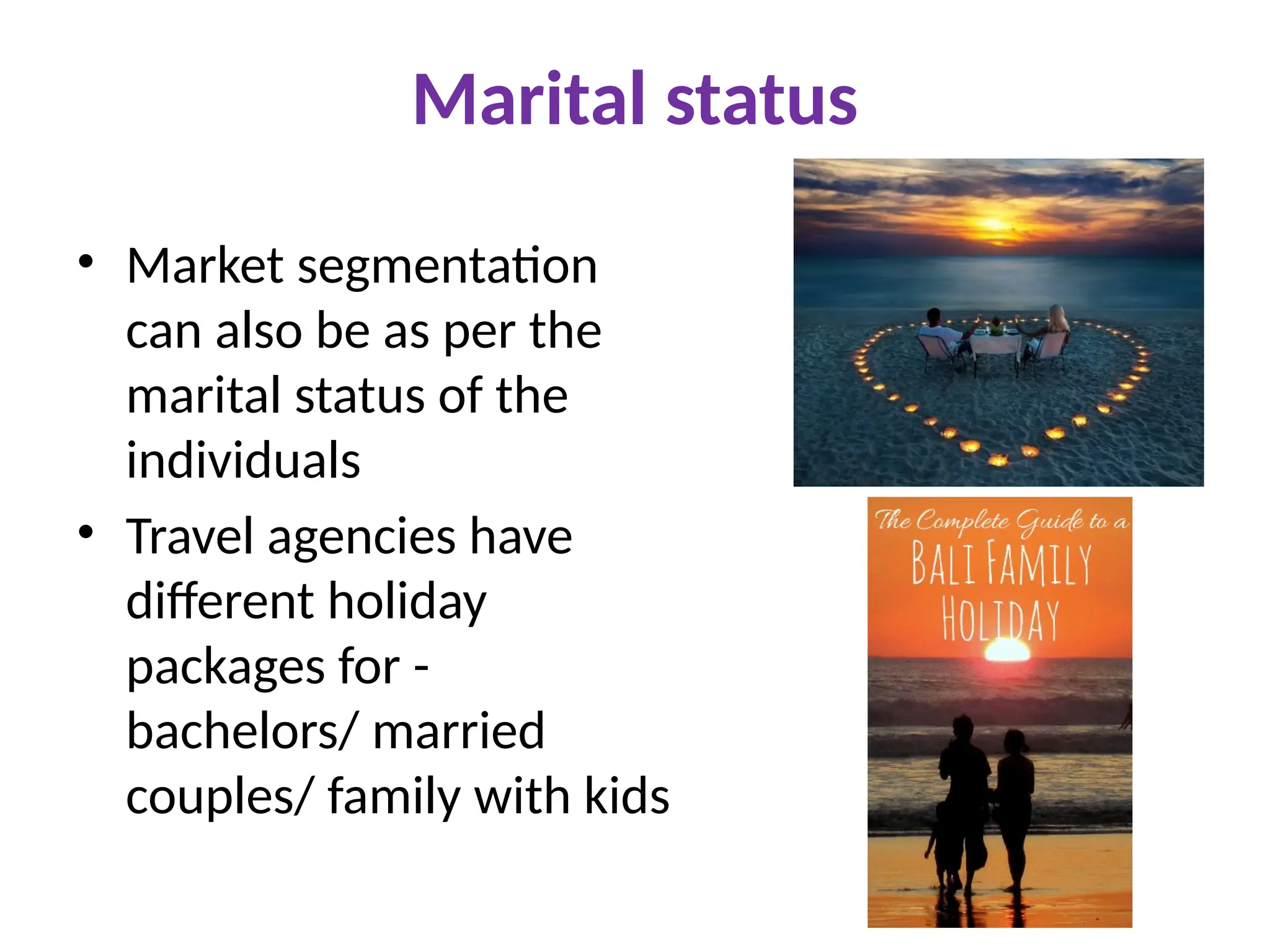
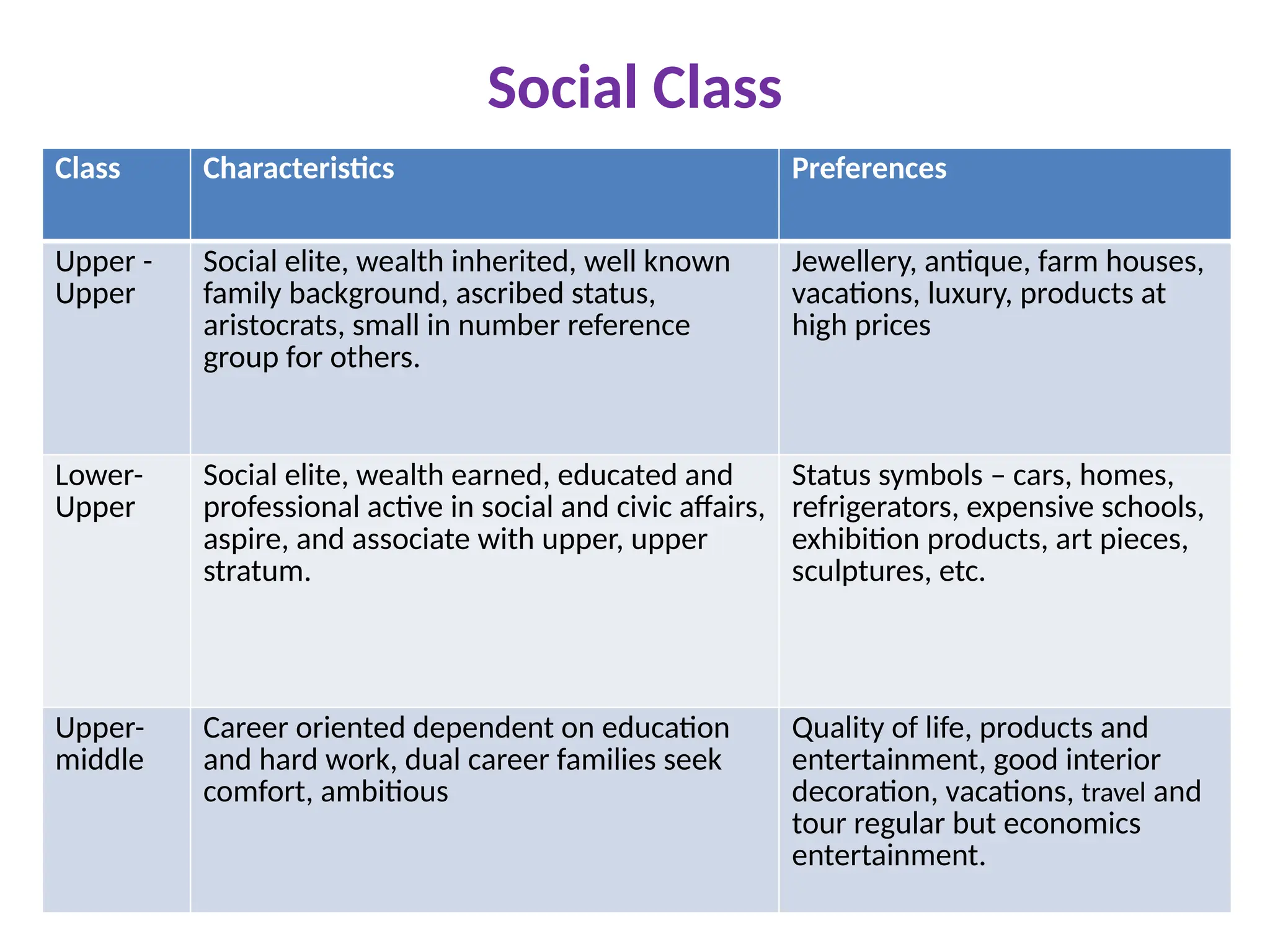
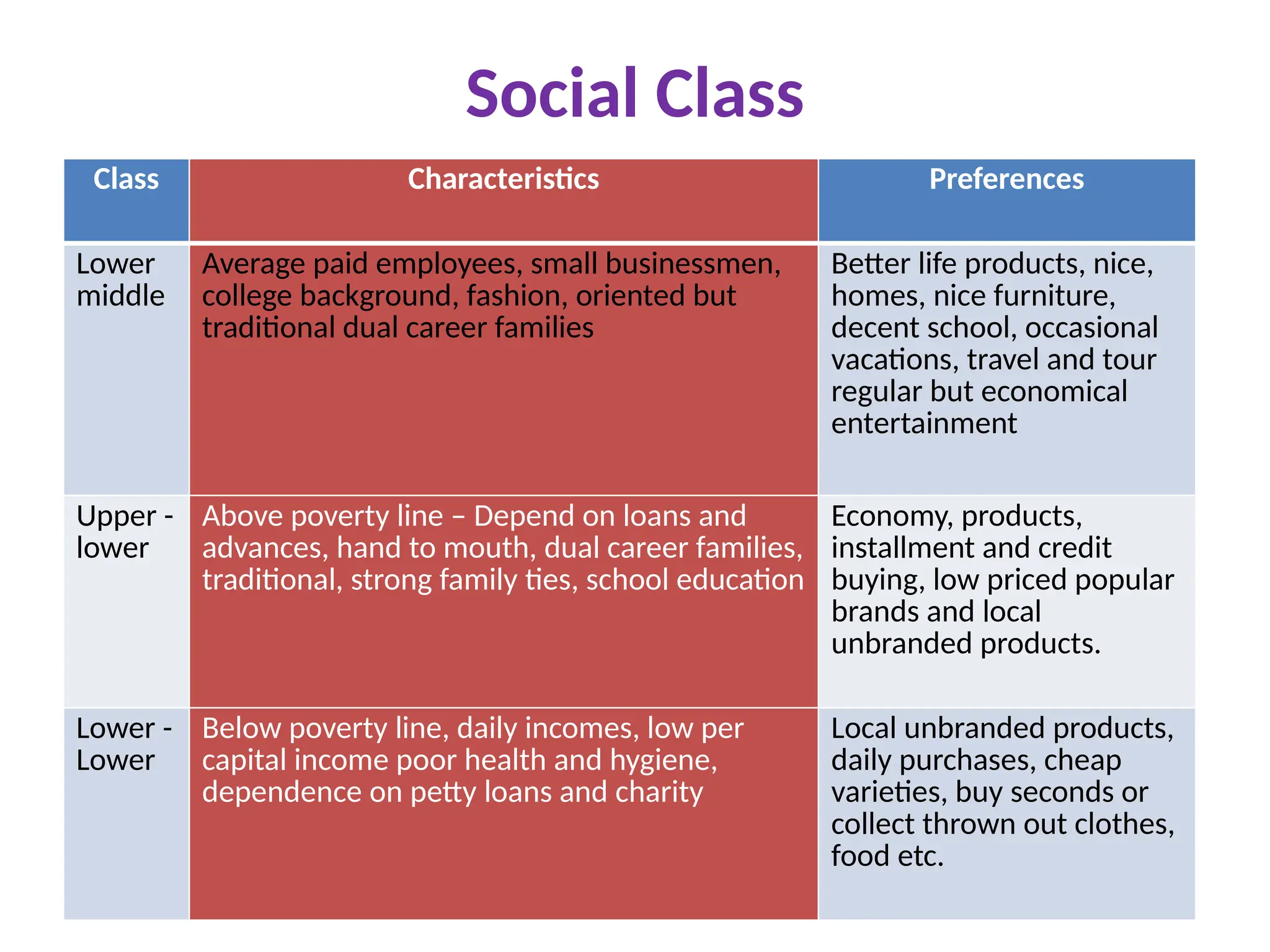
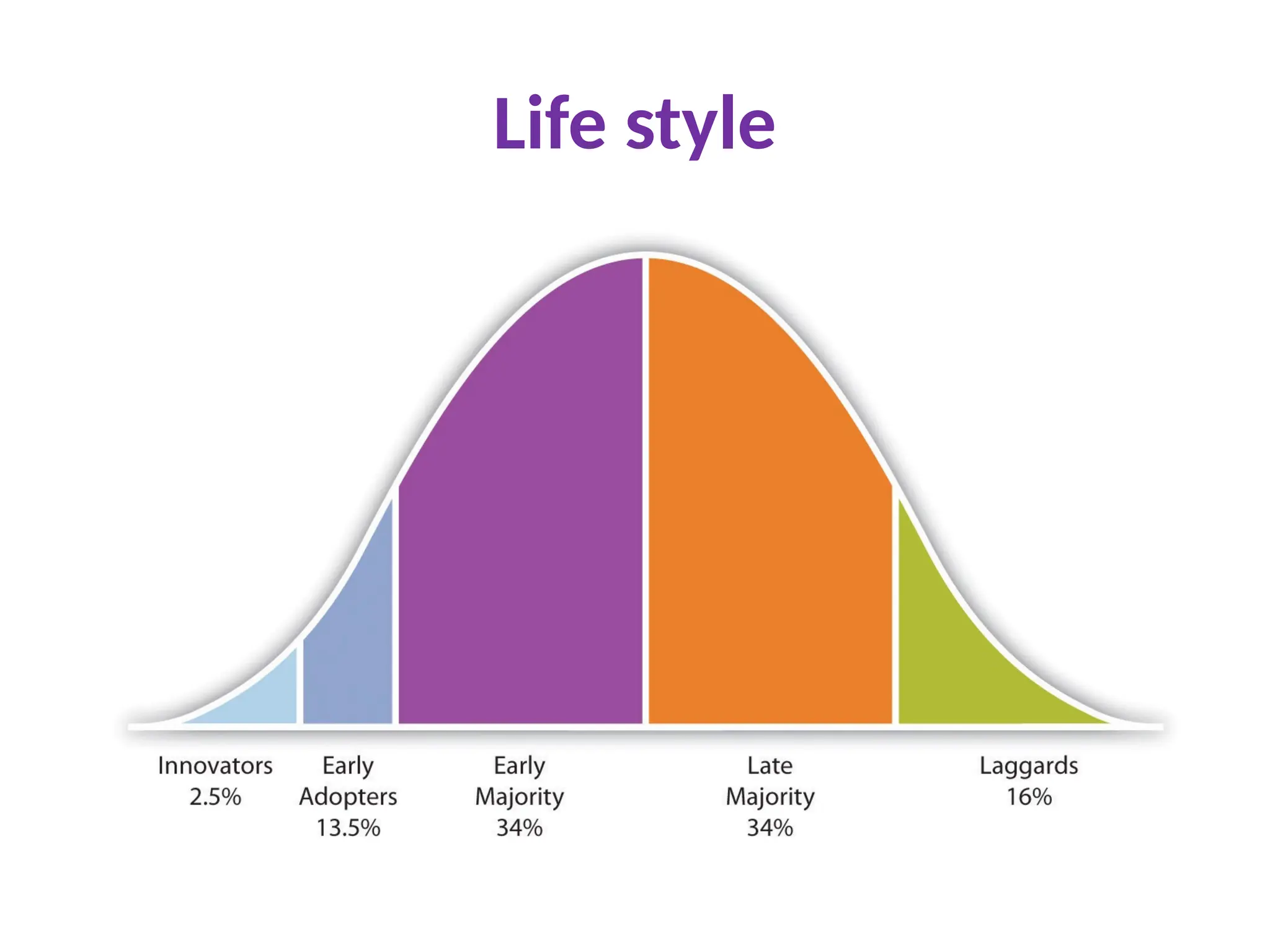
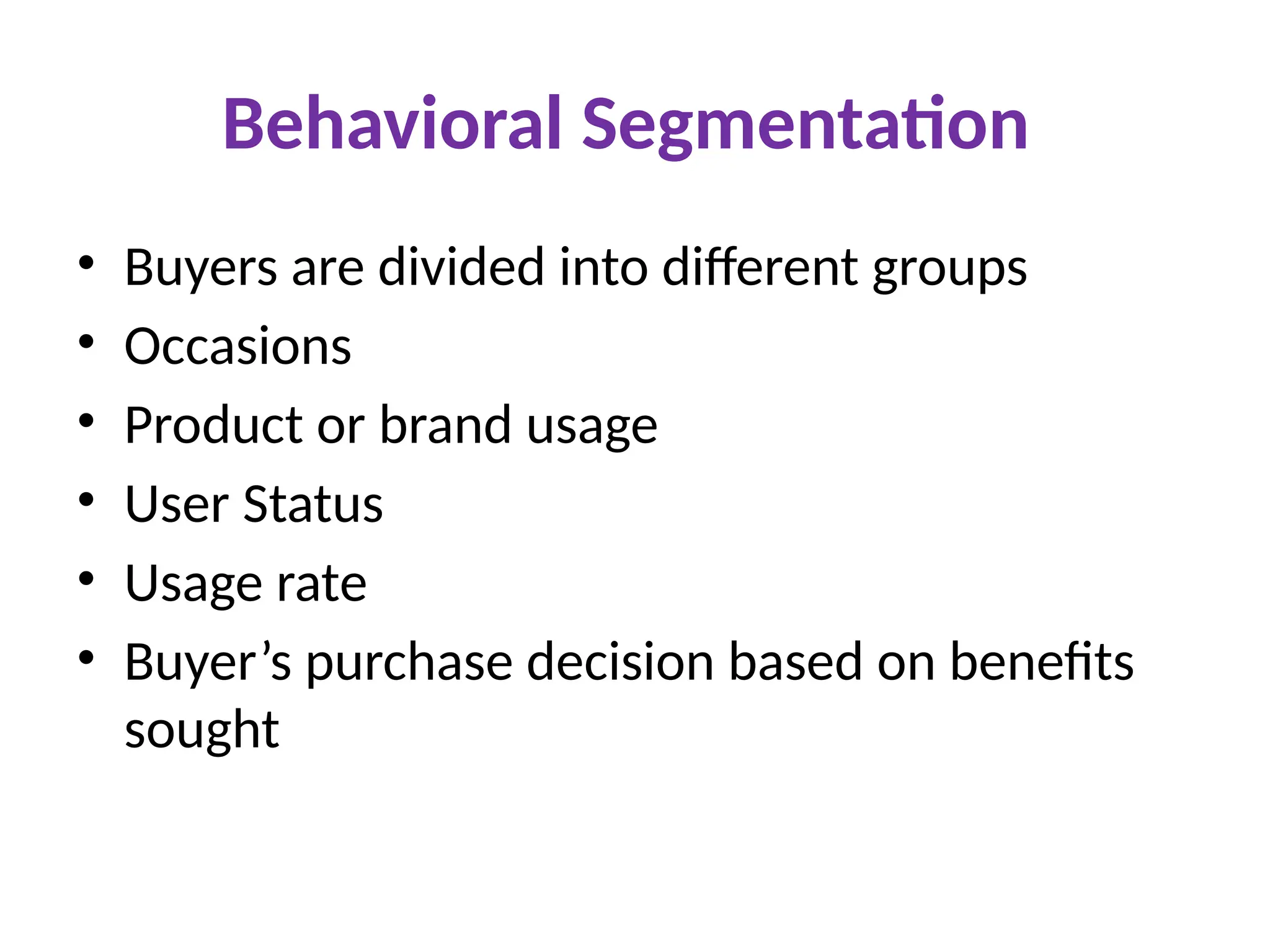
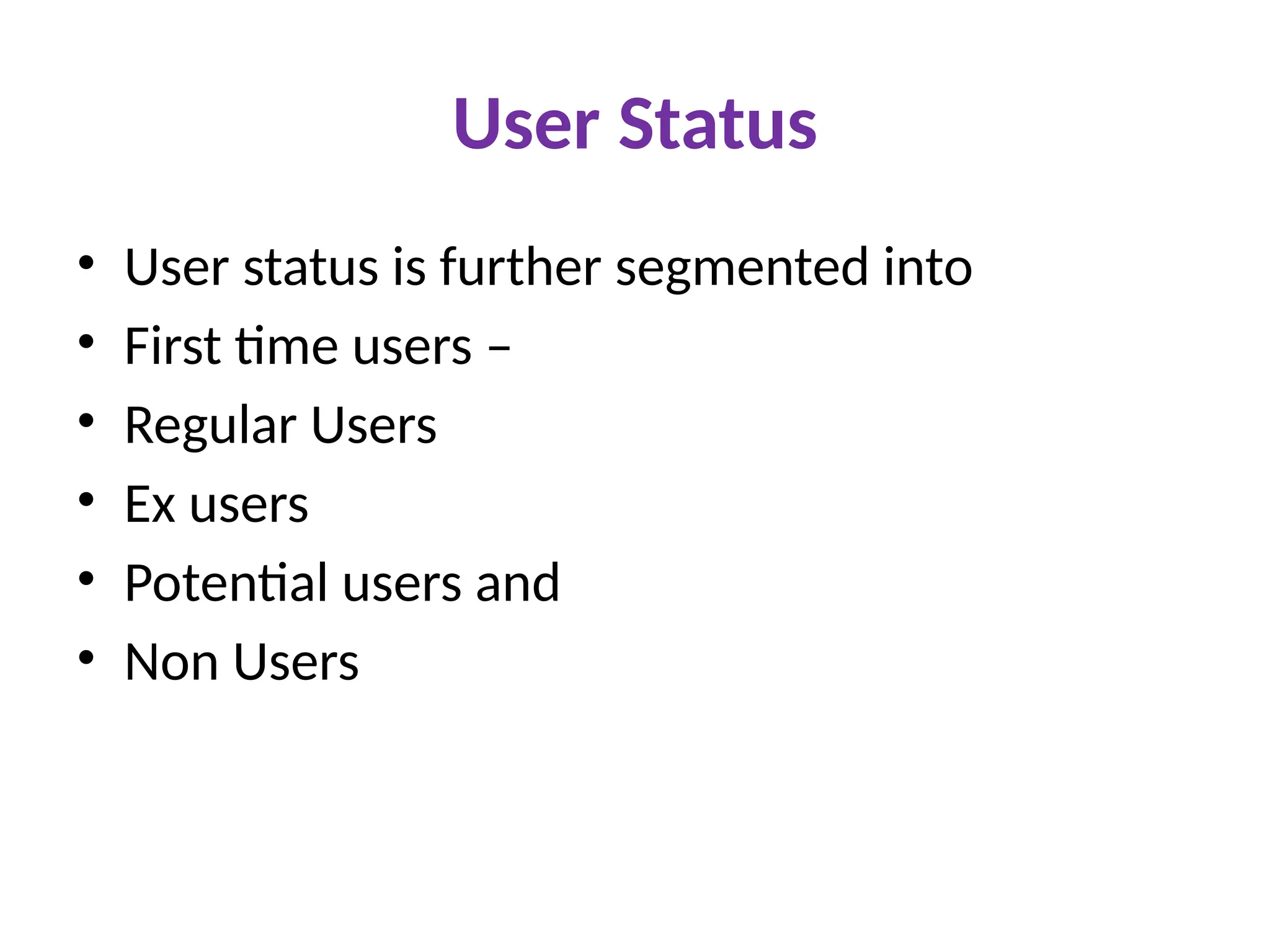
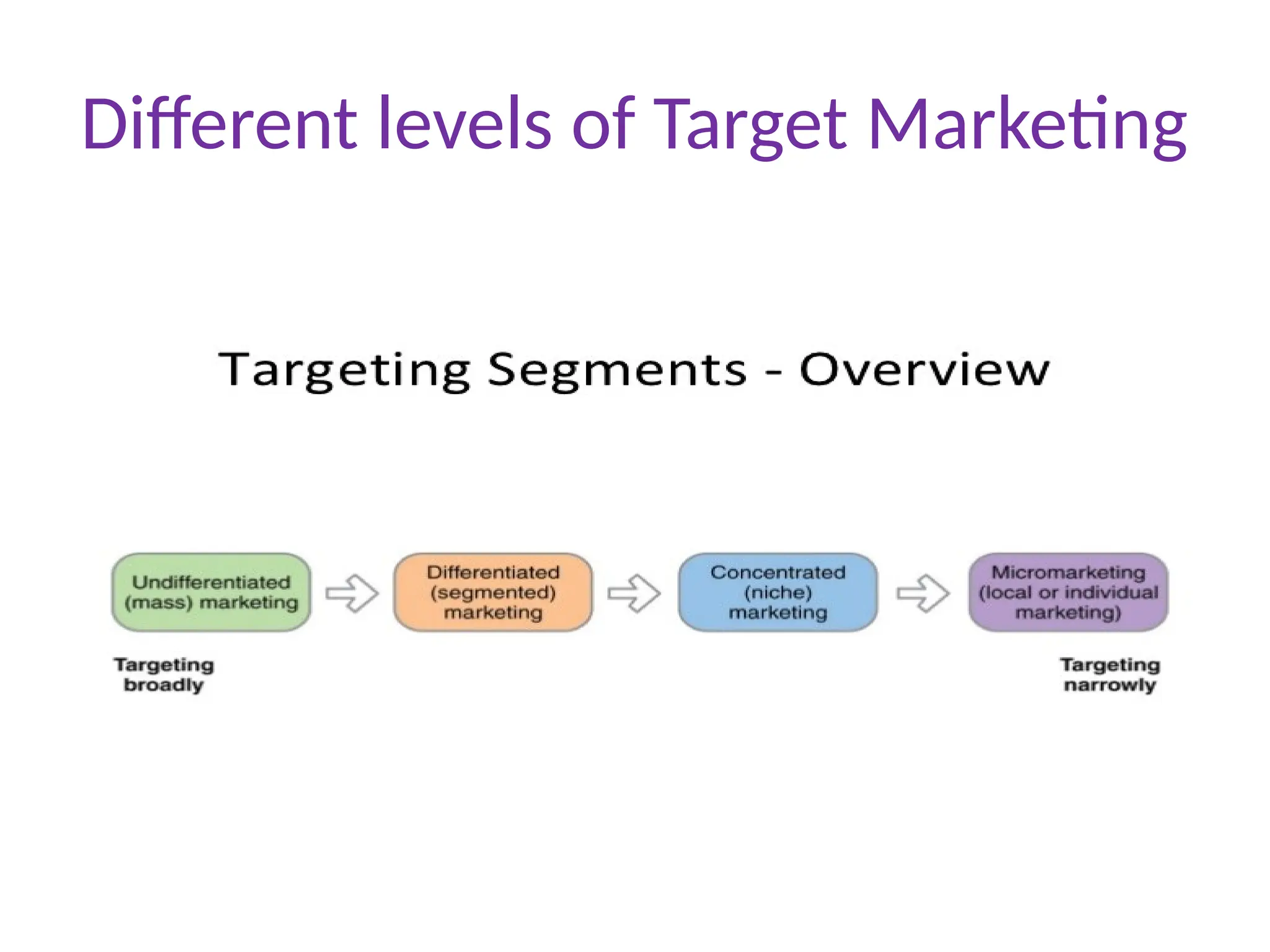
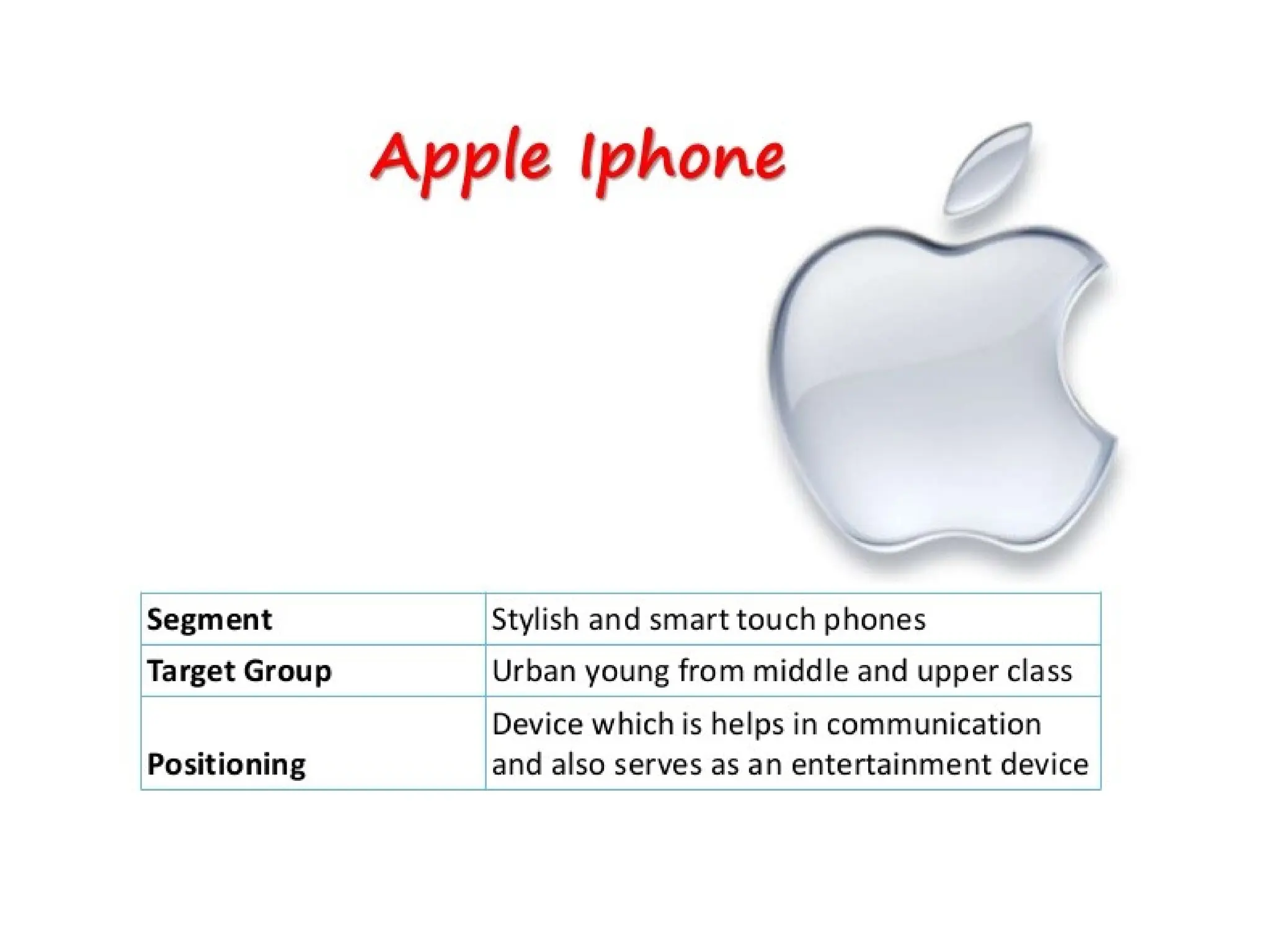
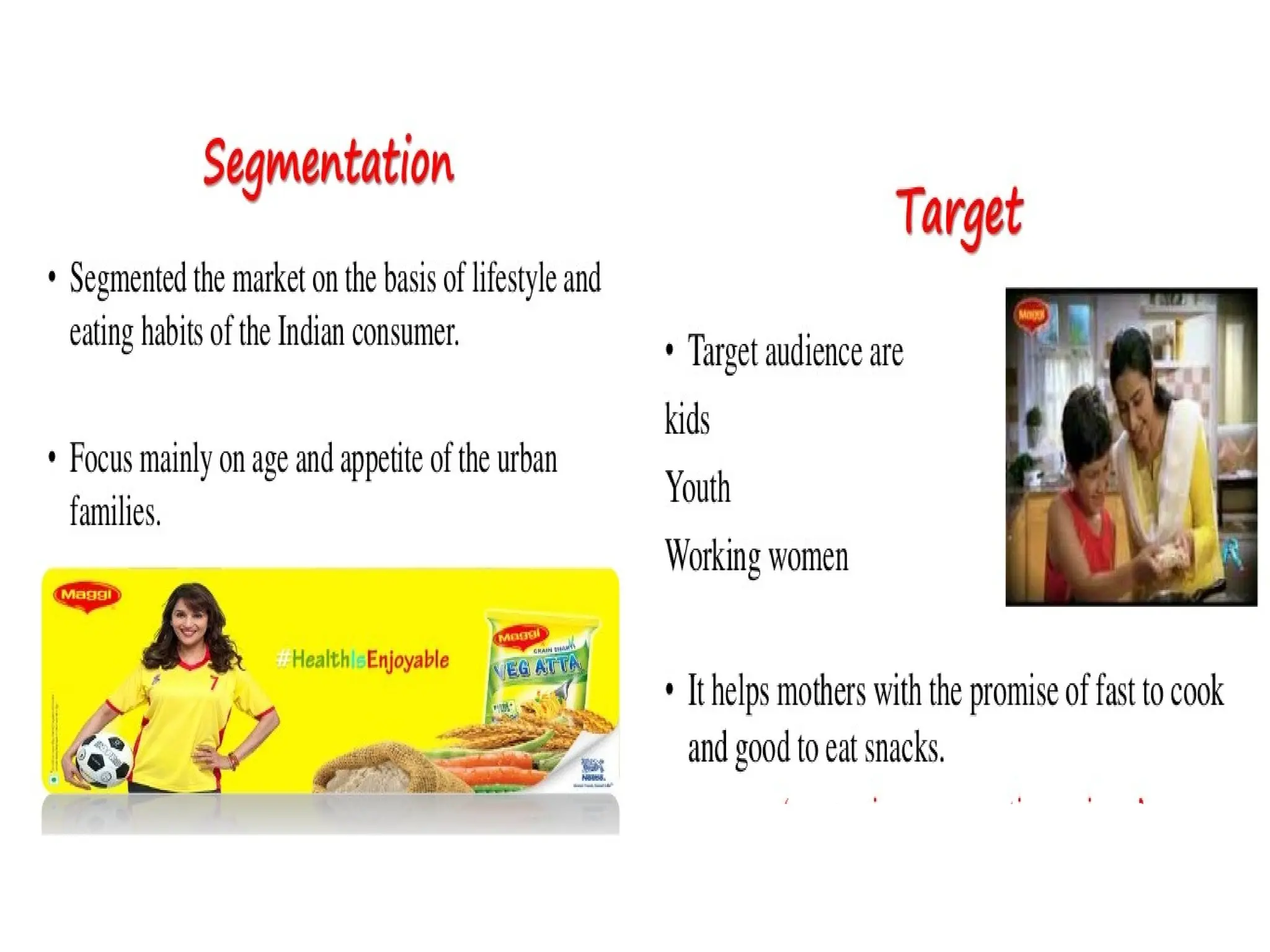
The document discusses marketing strategies focused on segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP), highlighting various segmentation criteria such as demographics, income, age, occupation, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral factors. It emphasizes the need for targeted marketing to effectively reach distinct consumer groups and improve brand perception through strategic positioning. Additionally, it outlines different market strategies, including undifferentiated, differentiated, concentrated, and niche marketing approaches.