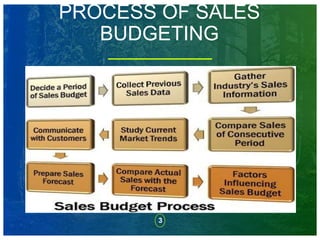
This document discusses sales budgeting and provides steps for the sales budgeting process. It begins by defining a sales budget as the estimation of sales revenue and sales overheads for a given period, such as monthly, quarterly, or yearly. It then outlines 8 steps for preparing a sales budget, which include determining the budget period, collecting previous sales data, gathering industry sales information, comparing sales across periods, studying current market trends, communicating with customers, preparing sales forecasts, and comparing actual to forecasted sales. Finally, it discusses factors that influence the sales budget and different budgeting methods.