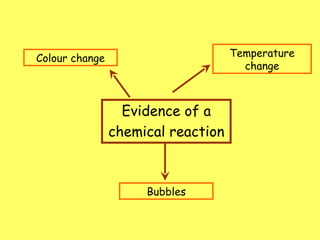
The document discusses factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction, including concentration, temperature, and surface area. It provides examples of reactions that occur at different rates, such as paint drying versus metal nail rusting. The document also describes an experiment to investigate how concentration affects the rate of a reaction between solutions X and Y by measuring the time taken for the solution to change color when different amounts of solution Y are added.