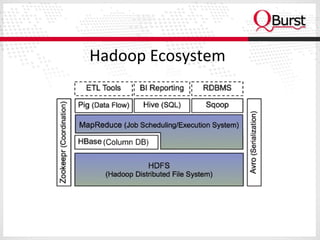
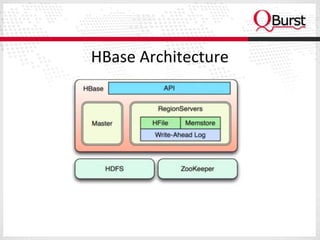
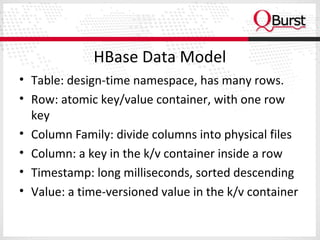
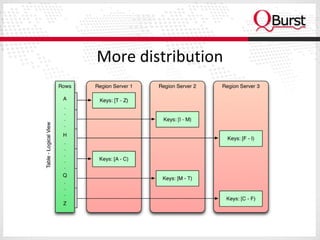
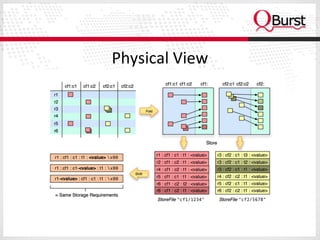
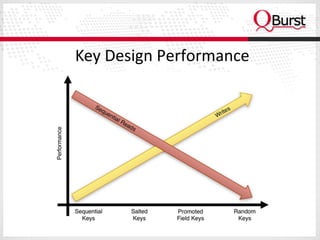
The document discusses the importance of schema design in big data, particularly with non-relational databases like HBase, which operates on HDFS due to its fault tolerance. It highlights the design principles, data models, and distribution strategies for scalability, along with insights on key design considerations to avoid performance issues. It emphasizes the suitability of NoSQL technologies for systems managing hundreds of millions to billions of rows without requiring advanced query languages.