Rural markets in India represent a large opportunity for consumer goods companies as rural populations and incomes grow. However, rural distribution is challenging due to factors like scattered populations and lack of infrastructure. Companies are experimenting with innovative distribution models like ITC's e-Choupal, HUL's Project Shakti, and rural retail formats to better reach rural consumers. Successful rural marketing requires adapting the four P's, especially developing new distribution channels suited to rural contexts.


![ Rural India The Changing Face The “culture of
non-indulgence” and abstinence in consumption is
well and truly over Rural India buys 46% of all soft
drinks sold [Coca-Cola is growing at 37% in rural
markets with only 25% penetration, compared with
24% in urban areas] 49% of motorcycles and 59%
of cigarettes Source: MART
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ruralmkt-130128223035-phpapp02/85/Rural-mkt-3-320.jpg)
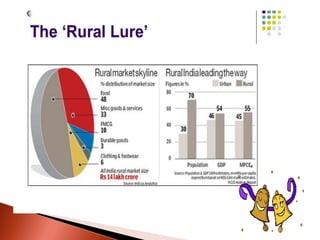






![ They have tried tinkering with all the four 'P's of the
marketing mix i.e. Product, Pricing, Promotion and
Place [ E.g. HUL has been a pioneer in reaching out to
the smallest of villages with innovative products such
as single-use packets of shampoo] To sell in villages,
products must be priced low, profit margins must be
kept to the minimum and the marketing message must
be kept simple.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ruralmkt-130128223035-phpapp02/85/Rural-mkt-12-320.jpg)


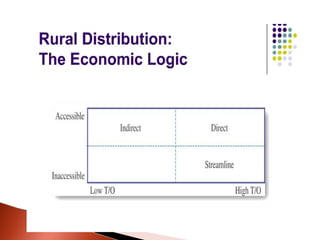
![The Distribution
Challenge Large and Scattered Markets
Dispersed population and trade Low density of
shops/village and high variation in their concentration
Inadequate Transport Facilities Lack of Retail
Infrastructure Poor visibility and display of product on
rural shop shelves Highly credit driven market and low
investment capacity of retailers Inadequate bank and
credit facilities for rural retailers Lack of proper
warehousing facility Multiple Tiers (large no. of
intermediaries) leading to higher costs *[ Though it
depends on Cost/Benefit ratio of the individual
organization] Poor Communication of due to Poor Reach
of Media](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ruralmkt-130128223035-phpapp02/85/Rural-mkt-16-320.jpg)
![Response to the
Issues Large and Scattered Markets
Inadequate Transport Facilities
Marico and HLL have started using delivery vans to
cater to rural markets. Coca Cola has opted for a ‘hub
and spoke’ distribution system. [Coke bottles were
transported from the bottling plants to the hubs (large
distributors) and from hubs to spokes (smaller
distributors) situated in small towns. Further
distribution is done from there.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ruralmkt-130128223035-phpapp02/85/Rural-mkt-17-320.jpg)







