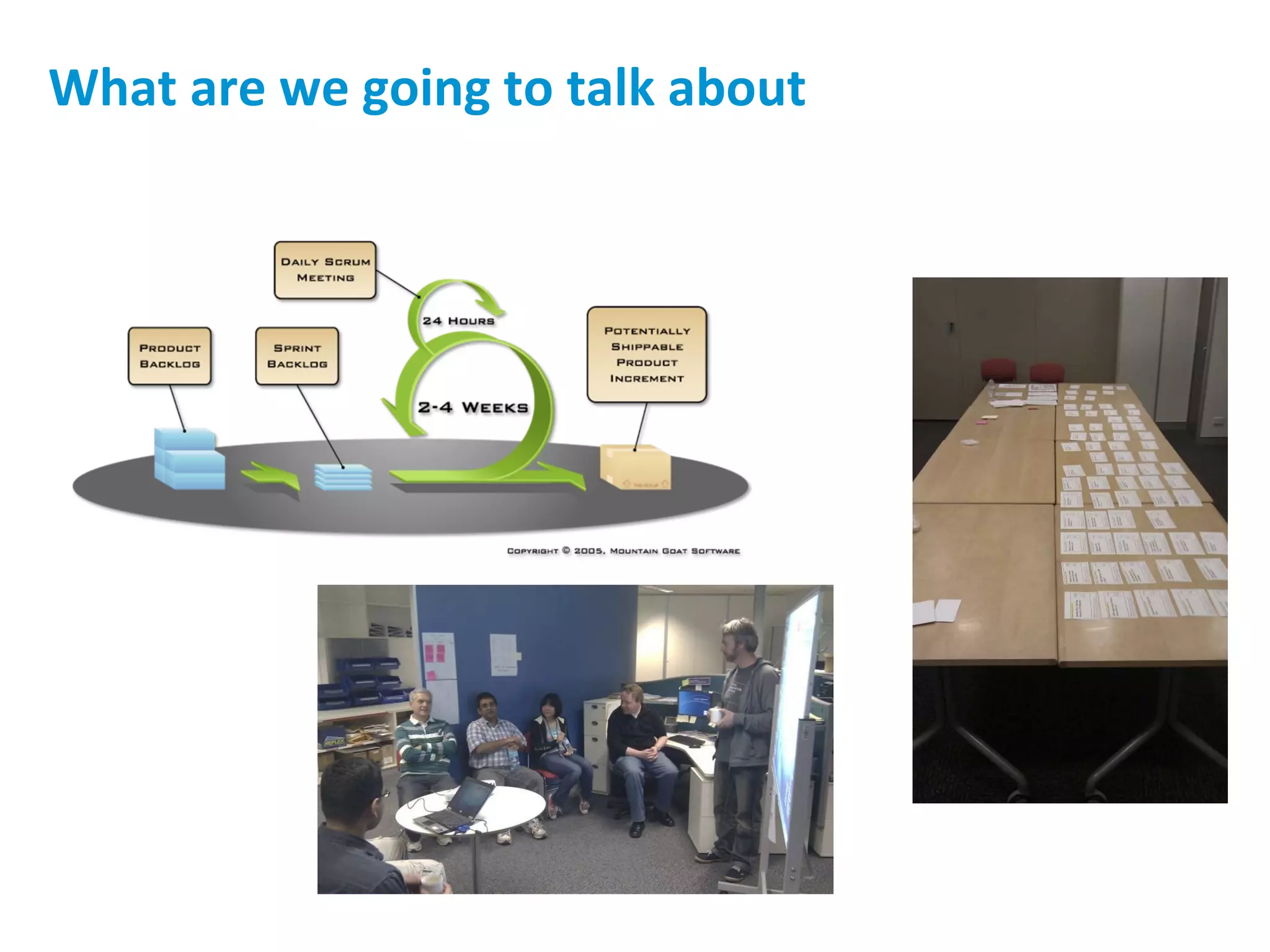
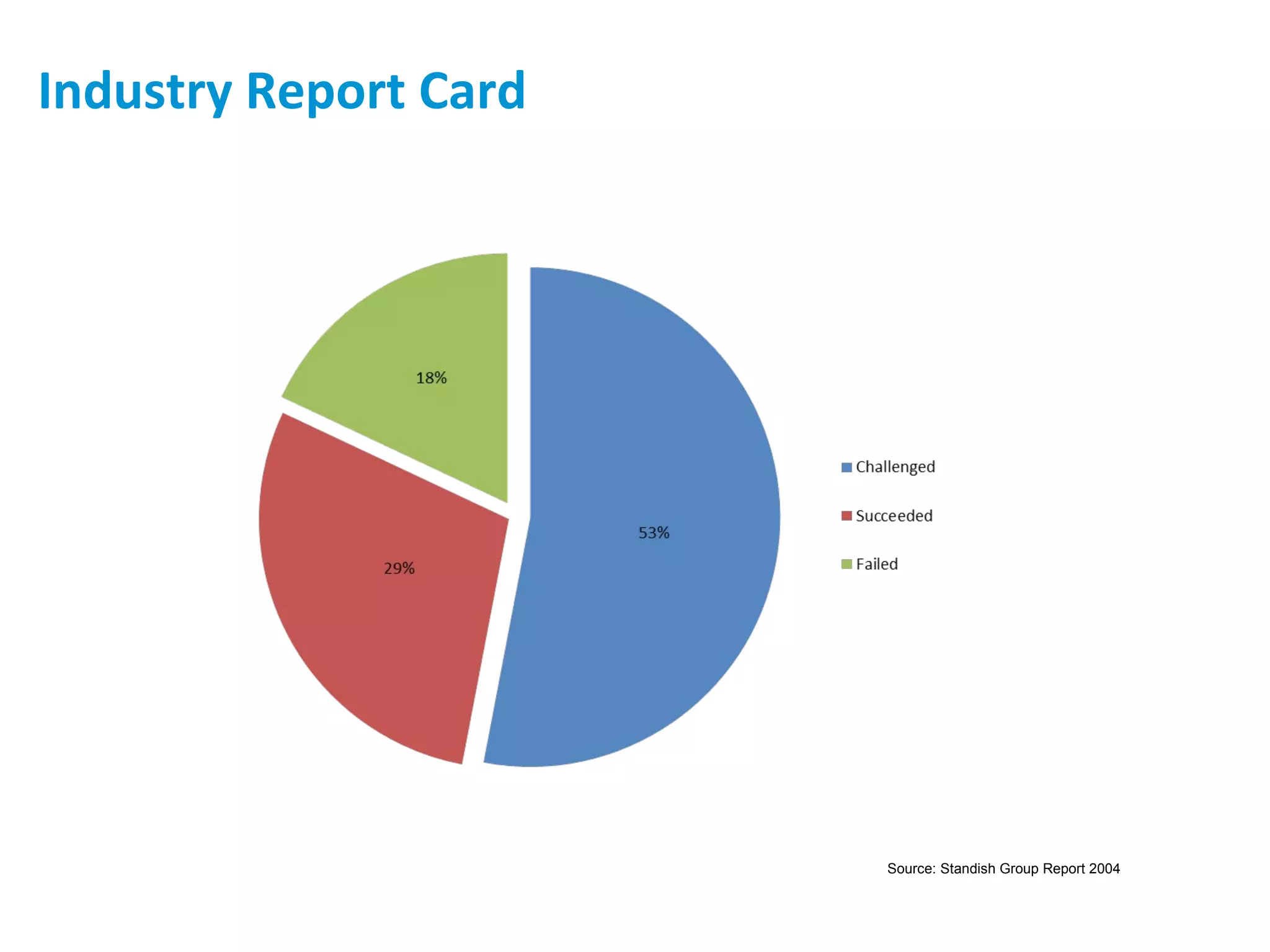
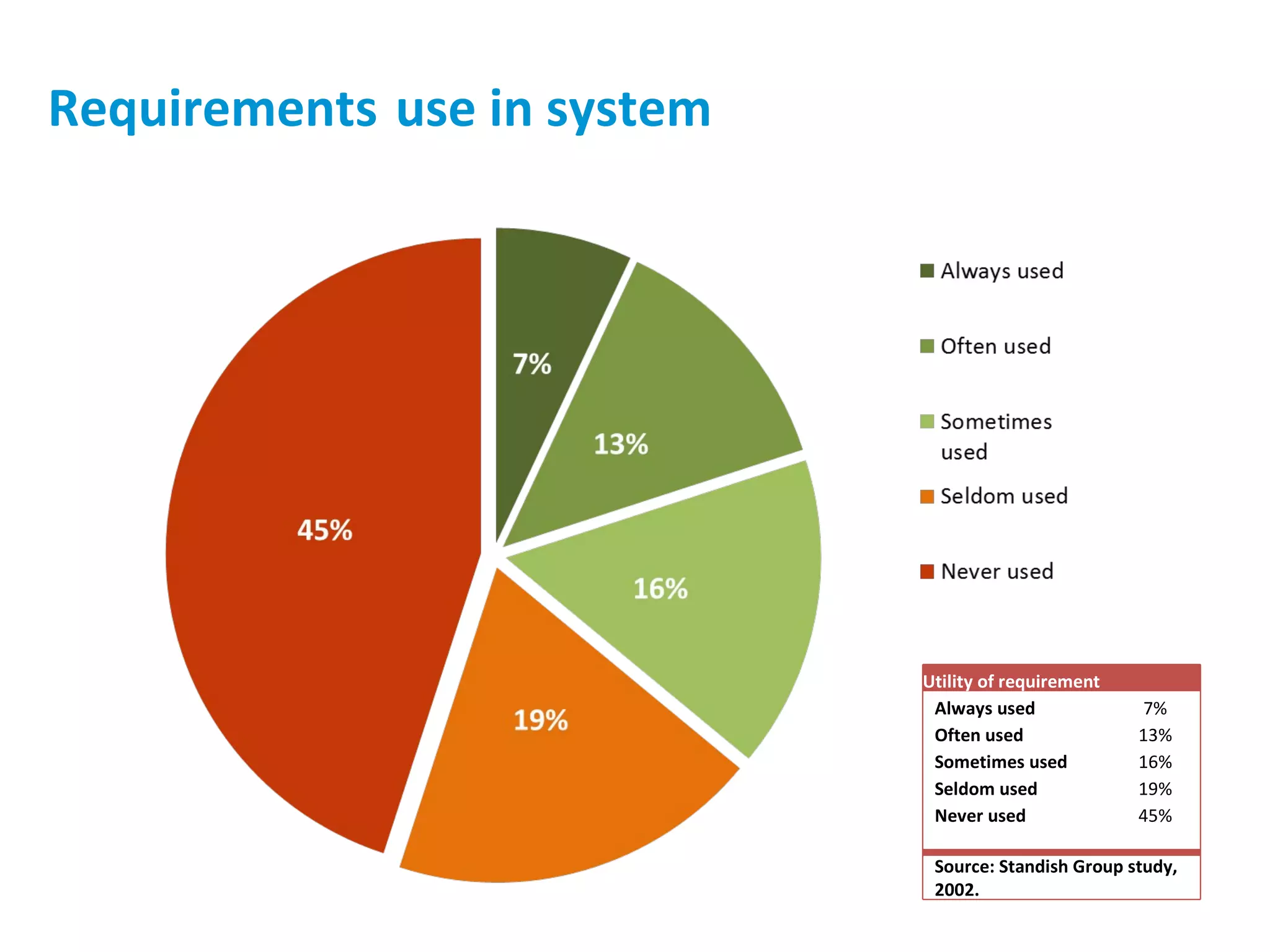
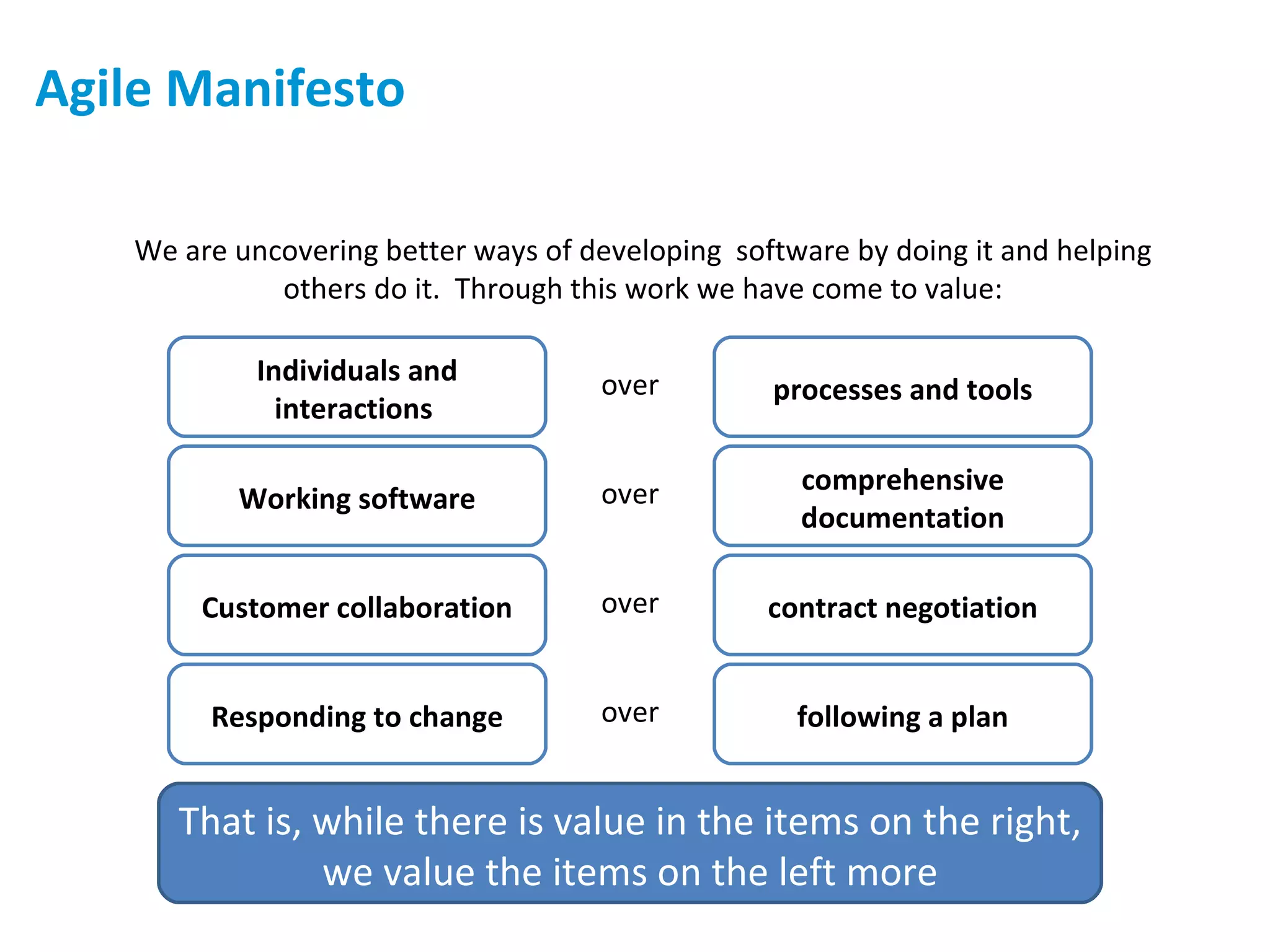
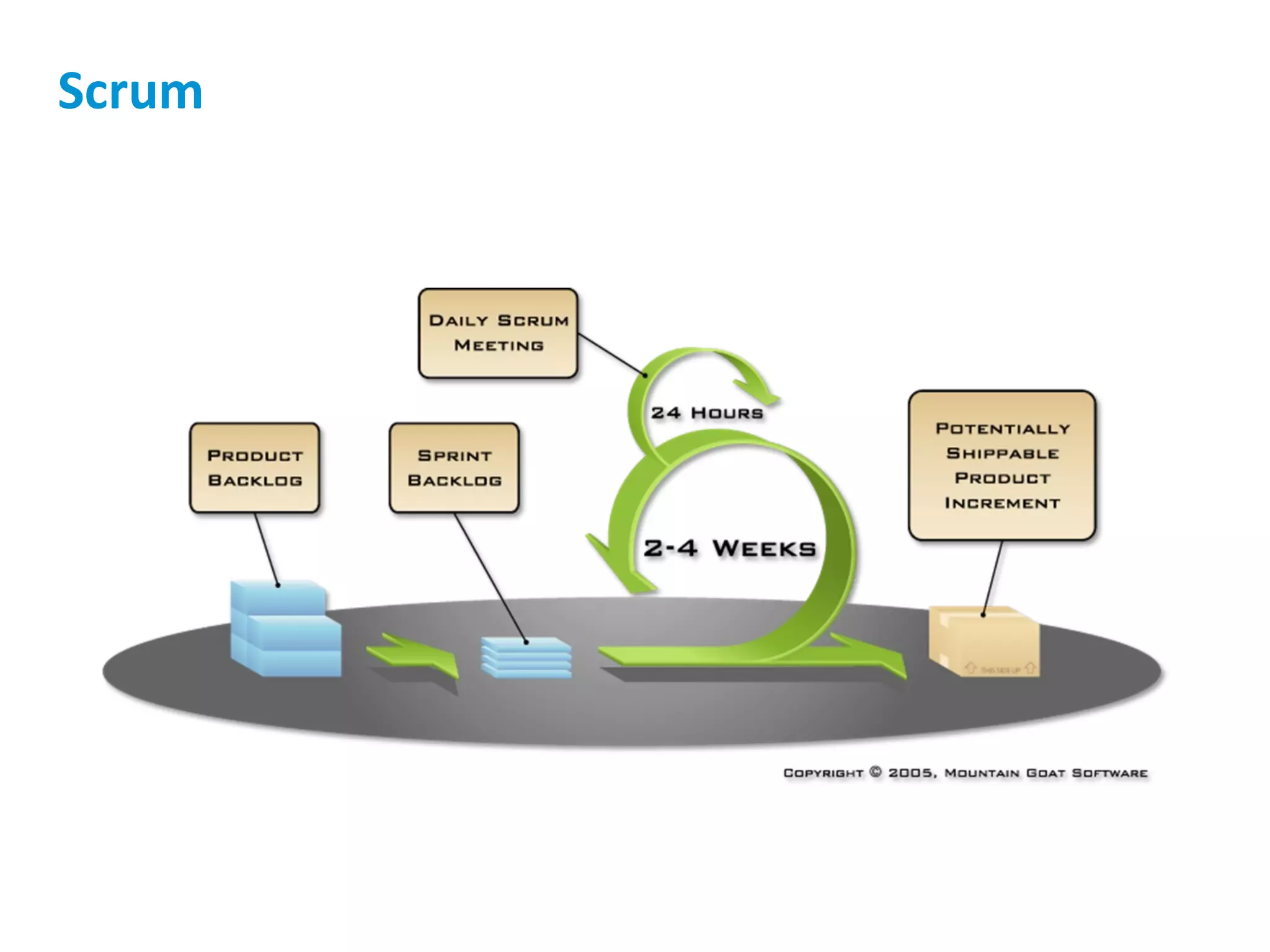
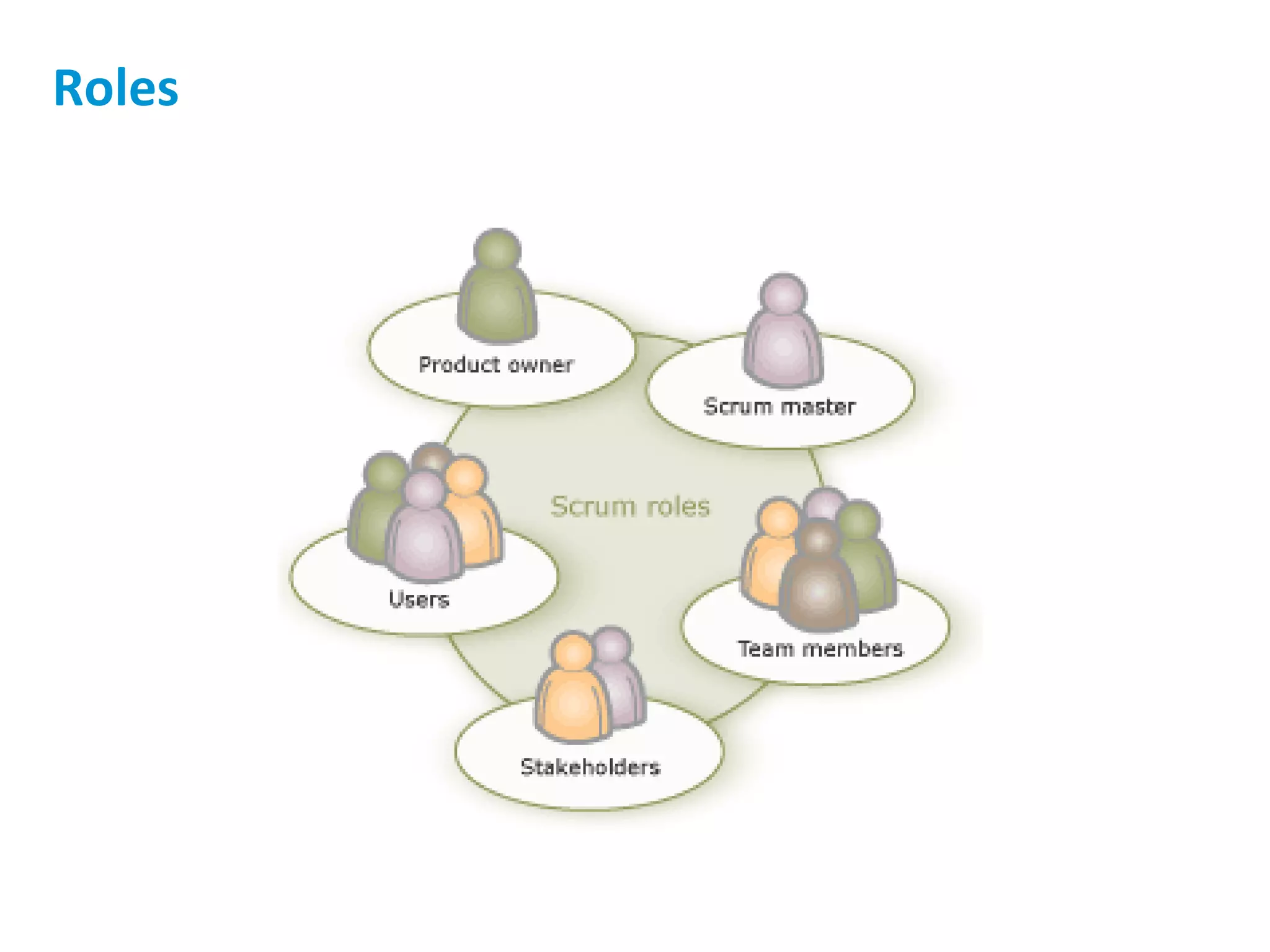
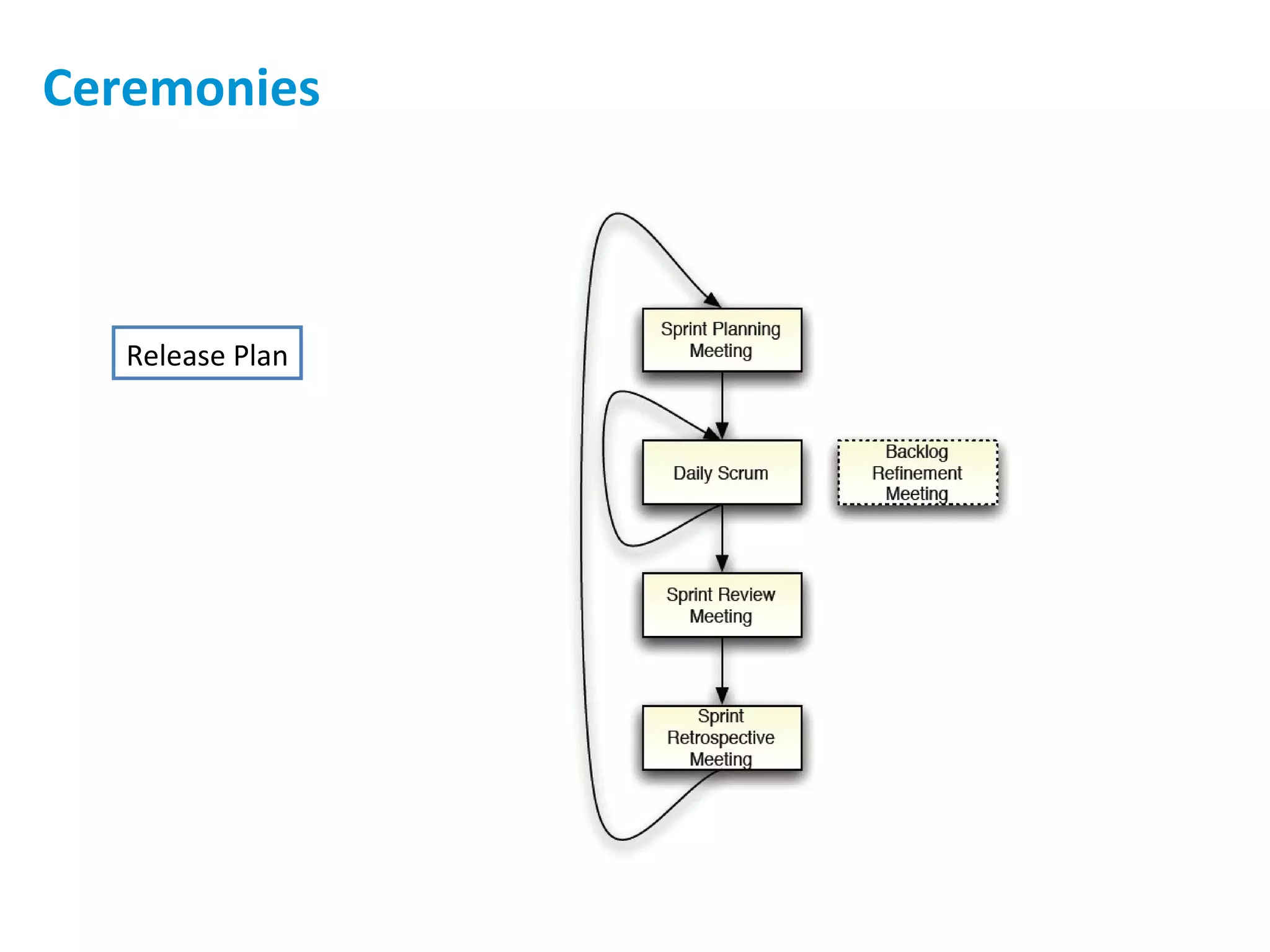
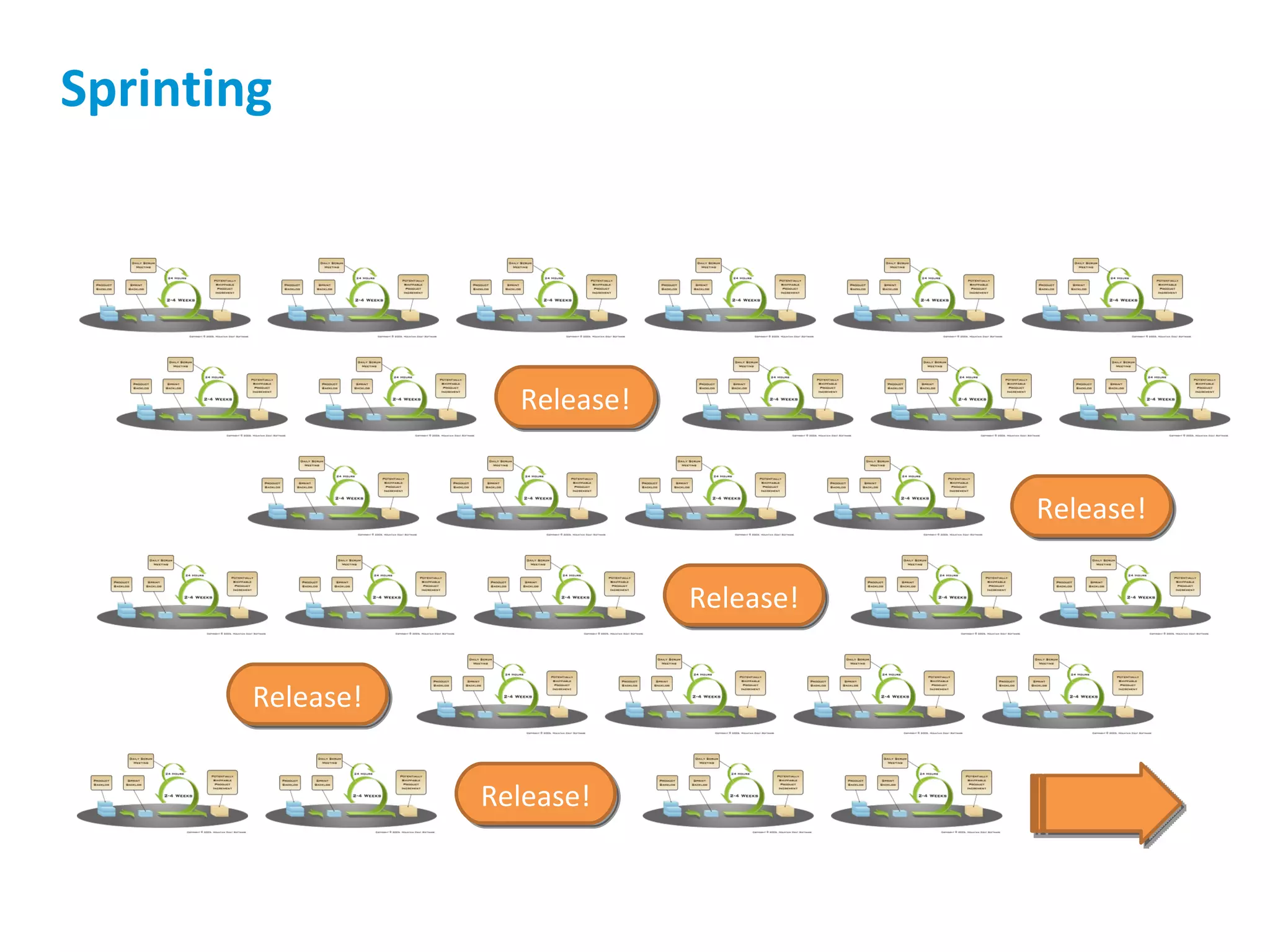
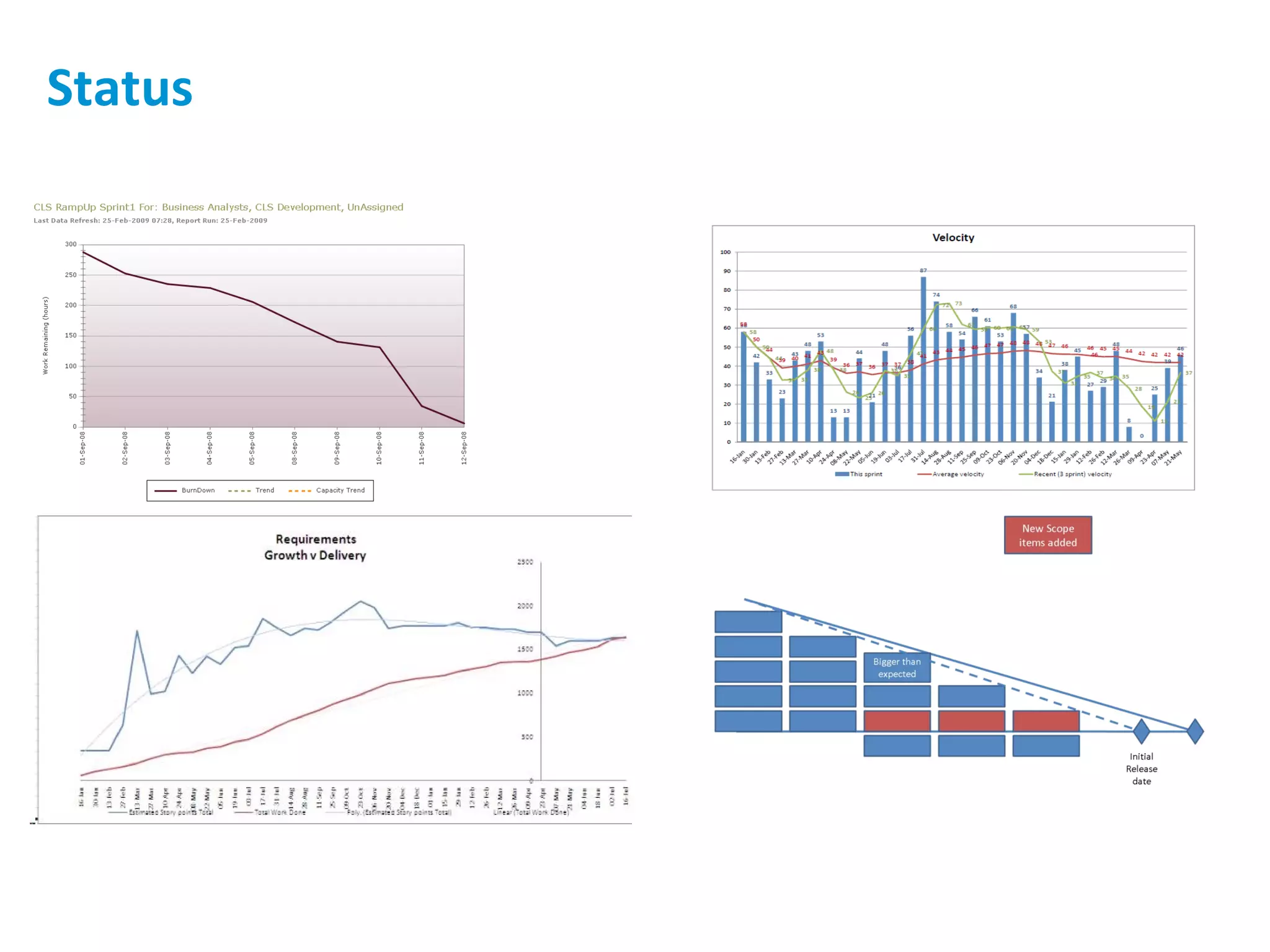
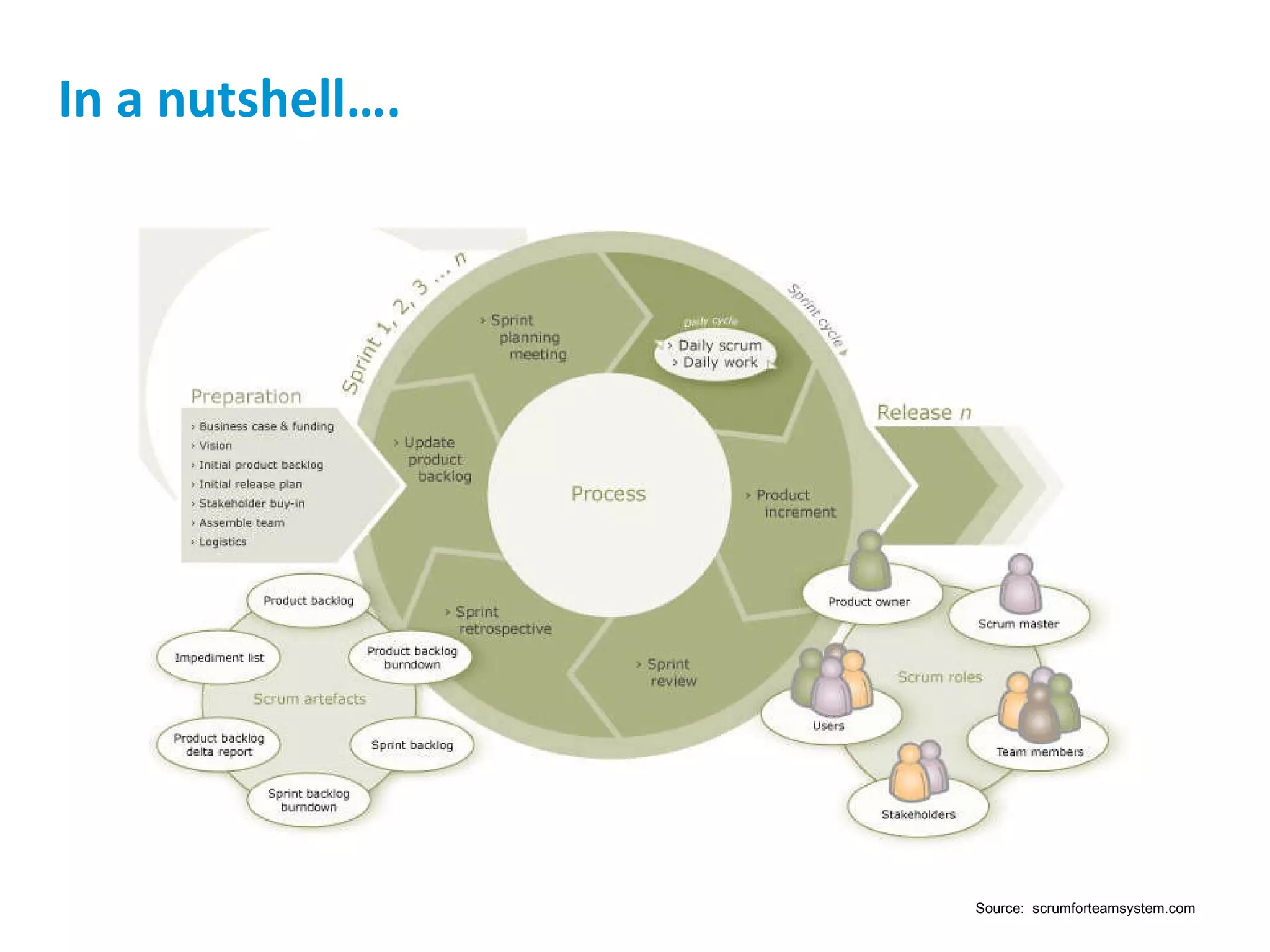
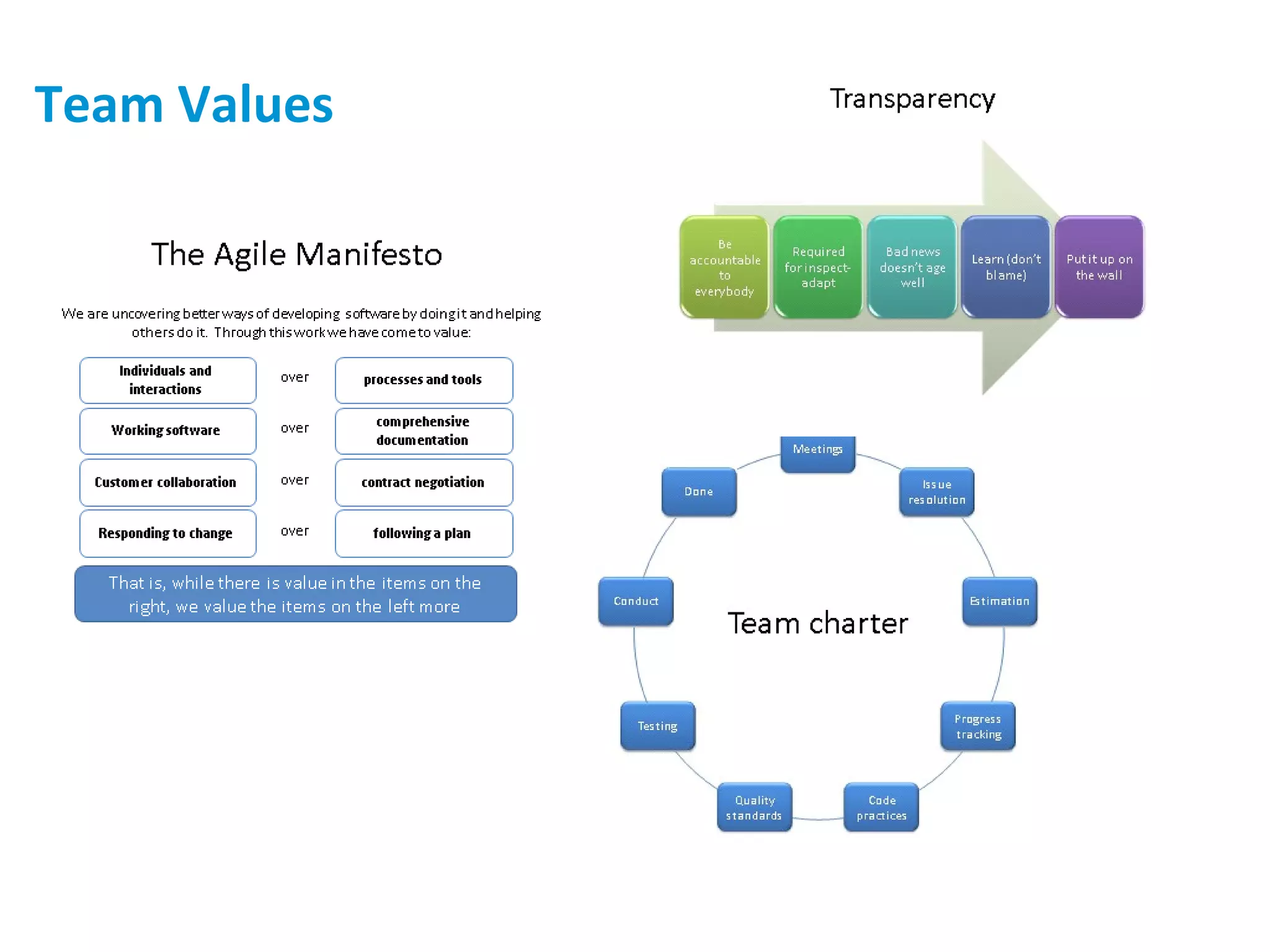
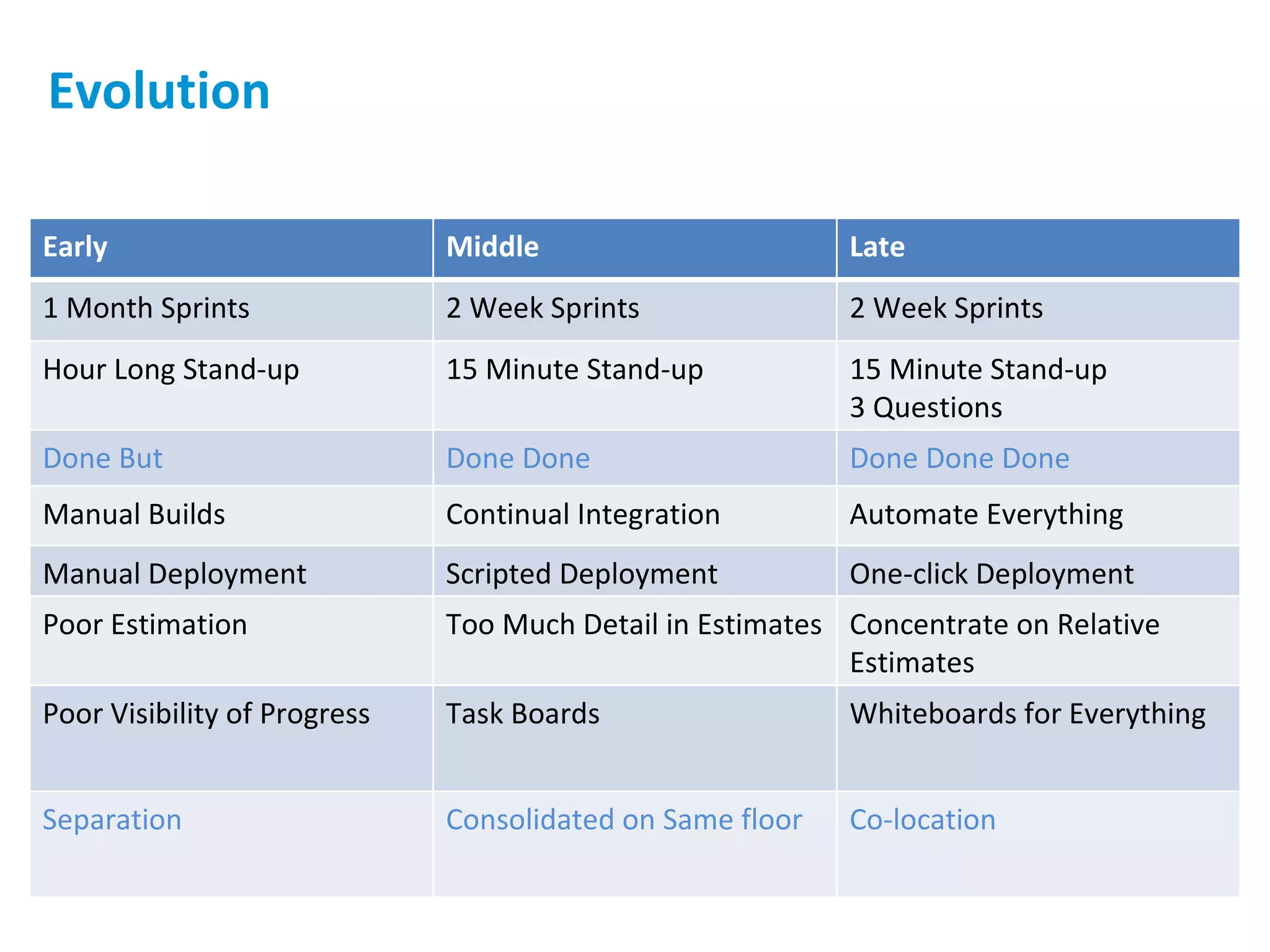
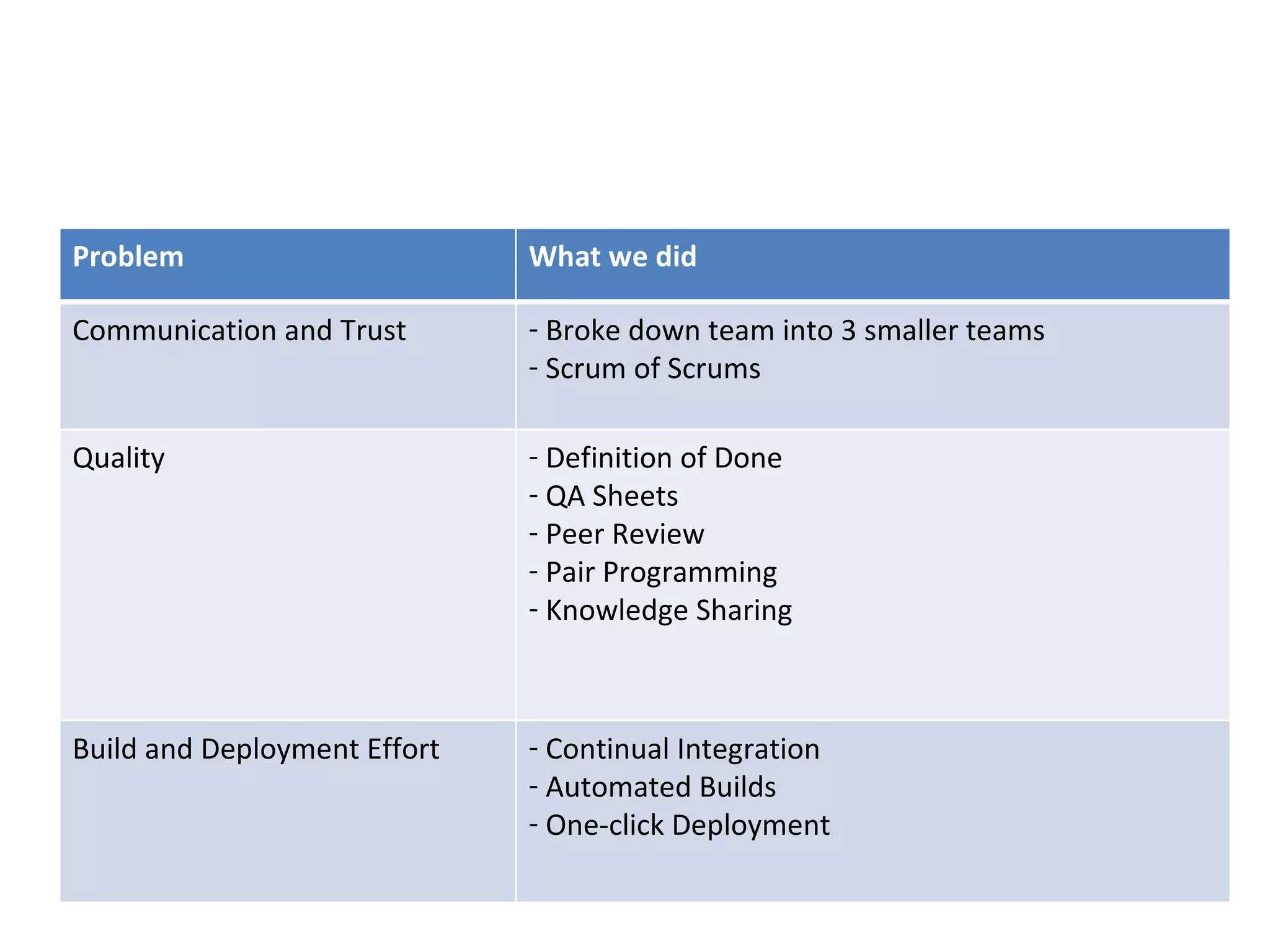
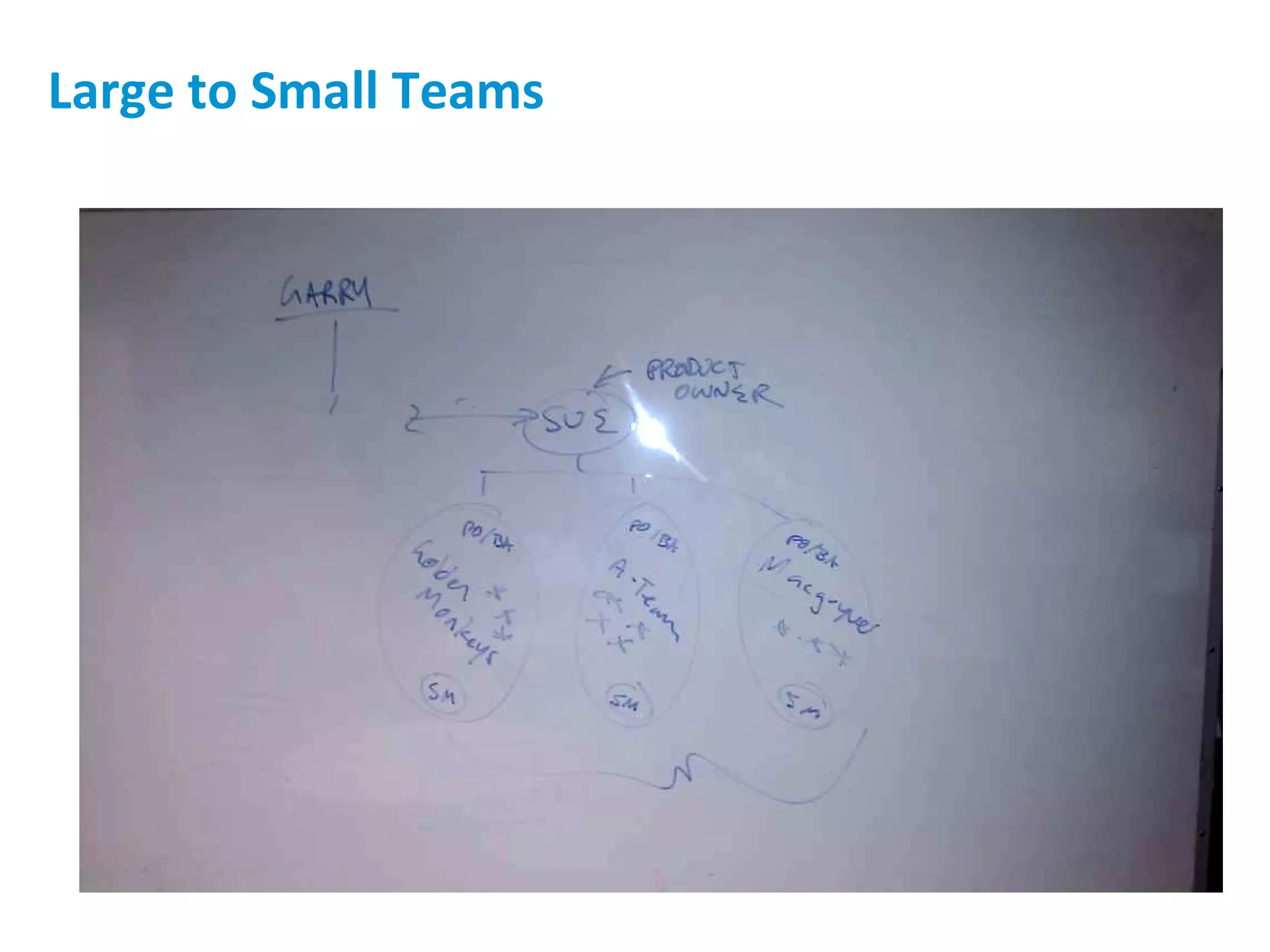
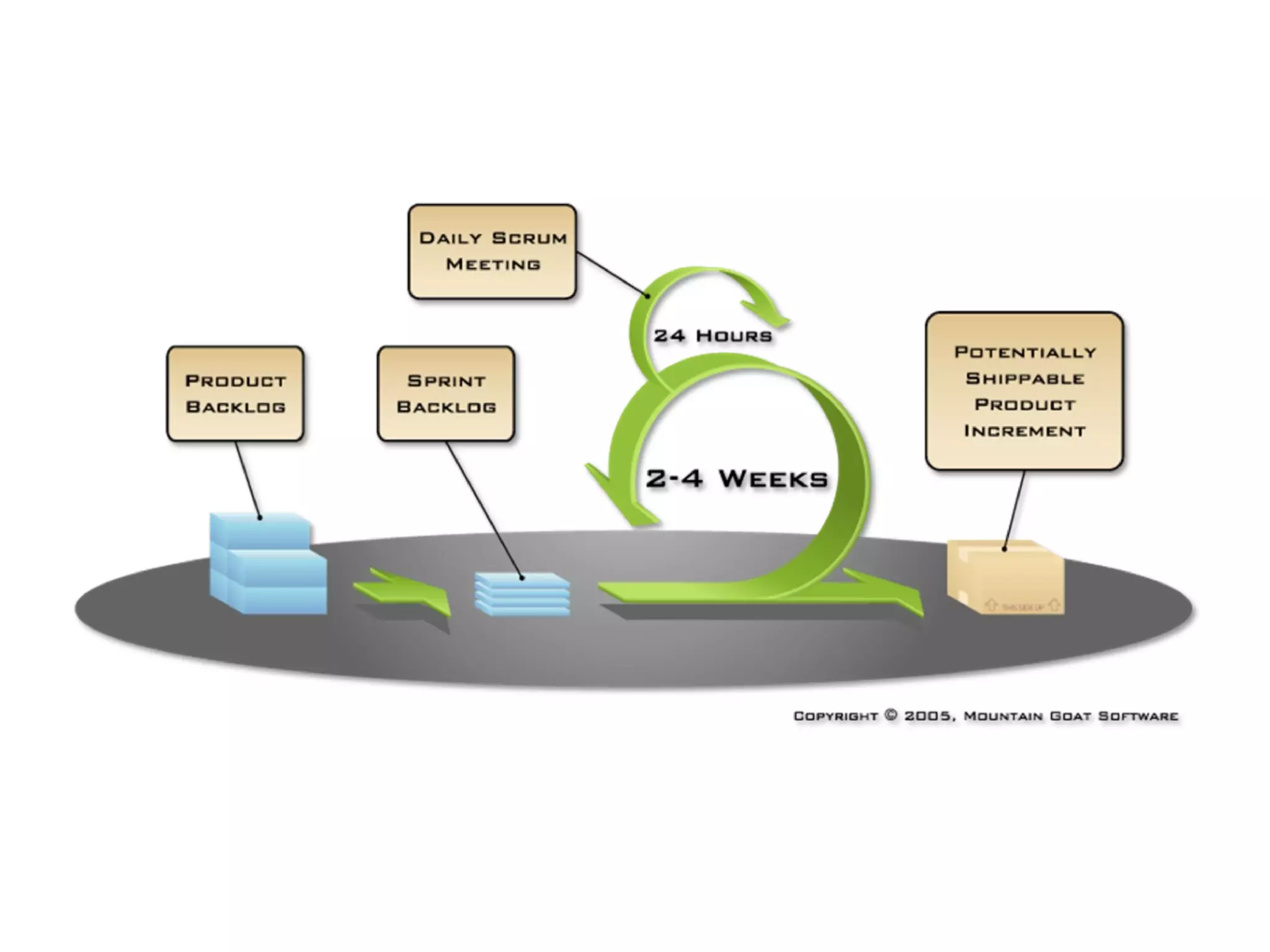
The presentation discusses implementing Scrum in government through a review of the Agile manifesto and Scrum practices, highlighting the project's successful elements like team structure, communication, and automated testing. Key metrics indicate high performance with a low bug rate and strong unit test coverage, showcasing the team's capability. It emphasizes the importance of cultural change, trust, and reduced process overhead for continuous improvement.