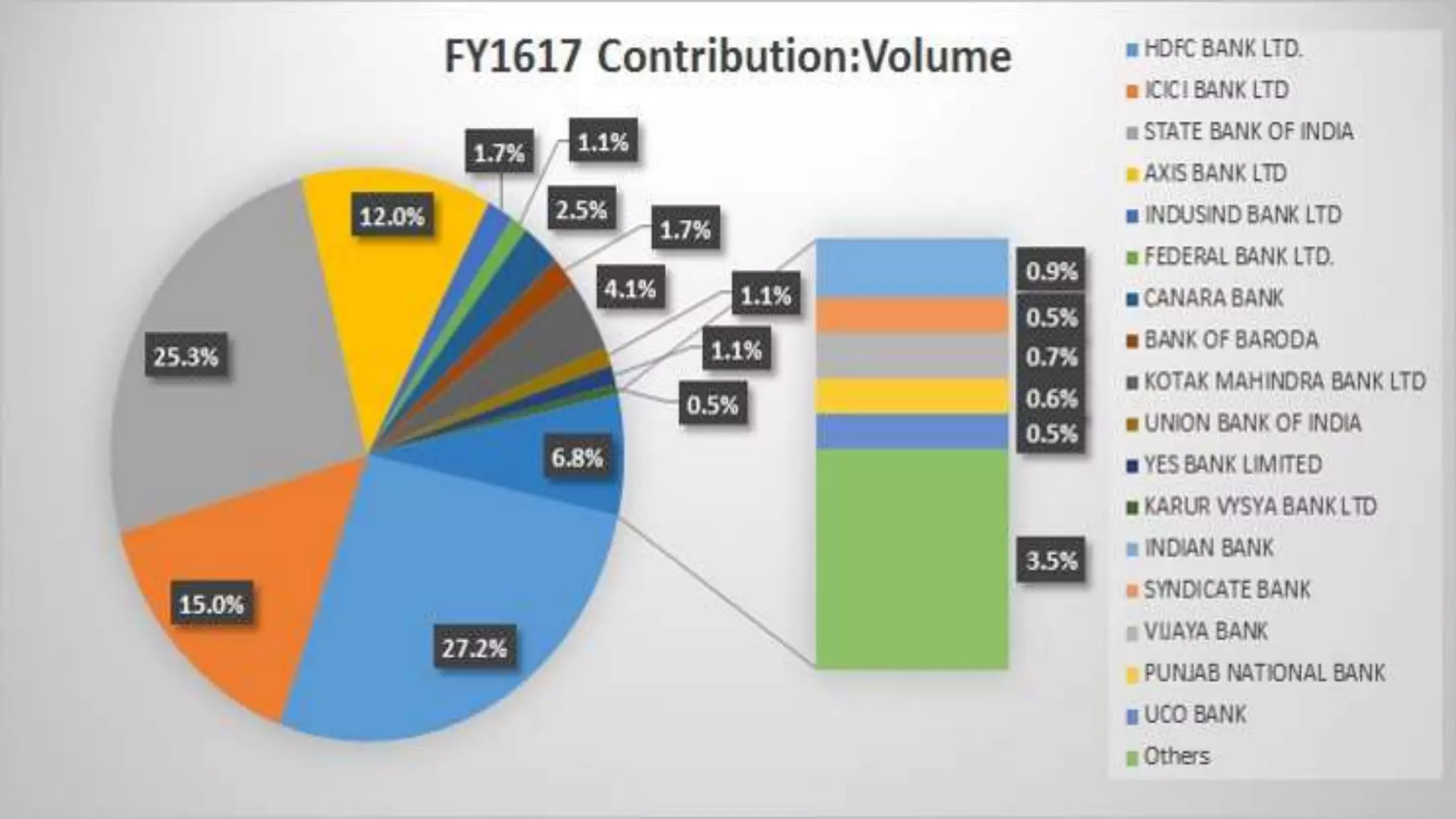
State Bank of India (SBI) is the largest bank in India, with over 22,000 branches and 278,000 employees. SBI originated in 1806 and was nationalized in 1955. It has a 60% market share and aims to be the most trusted financial services provider worldwide. SBI uses a three phase selection process for hiring and has a hierarchical organizational structure. It offers personal, NRI, agriculture, international, corporate, and small business services and sees opportunities for growth in rural expansion and talent replacement. SBI must also address threats from industry consolidation and new entrants.