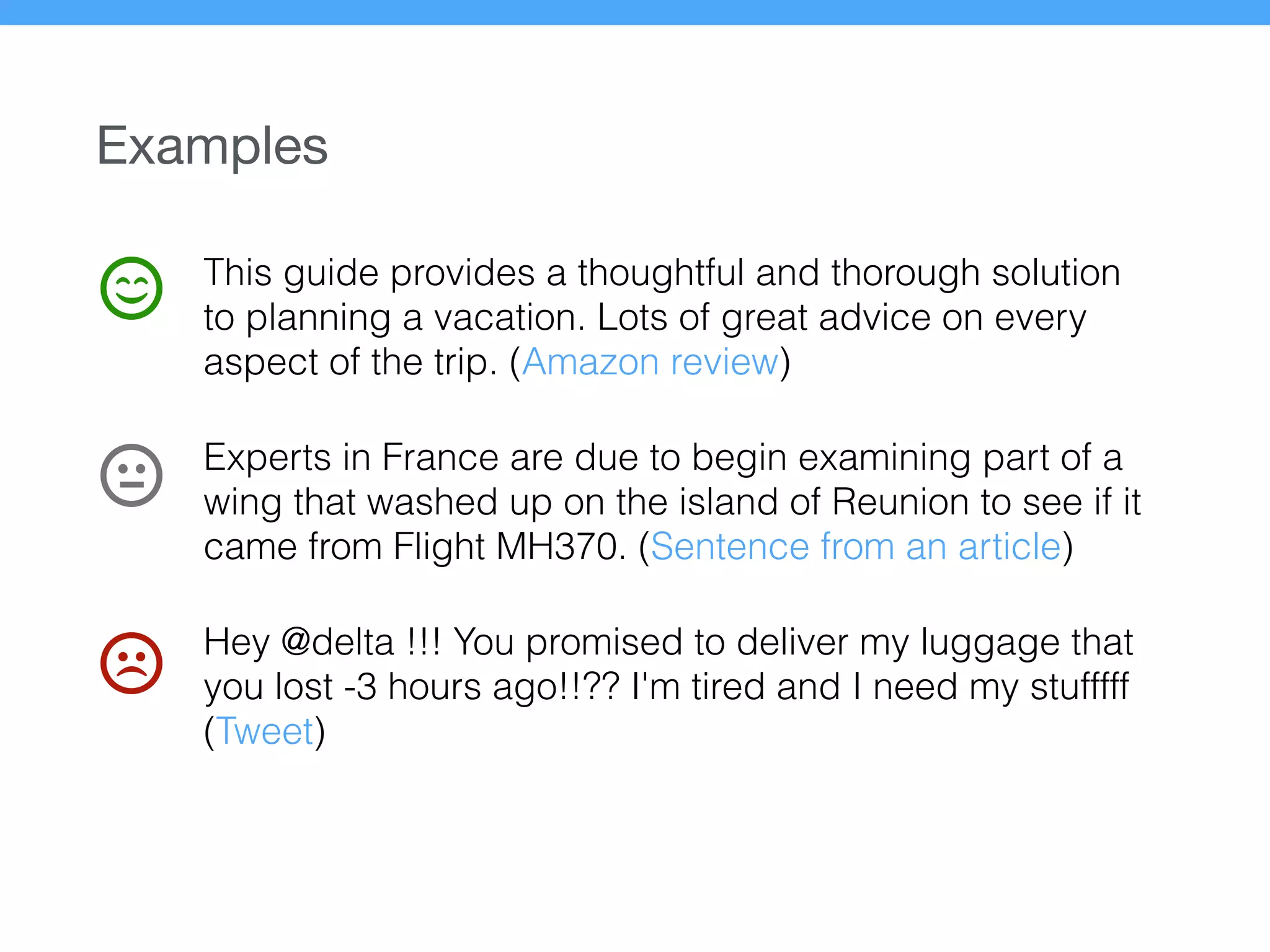
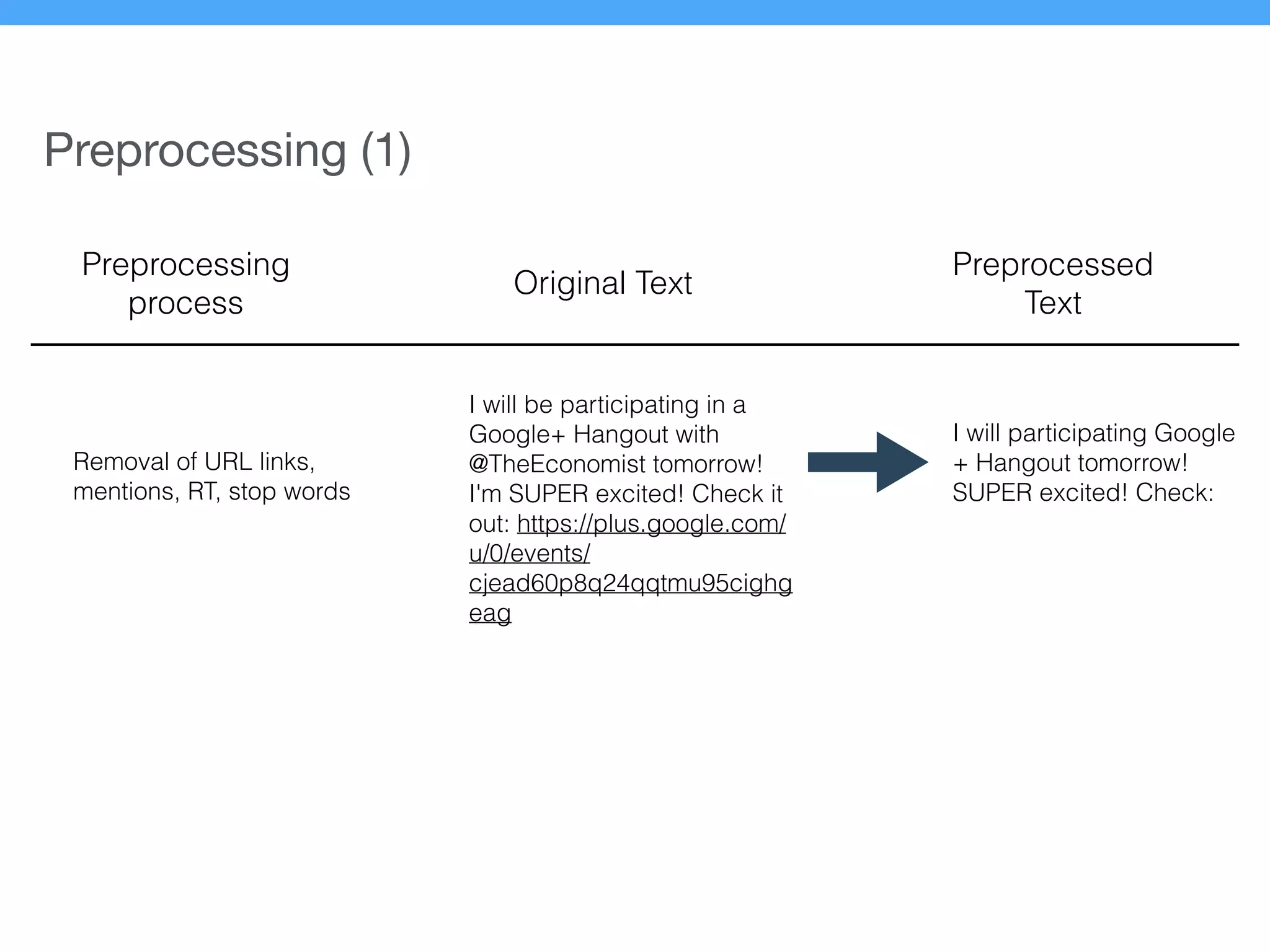
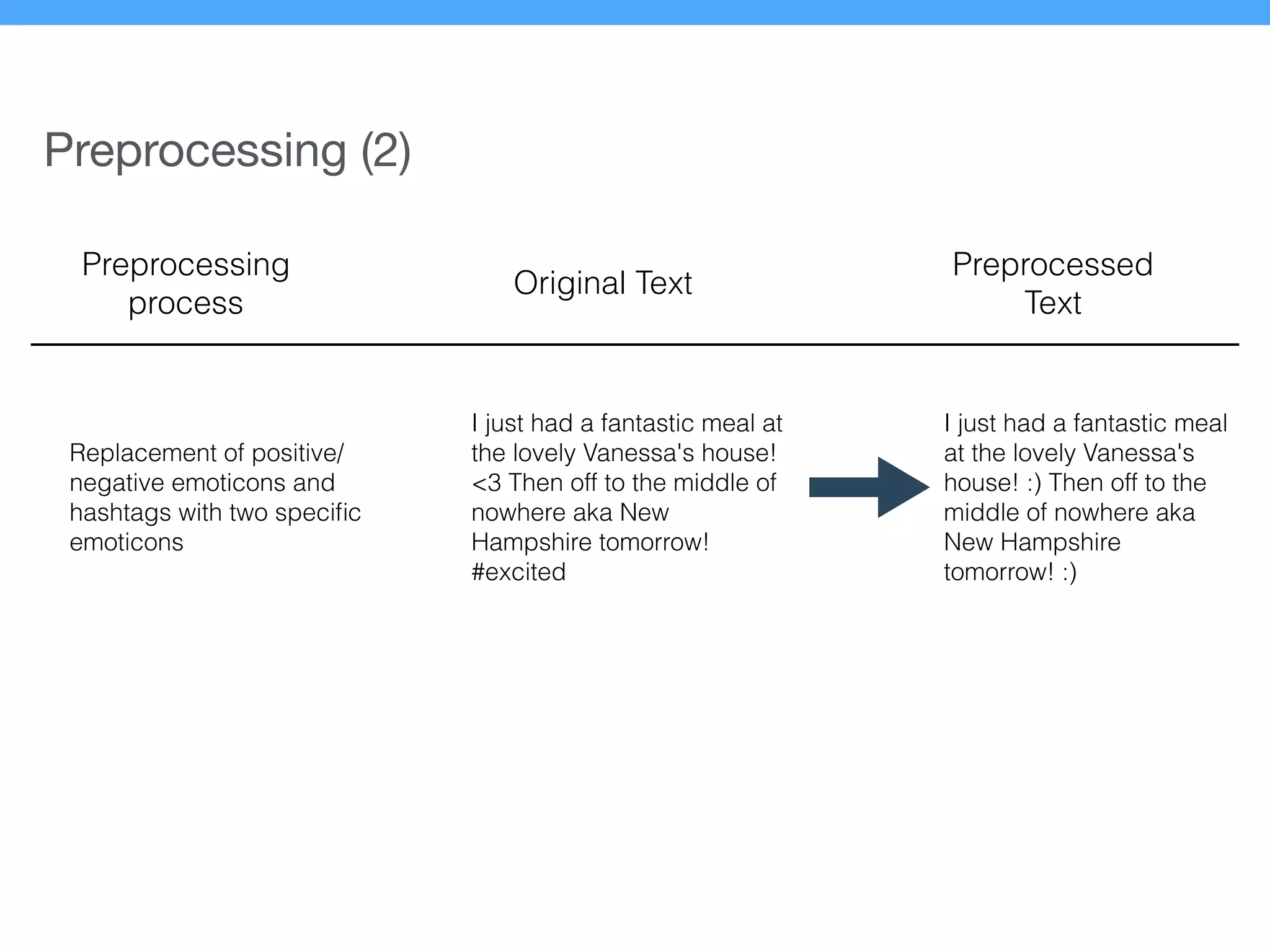
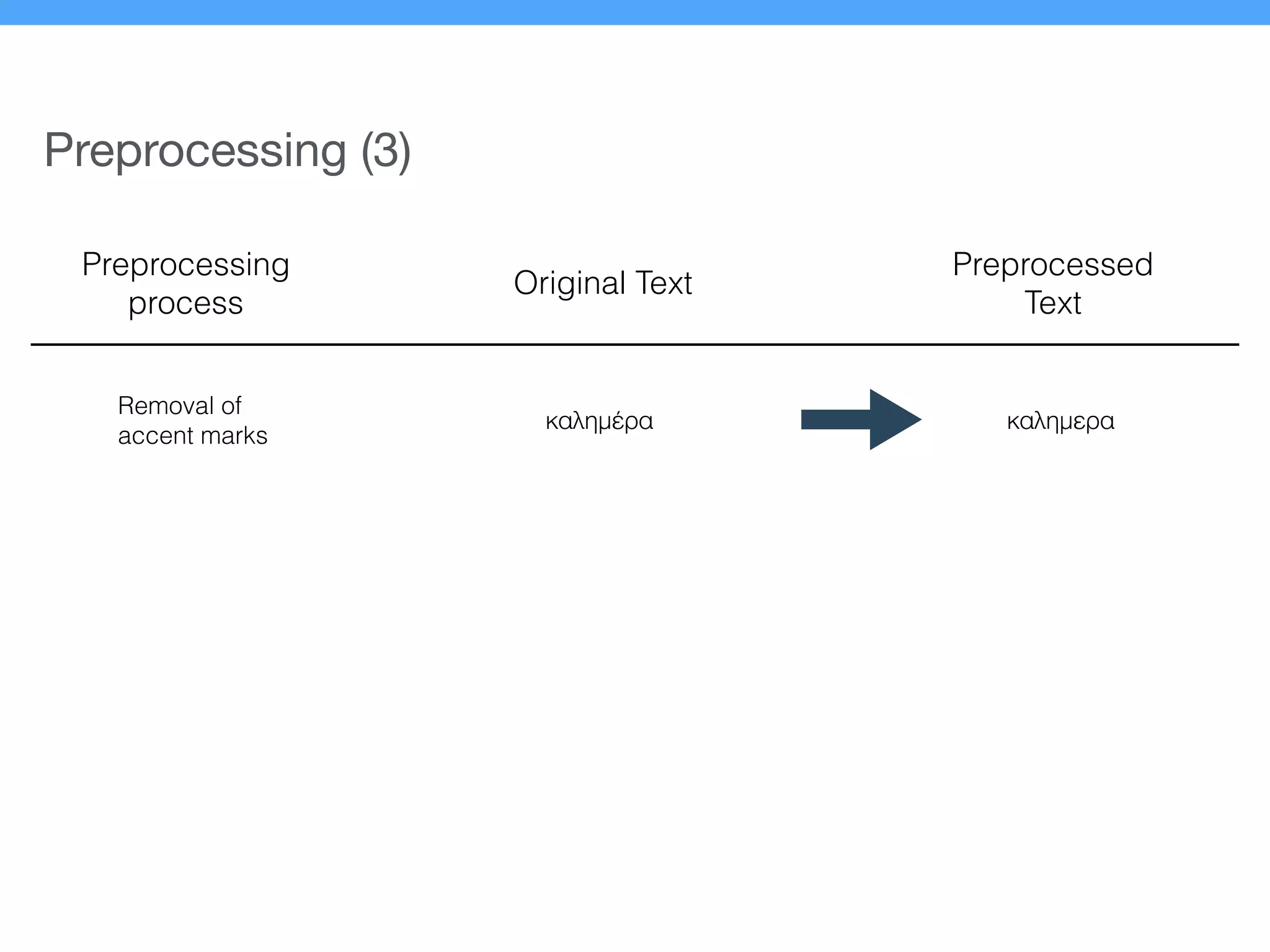
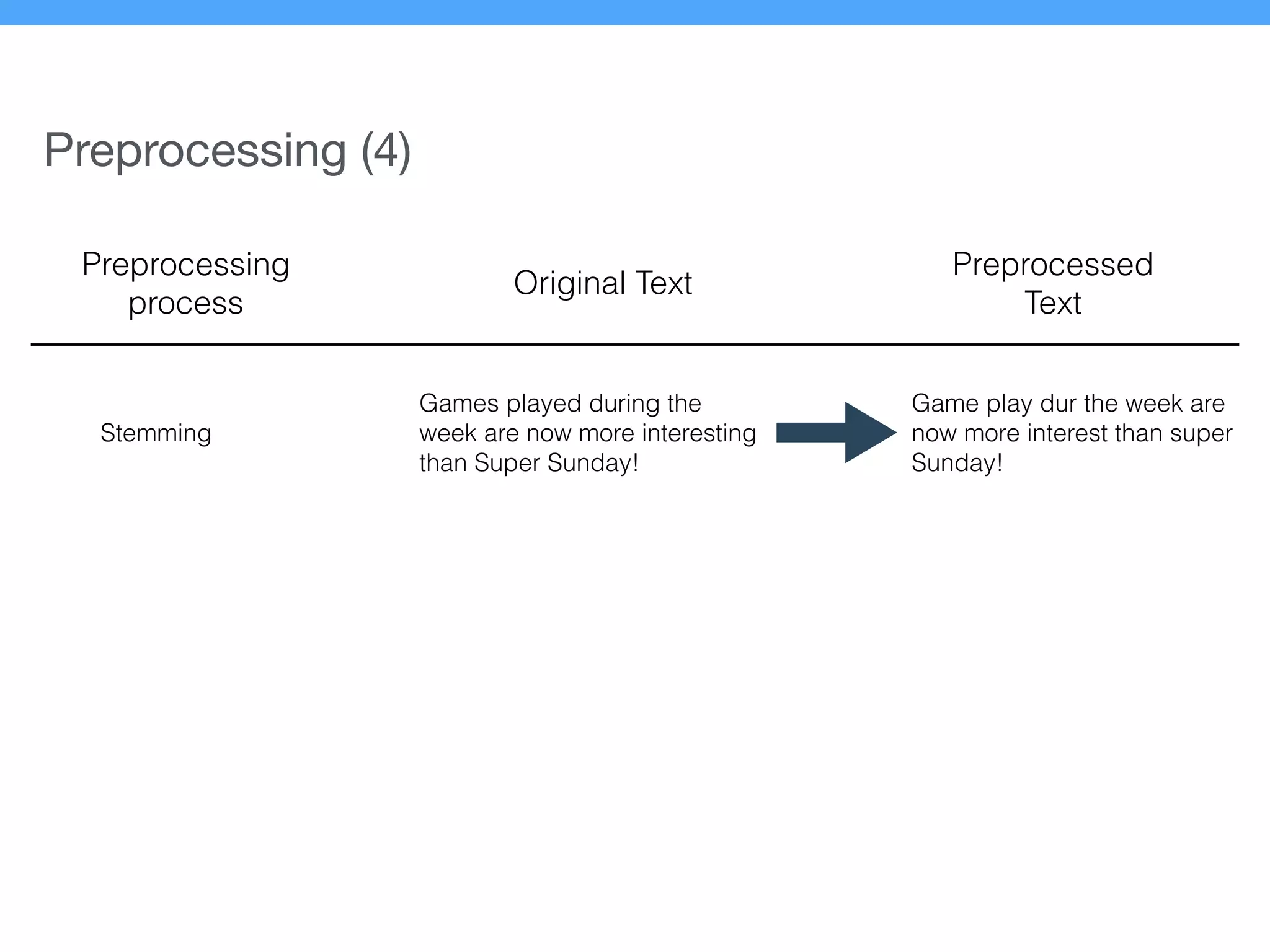
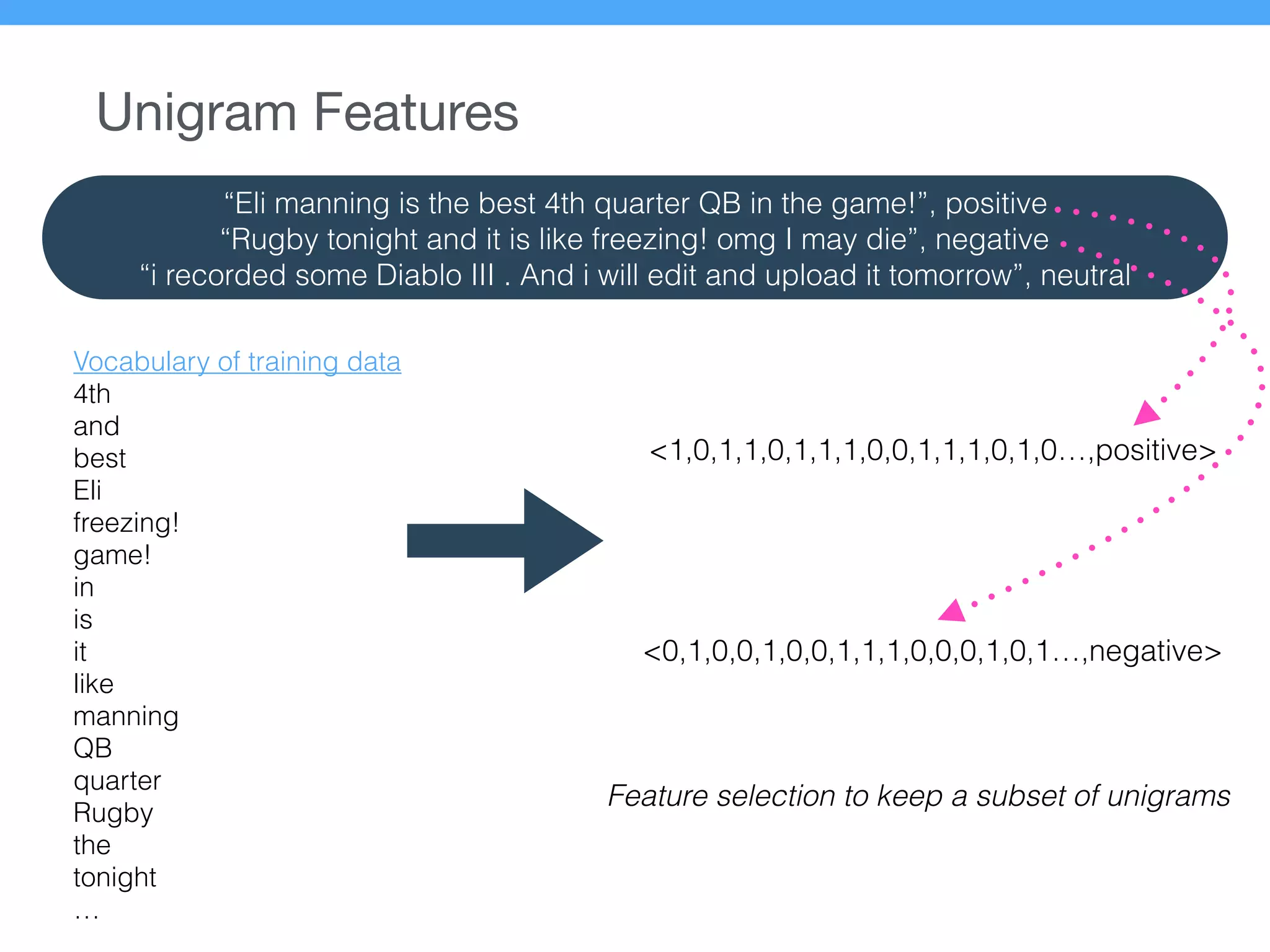
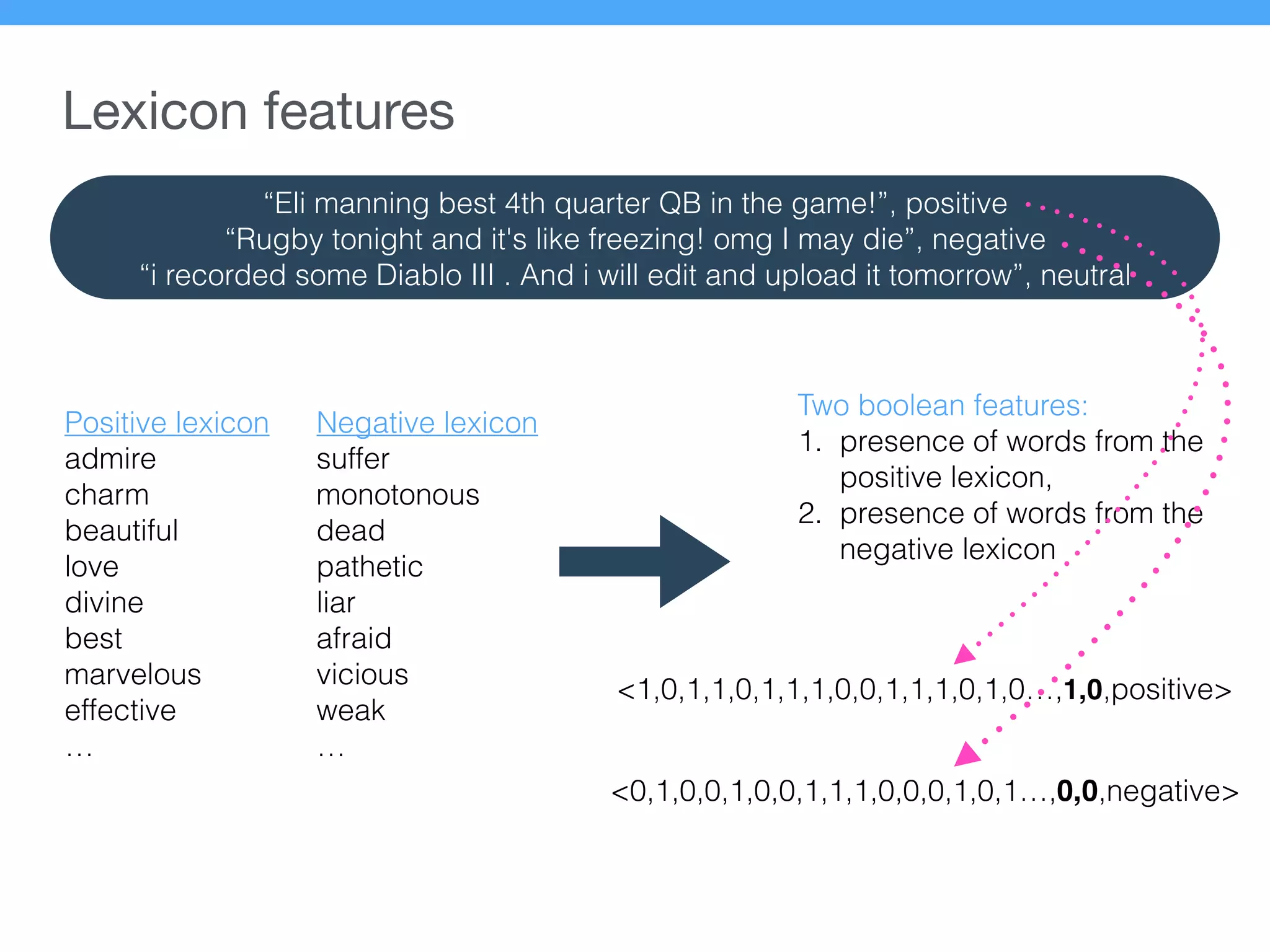
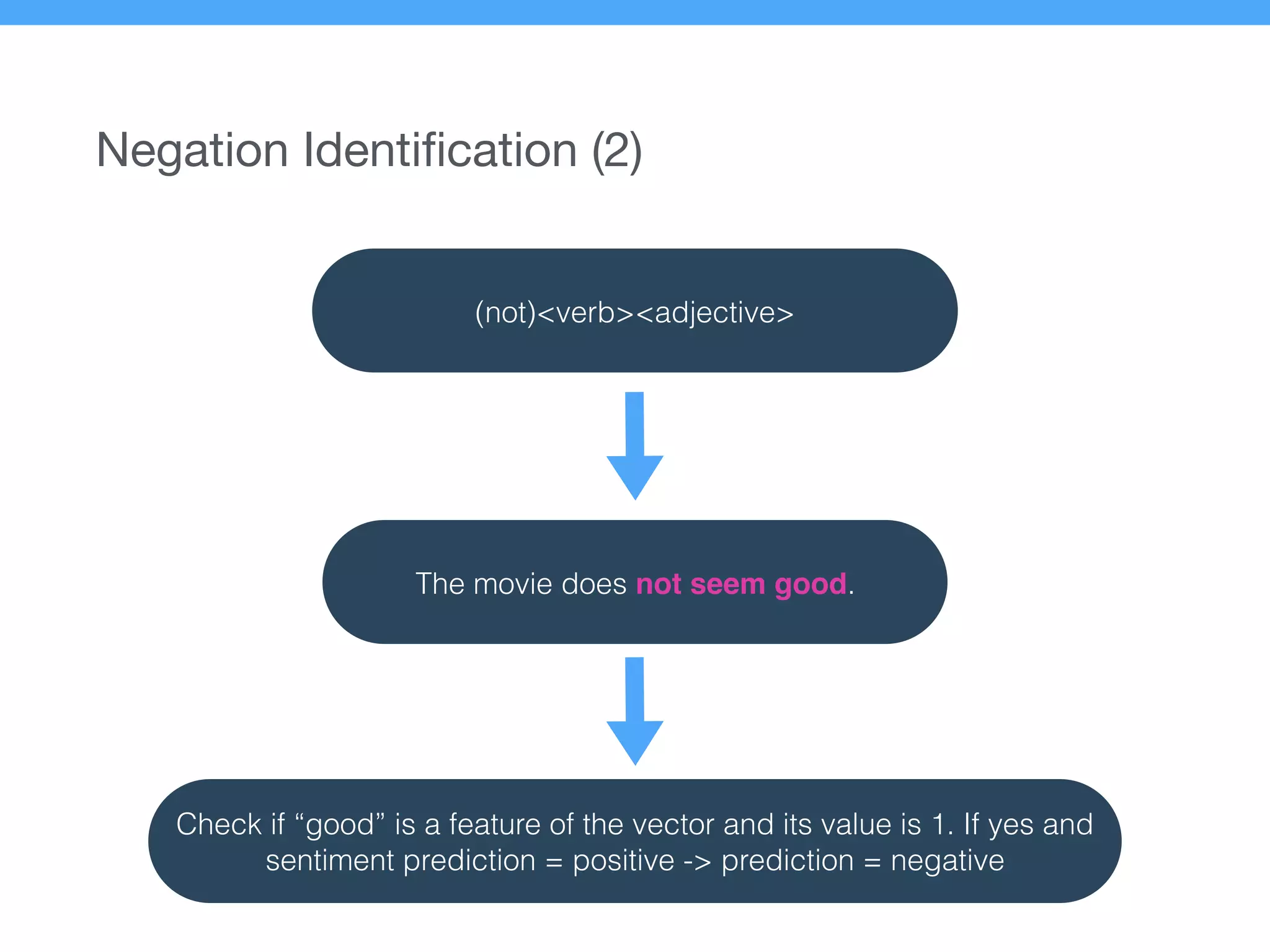
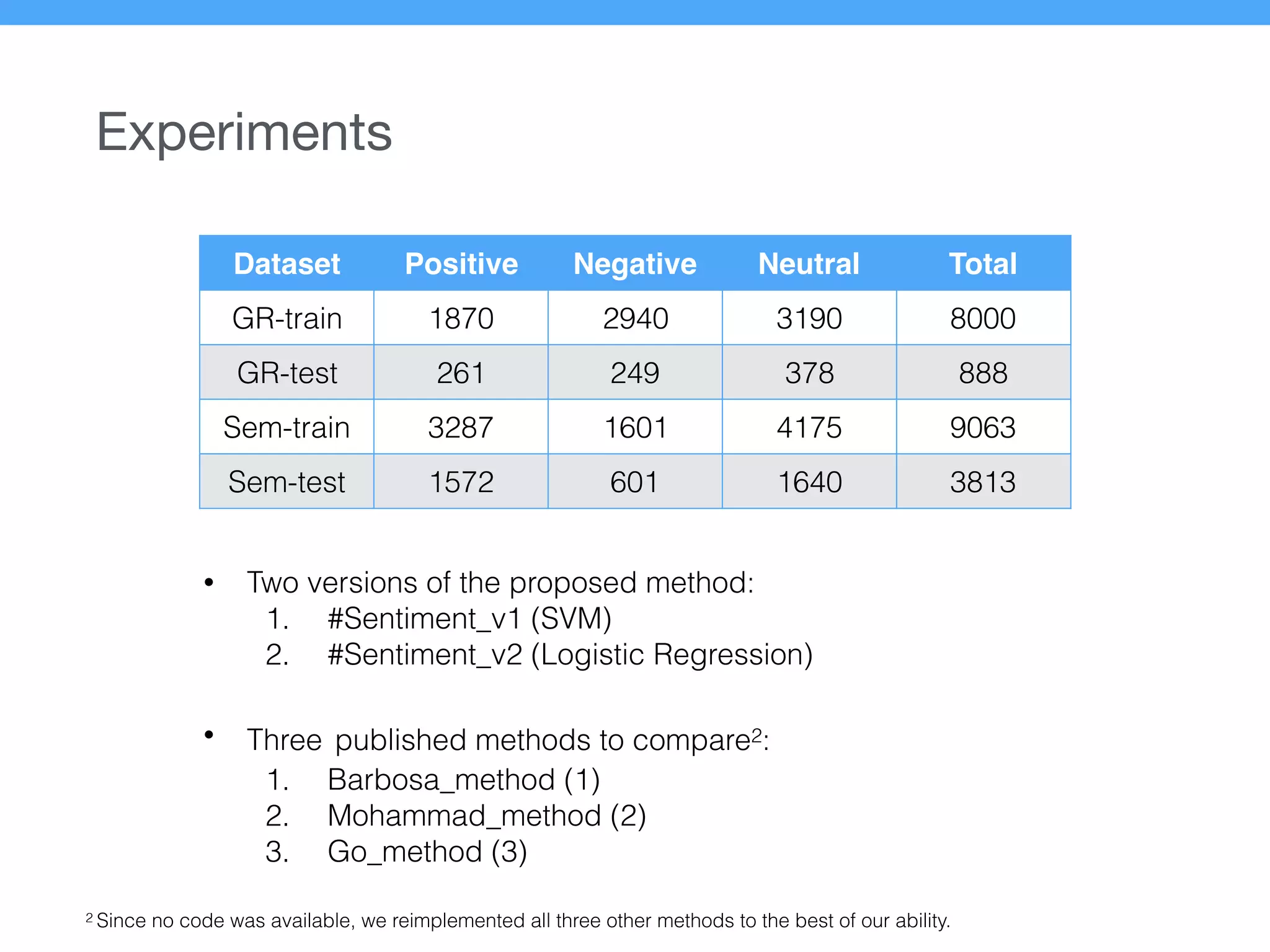
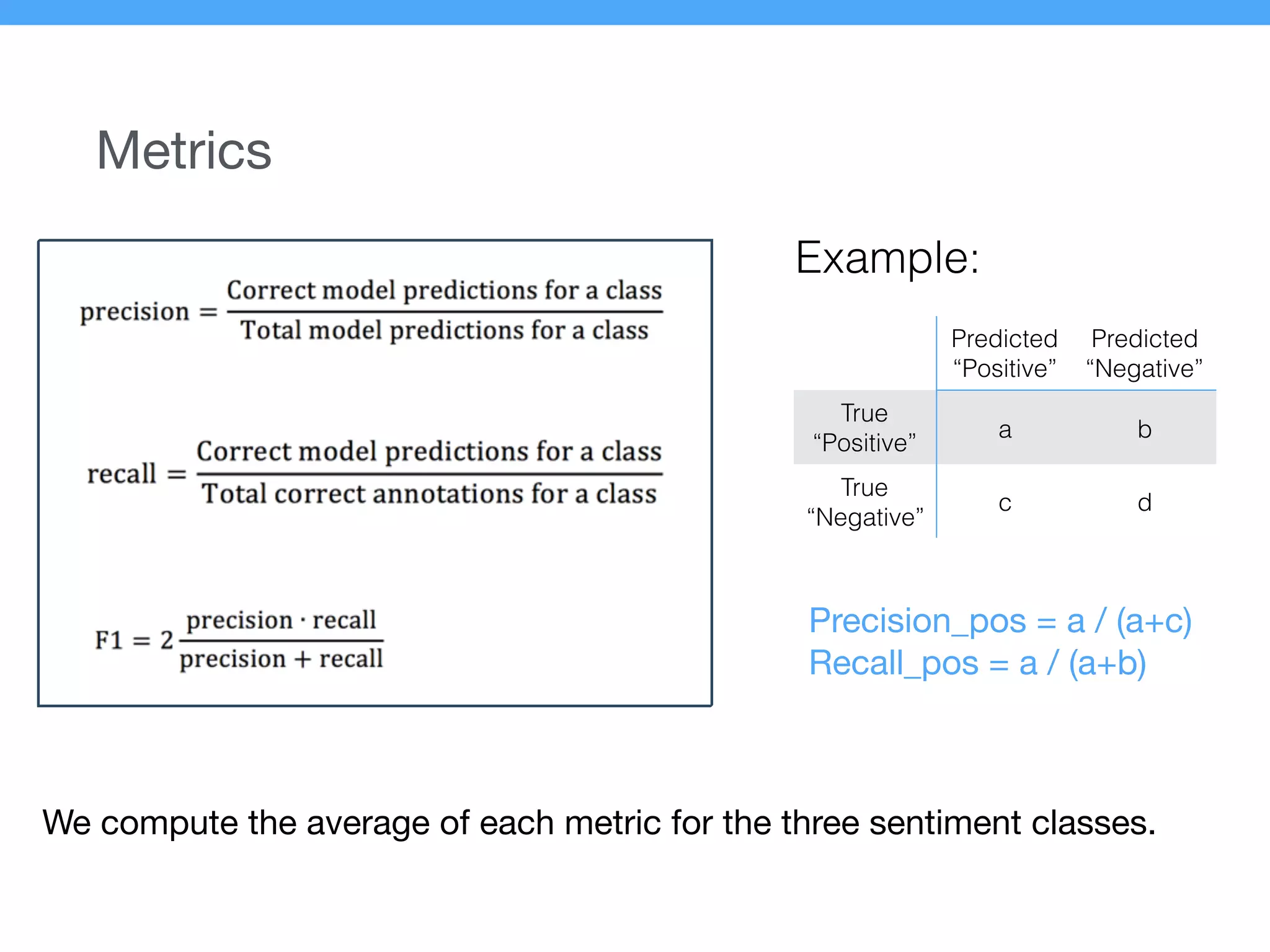
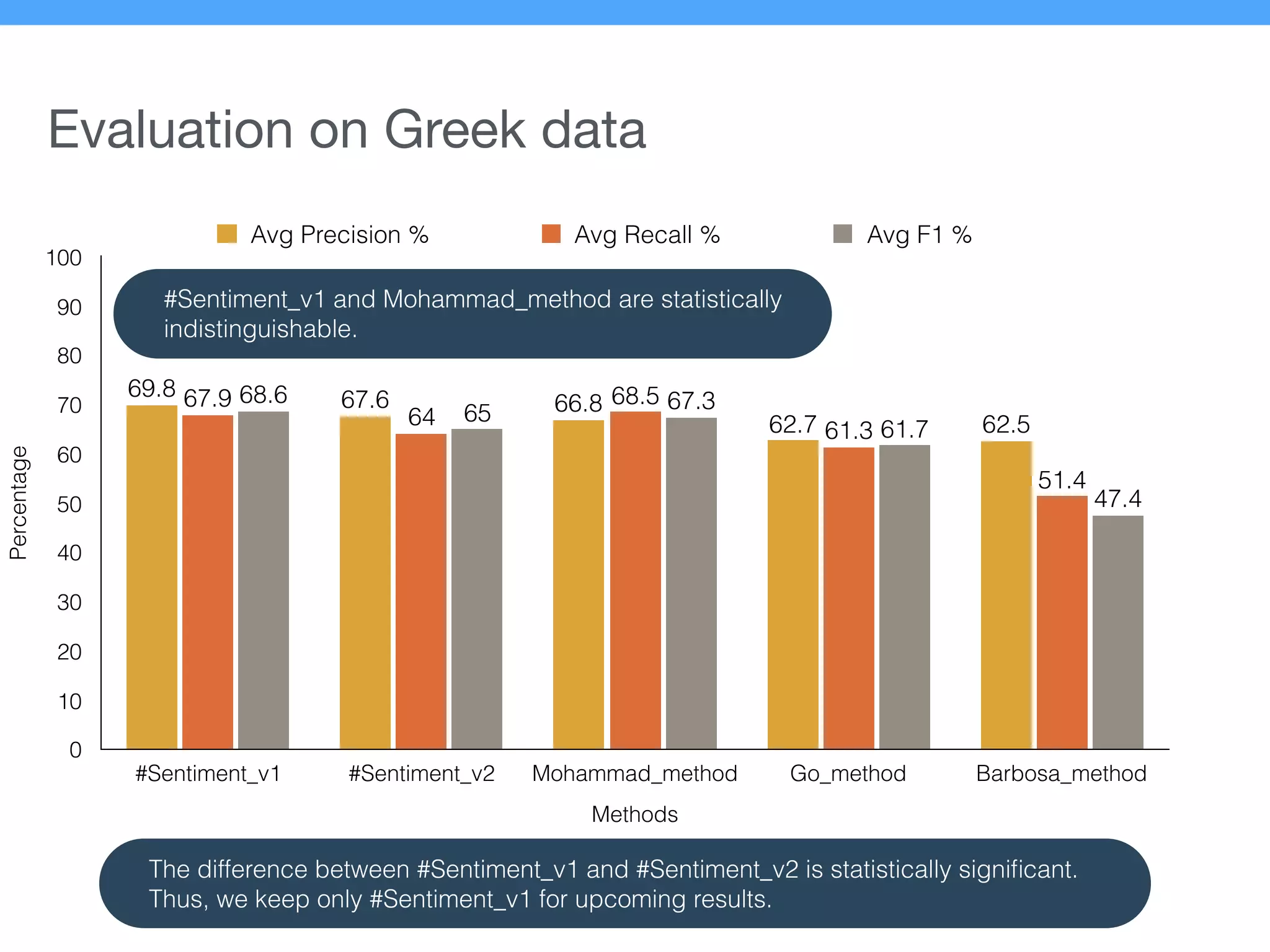
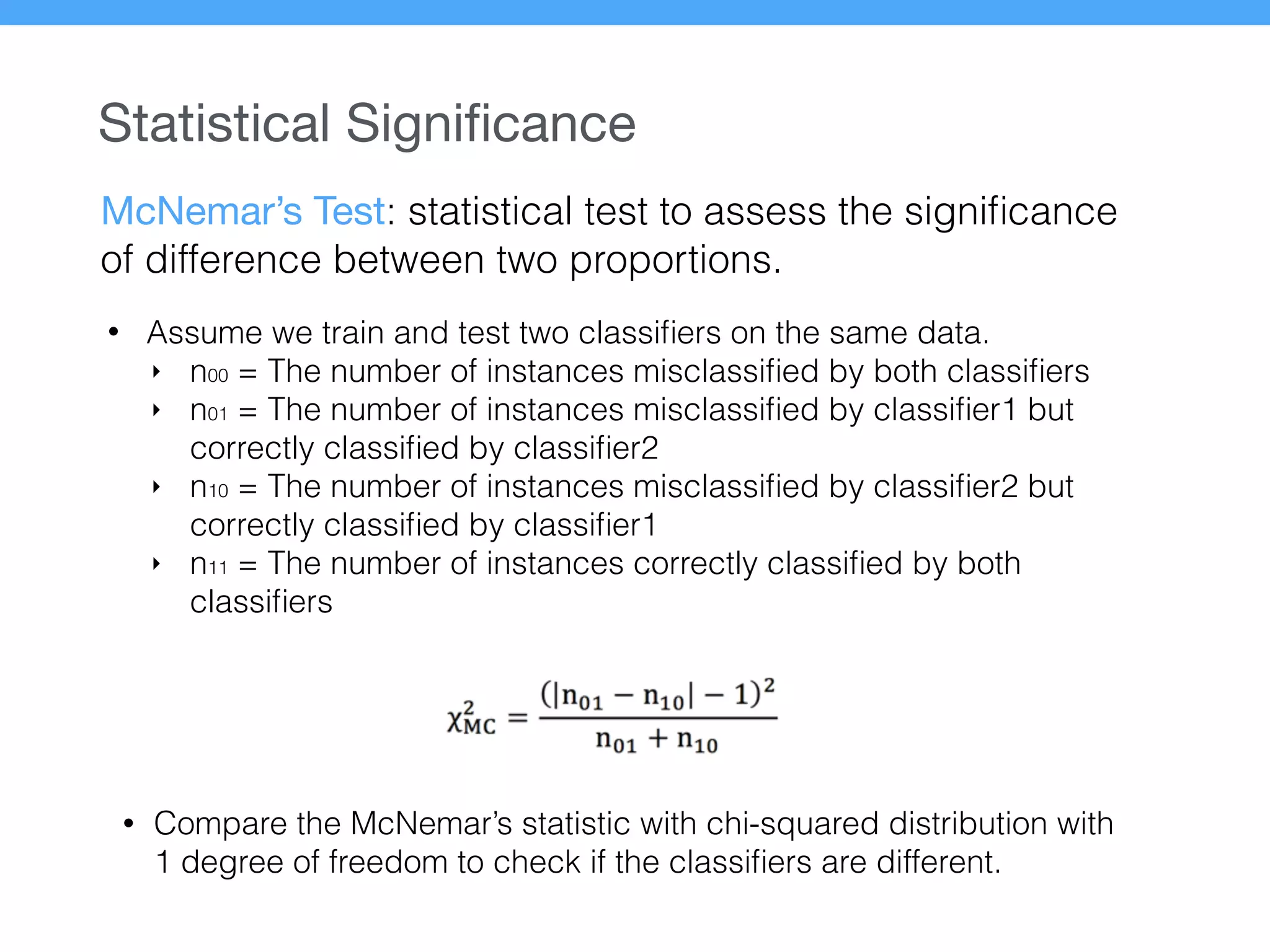
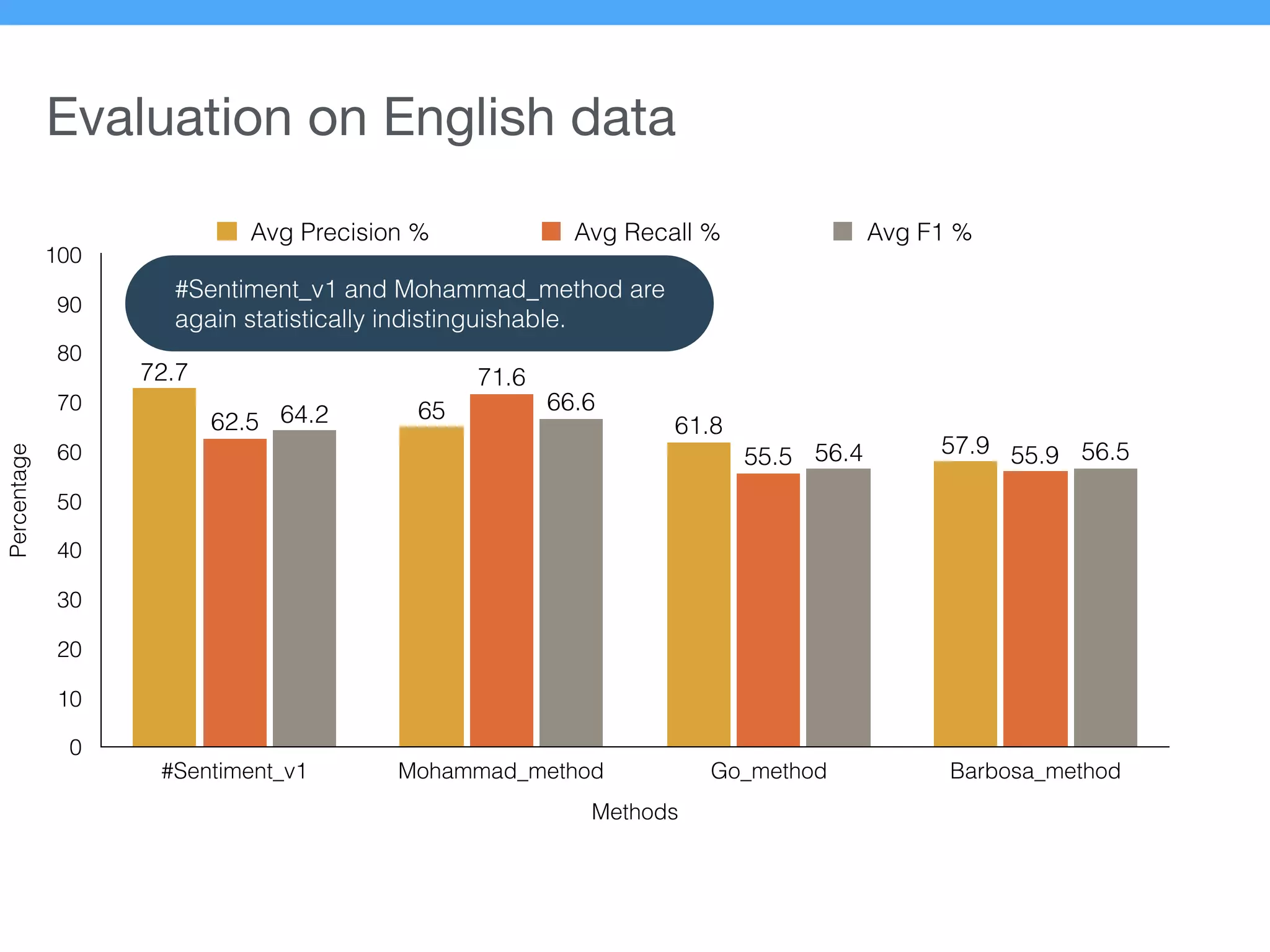
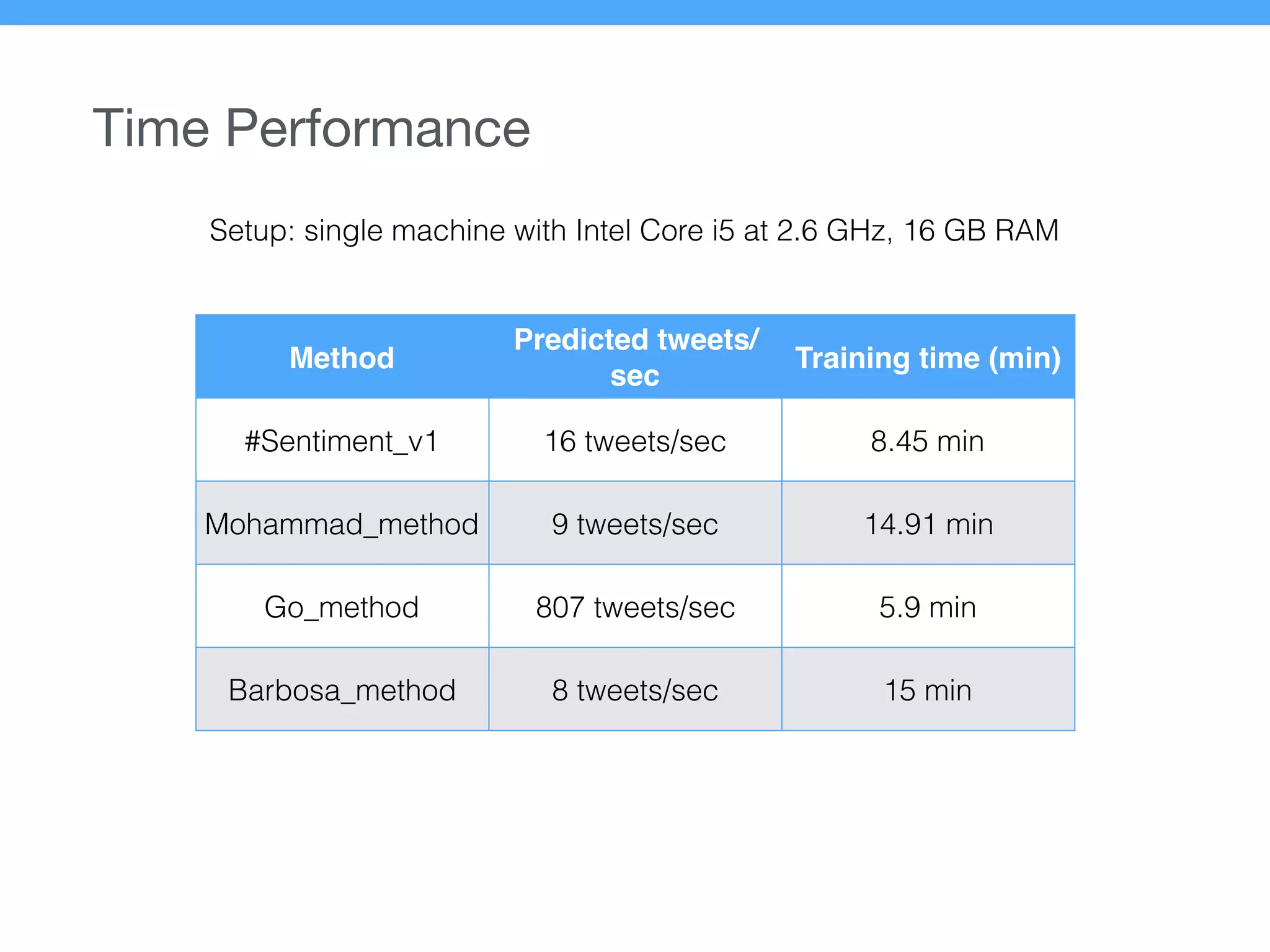
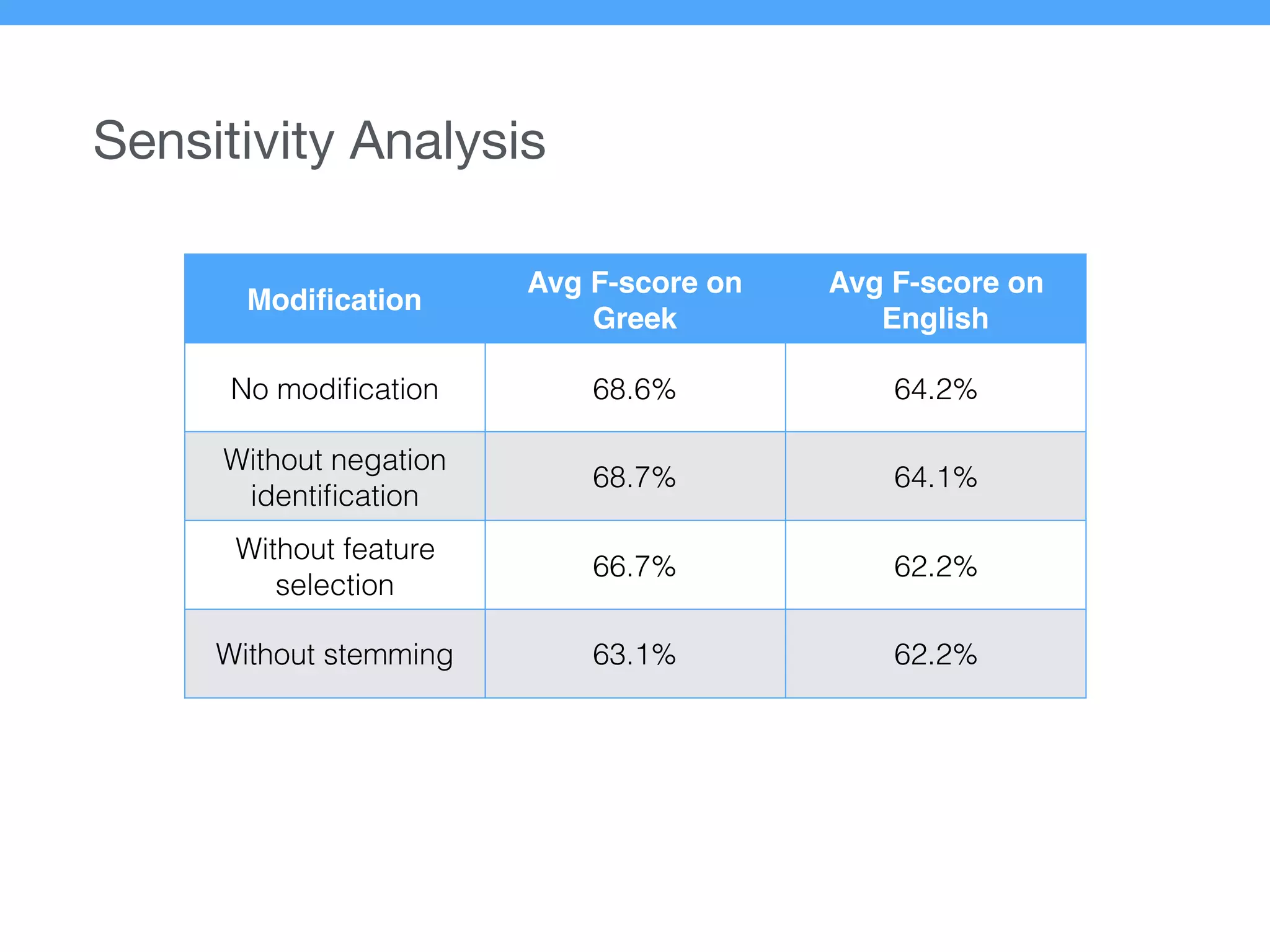
The document presents a new supervised method for sentiment analysis of tweets in Greek and English. It introduces techniques for preprocessing text, extracting features, training a classification model, and performing negation identification. Evaluation shows the method achieves comparable or better results than previous work, with faster prediction speed. Analysis found preprocessing and features had different impacts on performance for Greek vs English. Future work is outlined on assigning sentiment to entities in tweets.