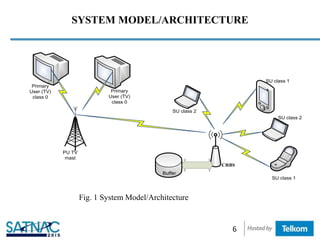
This document presents three channel assembling strategies - Immediate Blocking Strategy (IBS), Reassignment Based Strategy (RBS), and Queuing Based Strategy (QBS) - for cognitive radio networks handling multi-class secondary users. The strategies are evaluated based on their blocking and forced termination probabilities. Simulation results show that QBS outperforms RBS and IBS by demonstrating lower blocking and forced termination probabilities for multi-class secondary users. QBS is found to be a more robust approach by incorporating queuing and adaptive modulation and coding techniques to improve dynamic channel allocation in cognitive radio networks.







![ALGORITHM FOR IBS
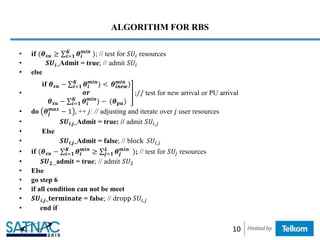
• 𝐢𝐟 (𝜽 𝒔𝒖 ≥ 𝒊=𝟏
𝑲
𝜽𝒊 ); // test for 𝑆𝑈𝑖 resources
• 𝑺𝑼 𝟏_Admit = true; // admit 𝑆𝑈1
• Else
• 𝑺𝑼 𝟏_Admit =false; // block 𝑆𝑈1
• 𝐢𝐟 [(𝜽 𝒔𝒖 − 𝒊=𝟏
𝑲
𝜽𝒊 ) − (𝜽 𝒑𝒖)];// PU arrival, pre-empt 𝑆𝑈1
• 𝑺𝑼 𝟏_𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐩 = true; // forced terminate on − going 𝑆𝑈1
• 𝐢𝐟 (𝜽 𝒔𝒖 − 𝒊=𝟏
𝑲
𝜽𝒊 ≥ 𝒋=𝟏
𝑳
𝜽𝒋 ) ;// enough resources
• 𝑺𝑼 𝟐_Admit = true: // admit 𝑆𝑈2
• Else
• 𝑺𝑼 𝟐_Admit = false; // block 𝑆𝑈2
• 𝐢𝐟 [[(𝜽 𝒔𝒖 − 𝒊=𝟏
𝑲
𝜽𝒊 ) ≥ 𝒋=𝟏
𝑳
𝜽𝒋
𝒎𝒊𝒏
] − (𝜽 𝒑𝒖)]; // PU arrival, pre-empt 𝑆𝑈2
• 𝑺𝑼 𝟐_𝐝𝐫𝐨𝐩 = true; // dropp 𝑆𝑈2
• end if
• Go to start
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01d7e5d9-1ad7-4d9b-a54f-99085b030cda-151210092310/85/SATNAC-PRESENTATION-FINAL-9-320.jpg)