This document discusses best practices for business communication. It emphasizes that good communication is important in today's global, knowledge-based world. Effective communication requires identifying your purpose and audience, and selecting the appropriate communication channel. Business communication should be professional, concise, and consider cultural differences. Both positive and negative messages require careful planning. Overall, communication skills are vital for all employees and businesses.




























![REFERENCES
Colorado State University – Global Campus. (2014). Module 7: Informal and formal business reports, plans , and proposals
[Blackboard ecourse]. In ORG536-1 – Contemporary Business Writing and Communication. Greenwood Village, CO:
Author.
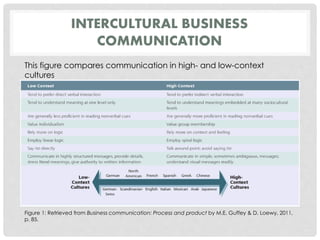
Guffey, M., & Loewy, D. (2011). Business communication: Process and product (7th ed.). Independence, KY: Cengage
Learning.
Gurău, C. (2012). Solving customer complaints: A study of multiple commercial settings. Annals Of The University Of Oradea,
Economic Science Series, 21(2), 827-833. Retrieved from https://eds-a-ebscohost-com.csuglobal.idm.oclc.org
Hajli, M. (2014). A study of the impact of social media on consumers. International Journal Of Market Research, 56(3), 387-
404. doi:10.2501/IJMR-2014-025
Halperin, D. (2014, June 20). For-profit Corinthian Colleges on the brink: Who’s responsible? Huffington Post. Retrieved from
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/davidhalperin/for-profit-corinthian-col_b_5516063.html
Inc. (2010). Ten ways to use texting for business. Retrieved from http://www.inc.com/ss/ten-ways-use-texting-business
Lloyd, J. (n.d.). Complaints offer opportunities. Retrieved from http://www.joanlloyd.com/Your-Career/Complaints-offer-opportunities.
aspx
Moth, D. (2013). How Walmart uses Pinterest, Facebook, Twitter and Google+. Retrieved from
https://econsultancy.com/blog/61827-how-walmart-uses-pinterest-facebook-twitter-and-google#i.14ocqor72eeqyp
Nordquist, R. (n.d.). 10 Tips on how to write a professional email. Retrieved from
http://grammar.about.com/od/developingessays/a/profemails.htm
Pollitt, C. (2014). An inside view of Walmart’s digital communications strategy. Retrieved from
http://www.socialmediatoday.com/content/inside-view-walmarts-digital-communications-strategy
Shanan. (2013, June 7). The three biggest mistakes in business writing [Web log post]. Retrieved from
http://www.theprocrastiwriter.com/the-three-biggest-mistakes-in-business-writing/
Tardanico, S. (2012, November 29). 5 Habits of highly effective communicators. Forbes. Retrieved from
http://www.forbes.com/sites/susantardanico/2012/11/29/5-habits-of-highly-effective-communicators/
Walmart. (2014). Walmart’s social media guidelines. Retrieved from http://corporate.walmart.com/social-media-guidelines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sanduskyorg536mod8-140929004604-phpapp01/85/Sandusky-org536-mod-8-30-320.jpg)