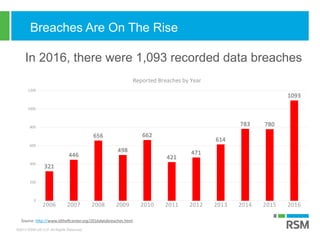
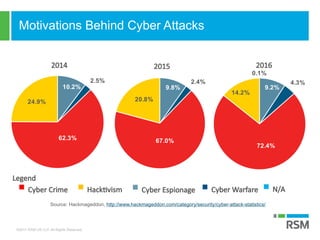
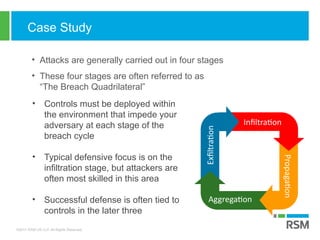
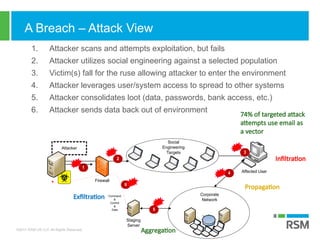
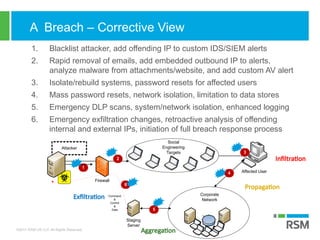
The document discusses the rising importance of information security due to increased data breaches, customer demand for security assurance, and regulatory requirements. It highlights that in 2016, there were 1,093 recorded data breaches and outlines key threats such as ransomware and phishing attacks. Additionally, it emphasizes the necessity of robust incident response planning and strategic security measures to mitigate risks.