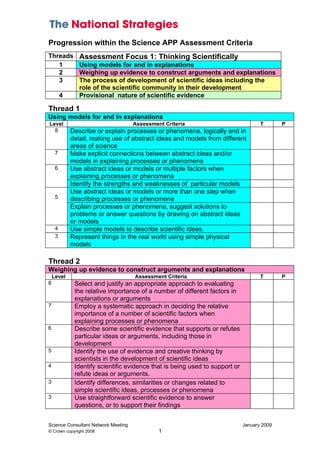
The document provides assessment criteria for evaluating student performance in science across four assessment focuses and various threads within each focus.
1) It outlines criteria for assessing students' abilities to think scientifically by using models, weighing evidence, understanding development of scientific ideas, and recognizing the provisional nature of evidence.
2) It also describes evaluating students' understanding of applications and implications of science in areas like societal influences, technological developments, and relationships between science and jobs.
3) Additionally, the document provides criteria for assessing students' communication and collaboration skills in science like presenting information and considering different views.
4) Finally, it outlines assessing students' use of investigative approaches including planning investigations, identifying variables, gathering reliable data, and