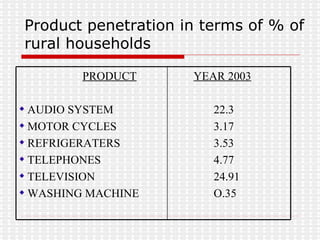
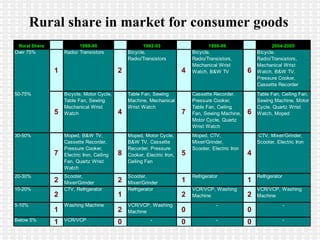
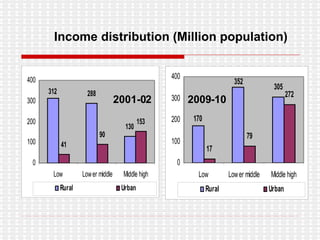
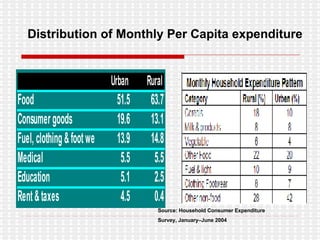
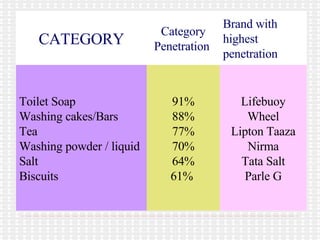
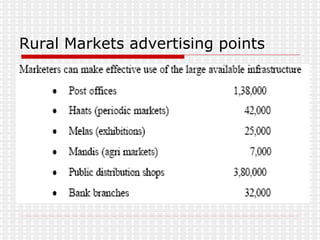
The document discusses the significance and challenges of rural marketing in India, emphasizing the large potential market of 742 million people. It highlights factors driving growth, including agricultural advancements, changing consumer behavior, and innovative marketing strategies used by companies like HLL and ITC. The document outlines obstacles such as distribution issues, low disposable incomes, and cultural gaps, while suggesting that those who adapt to the rural market's dynamics will find promising opportunities.