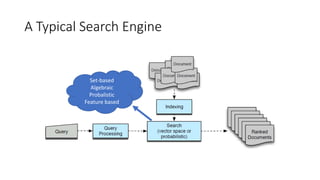
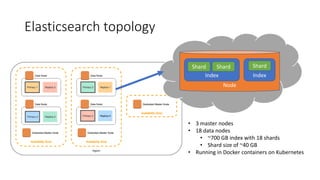
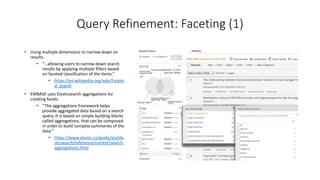
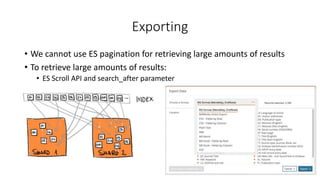
The document provides a technical introduction to Embase from a search engineer's perspective, detailing its architecture, indexing, and query processing systems. It discusses various query refinement techniques including autocomplete, synonyms, and faceting, and explains the use of Elasticsearch for data handling. Additionally, the document covers the exportation of large result sets and highlights key features such as document enrichment and ranking mechanisms.