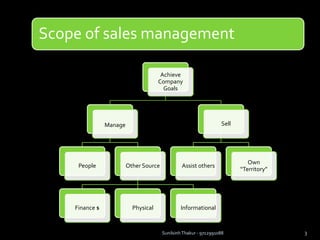
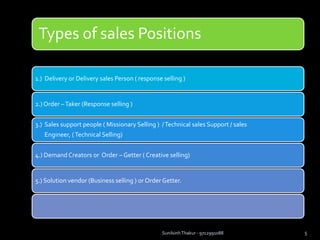
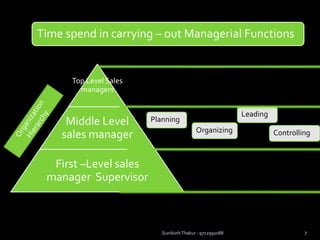
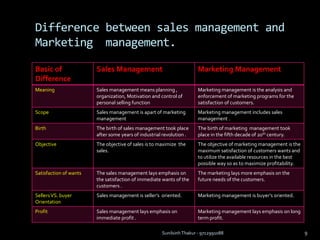
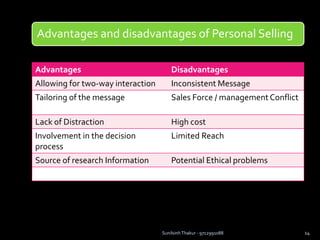
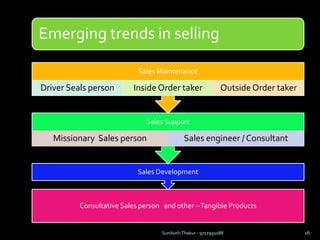
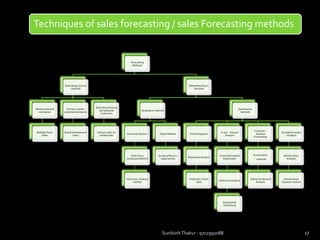
The document discusses sales management. It defines sales management and discusses its nature, scope, and objectives. It also covers types of sales positions, leadership levels in sales organizations, functions of sales managers, and the importance of sales management. Additionally, it compares sales management to marketing management and outlines the sales management process.