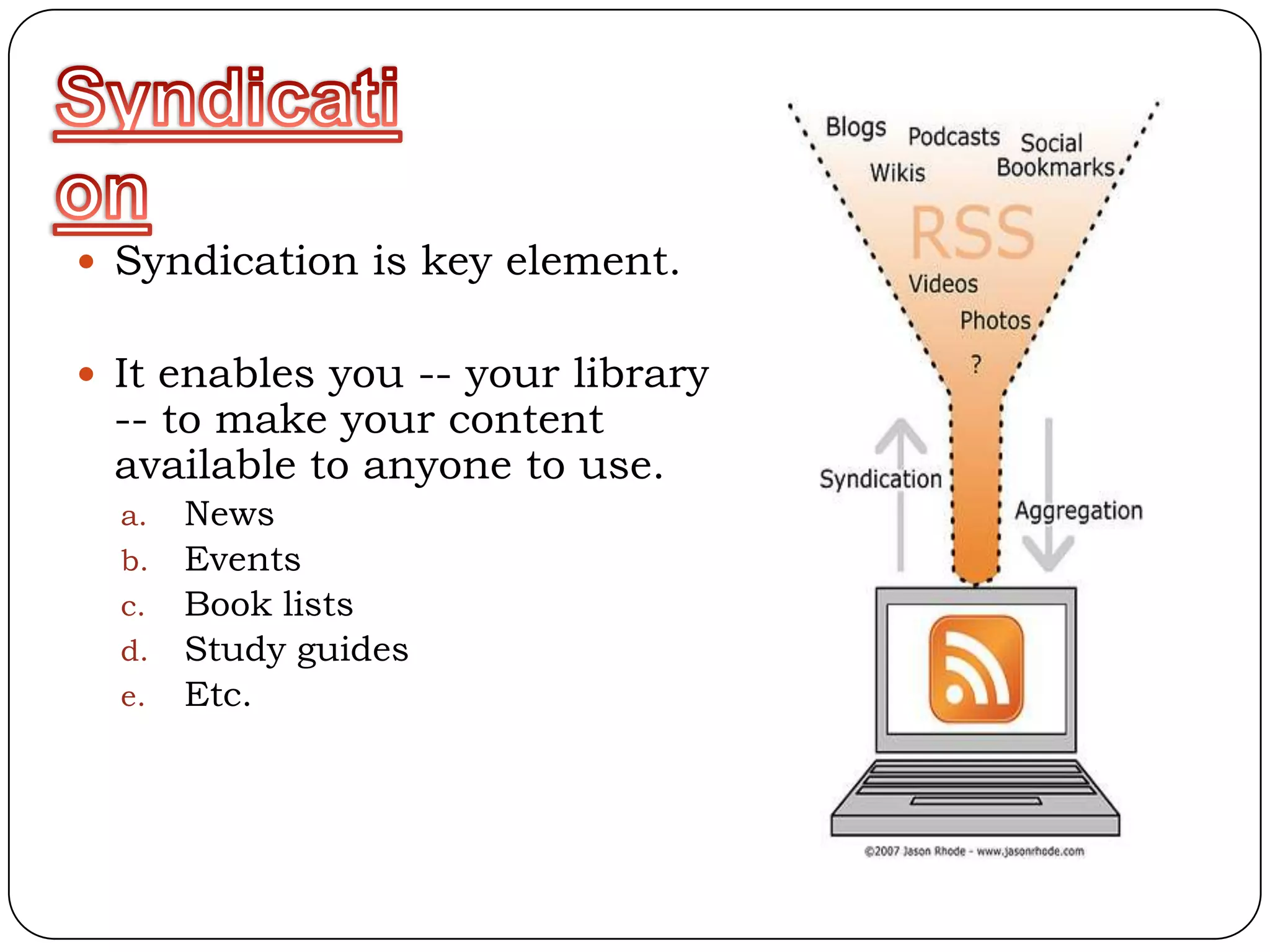
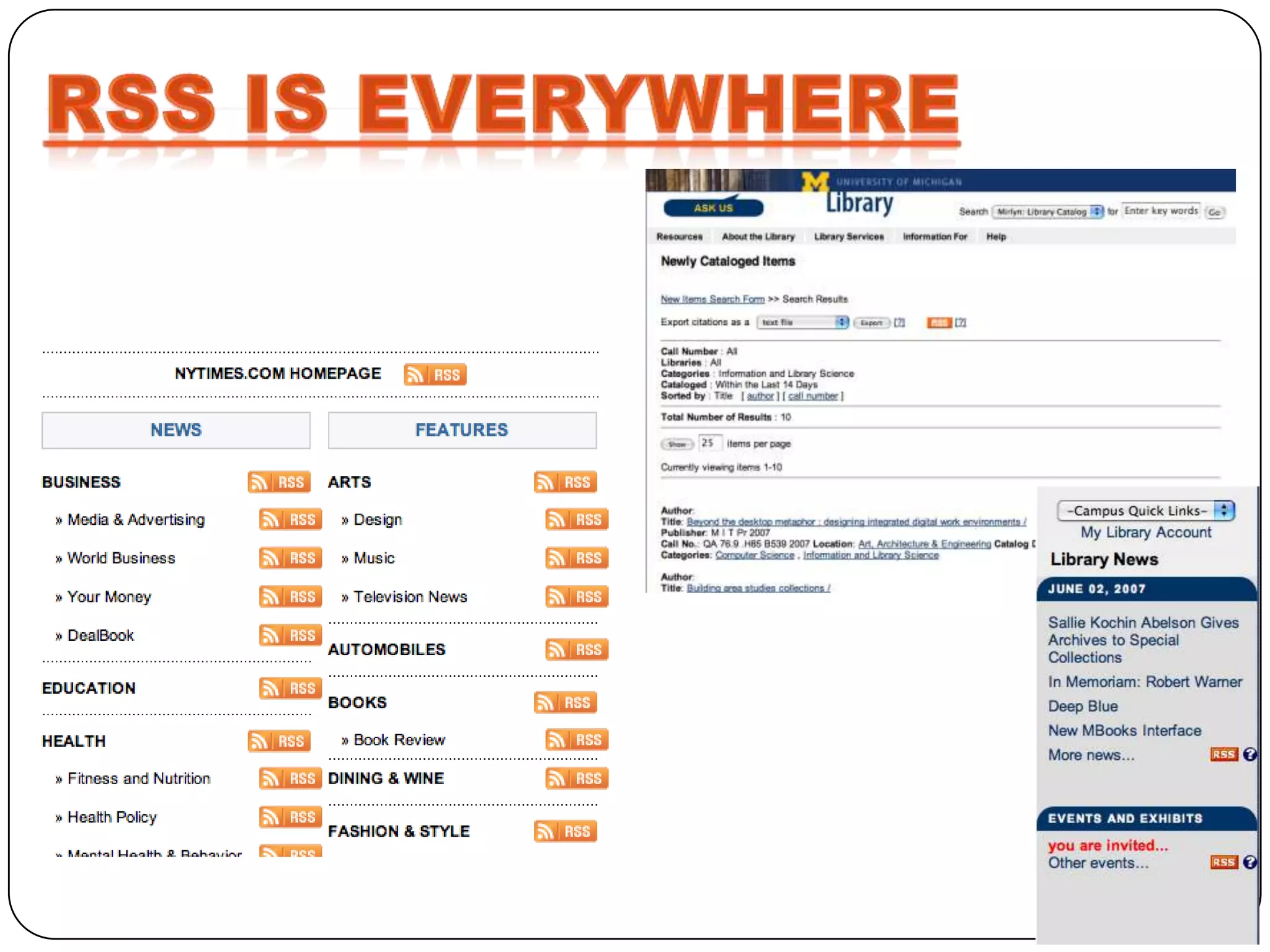
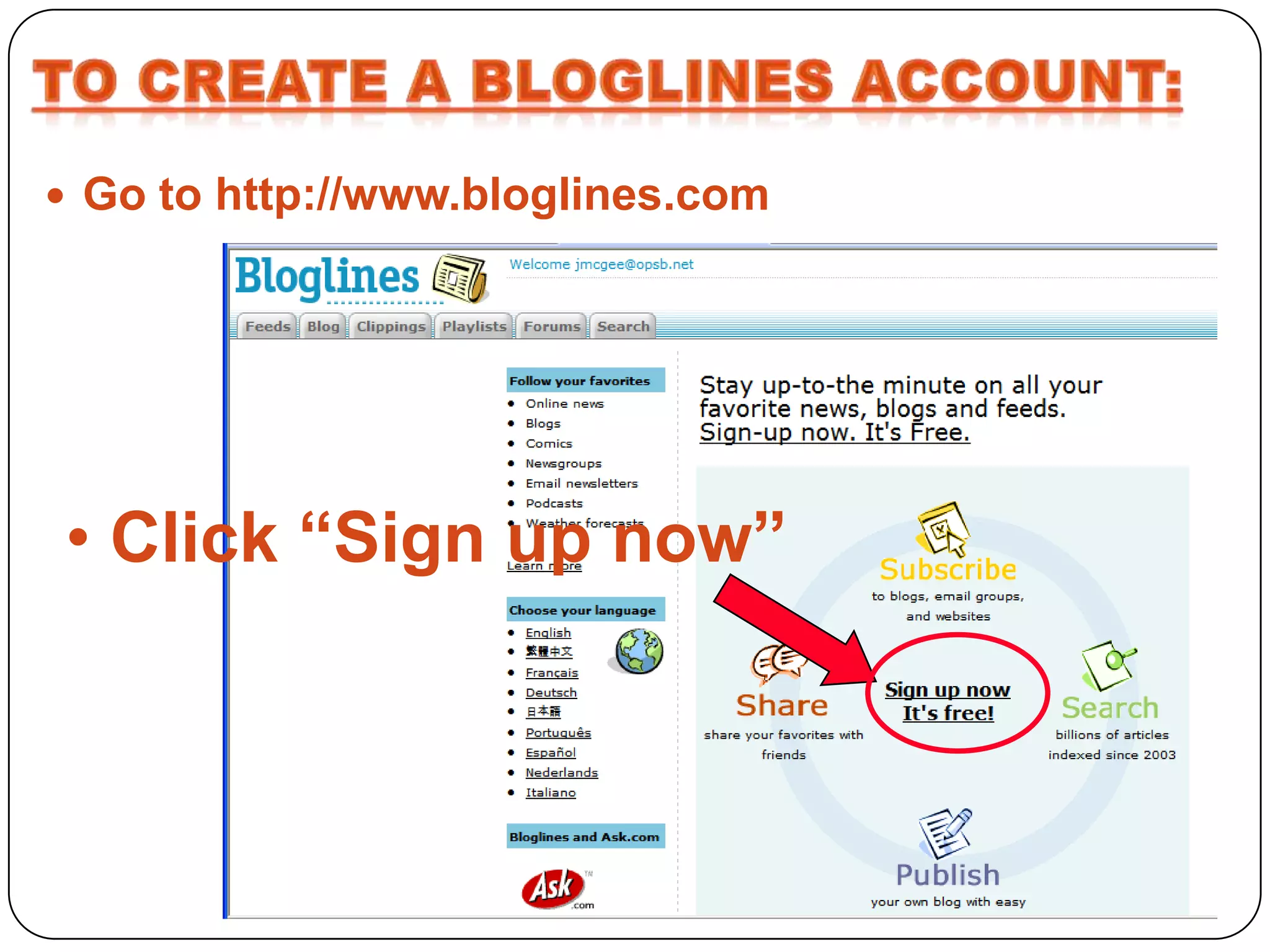
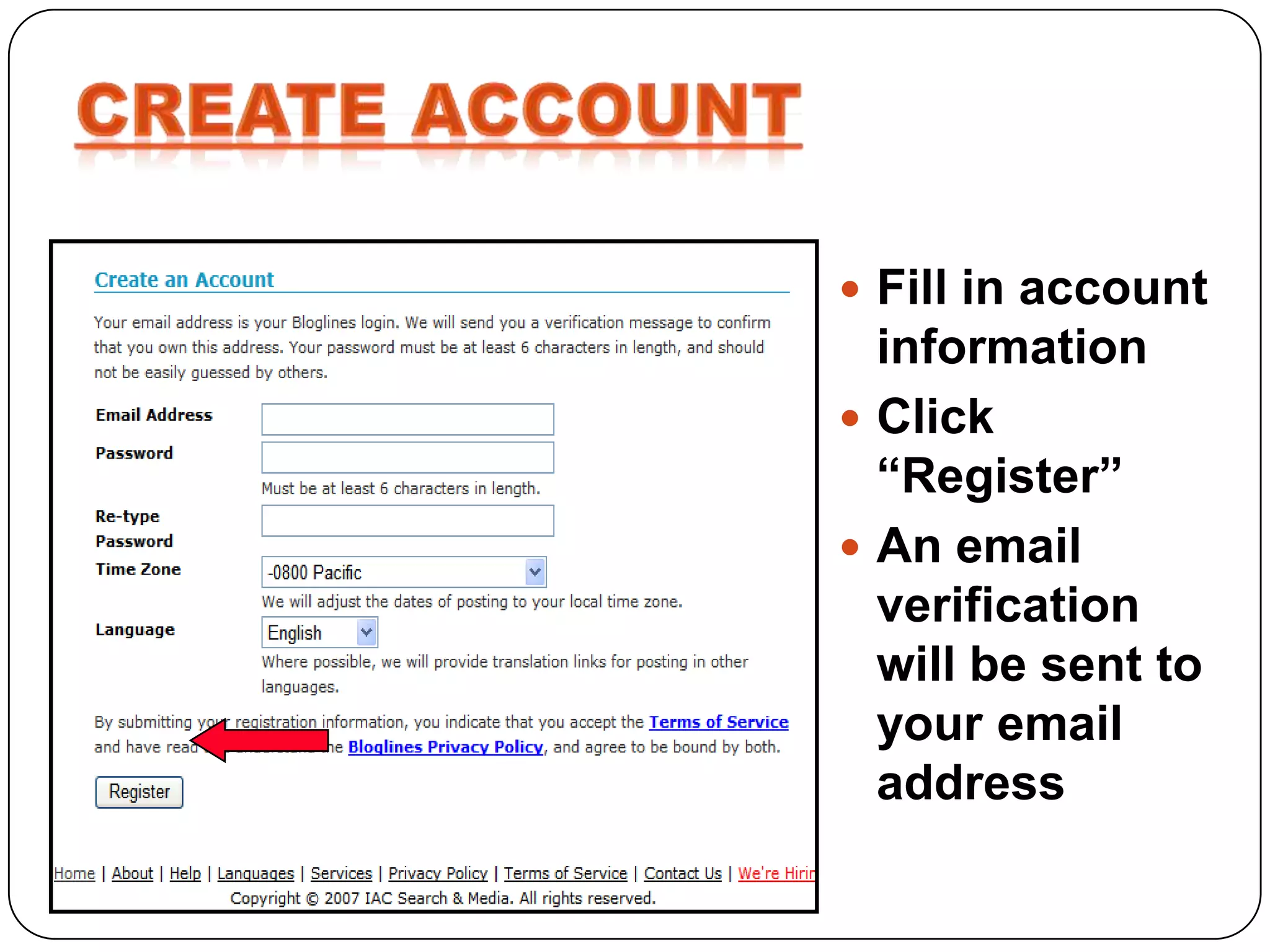
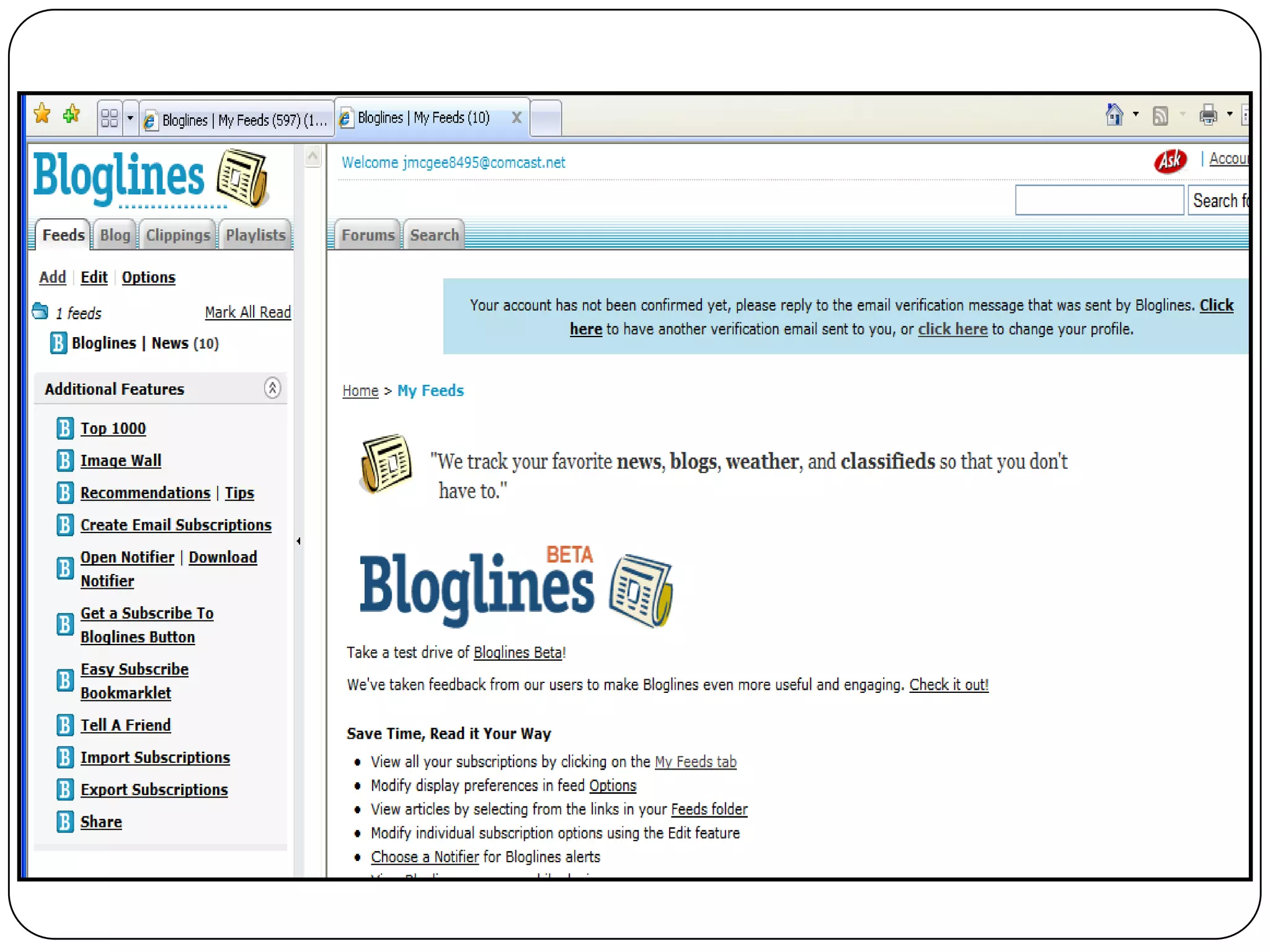
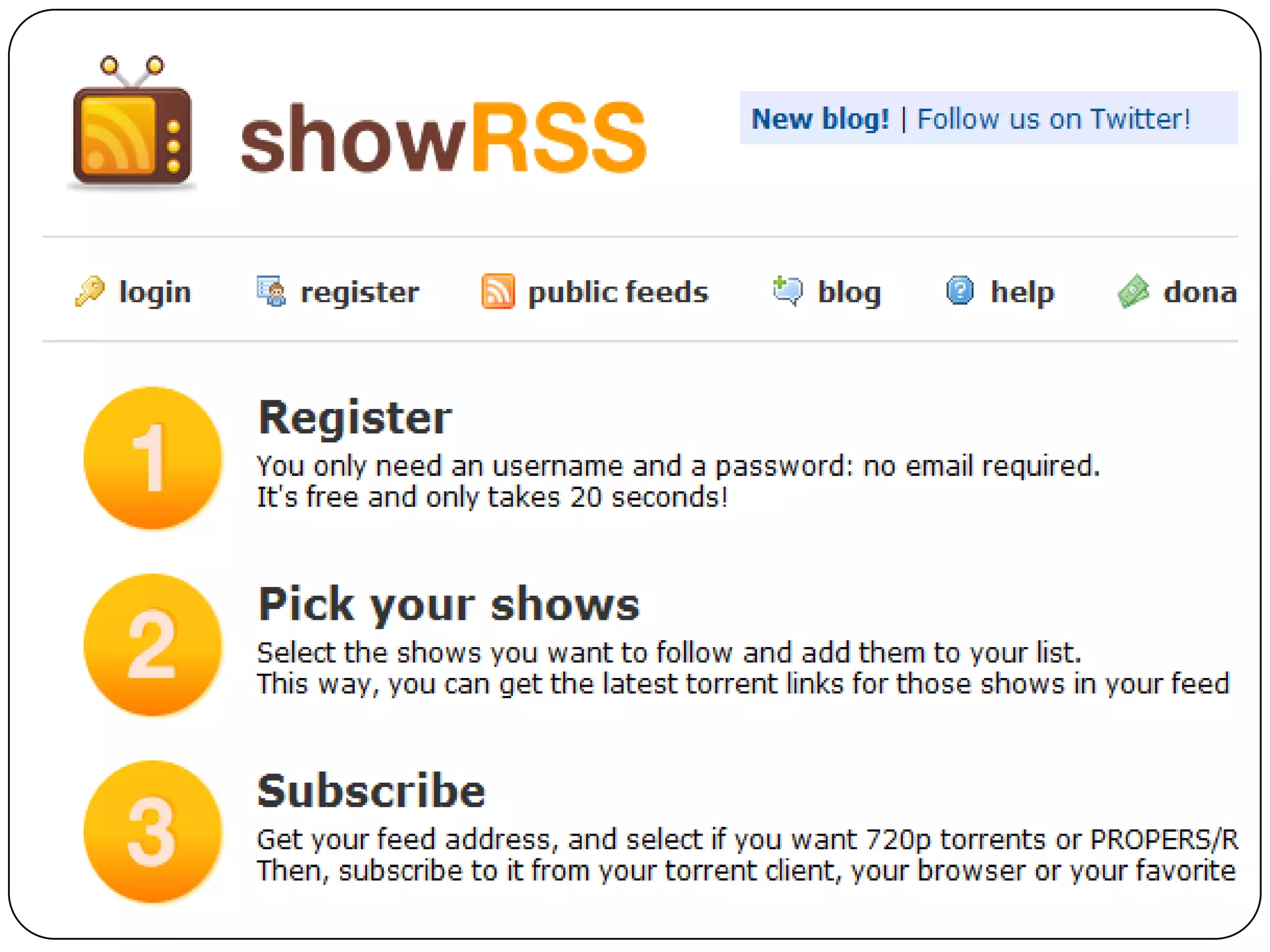
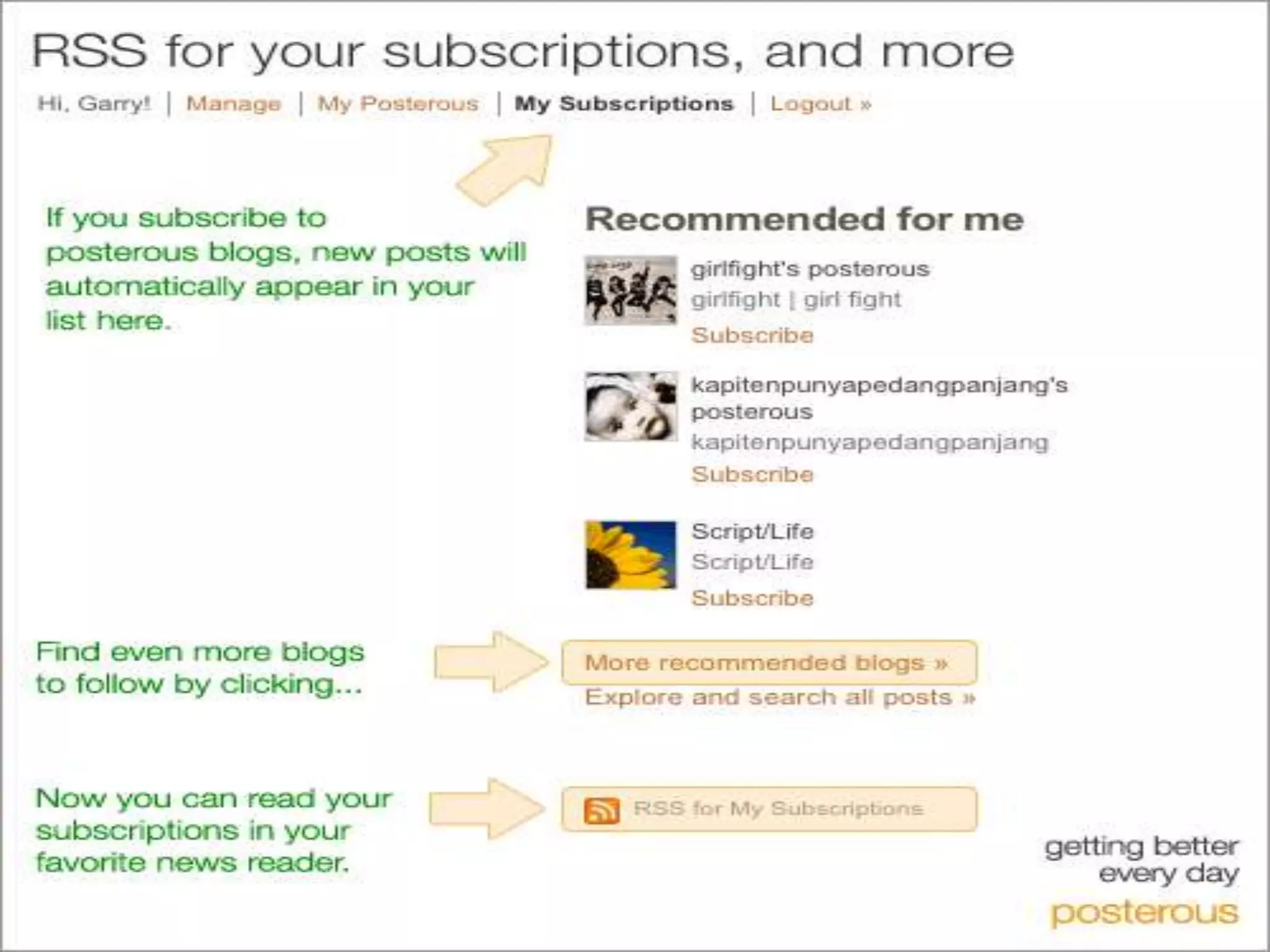
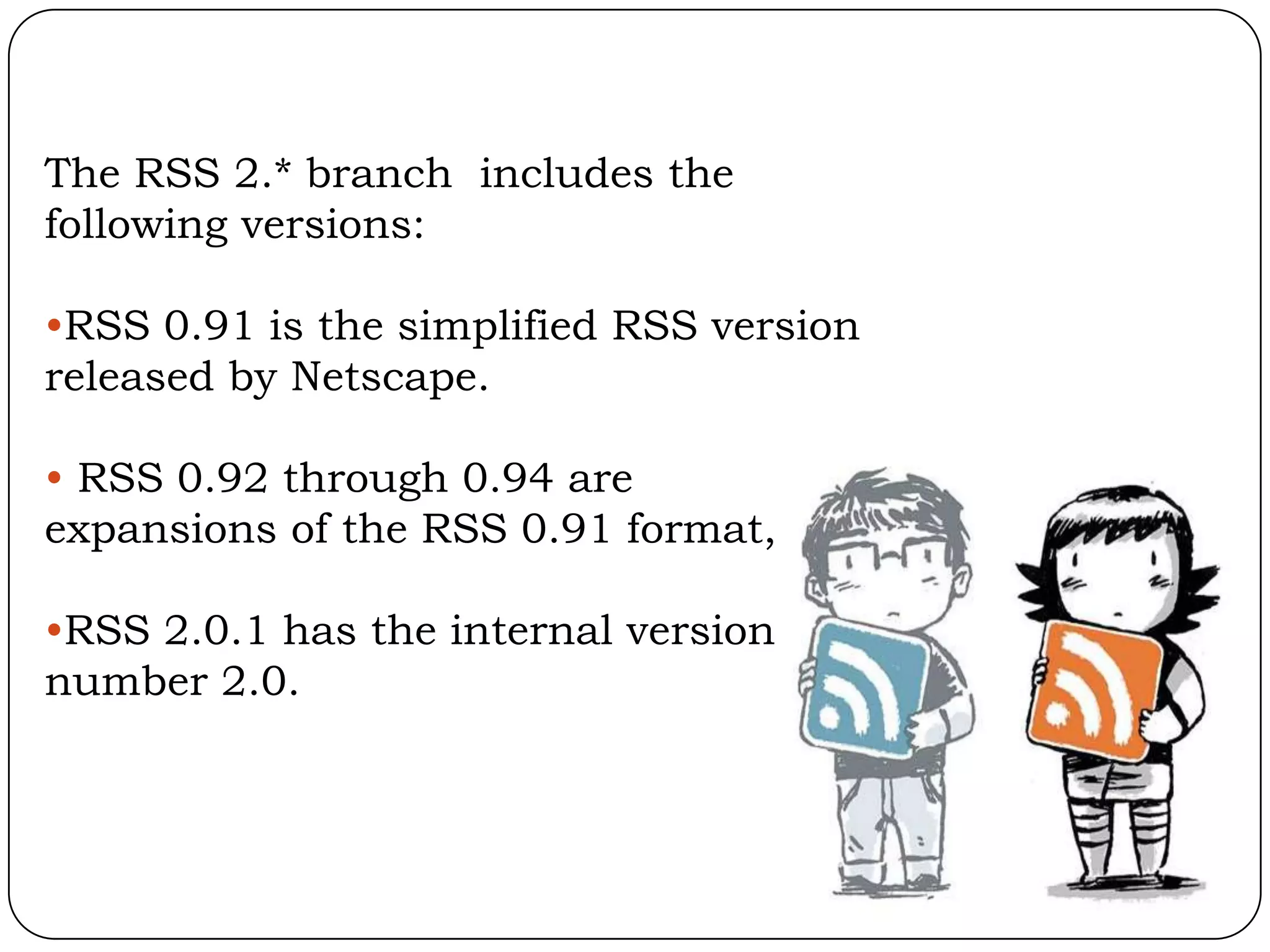
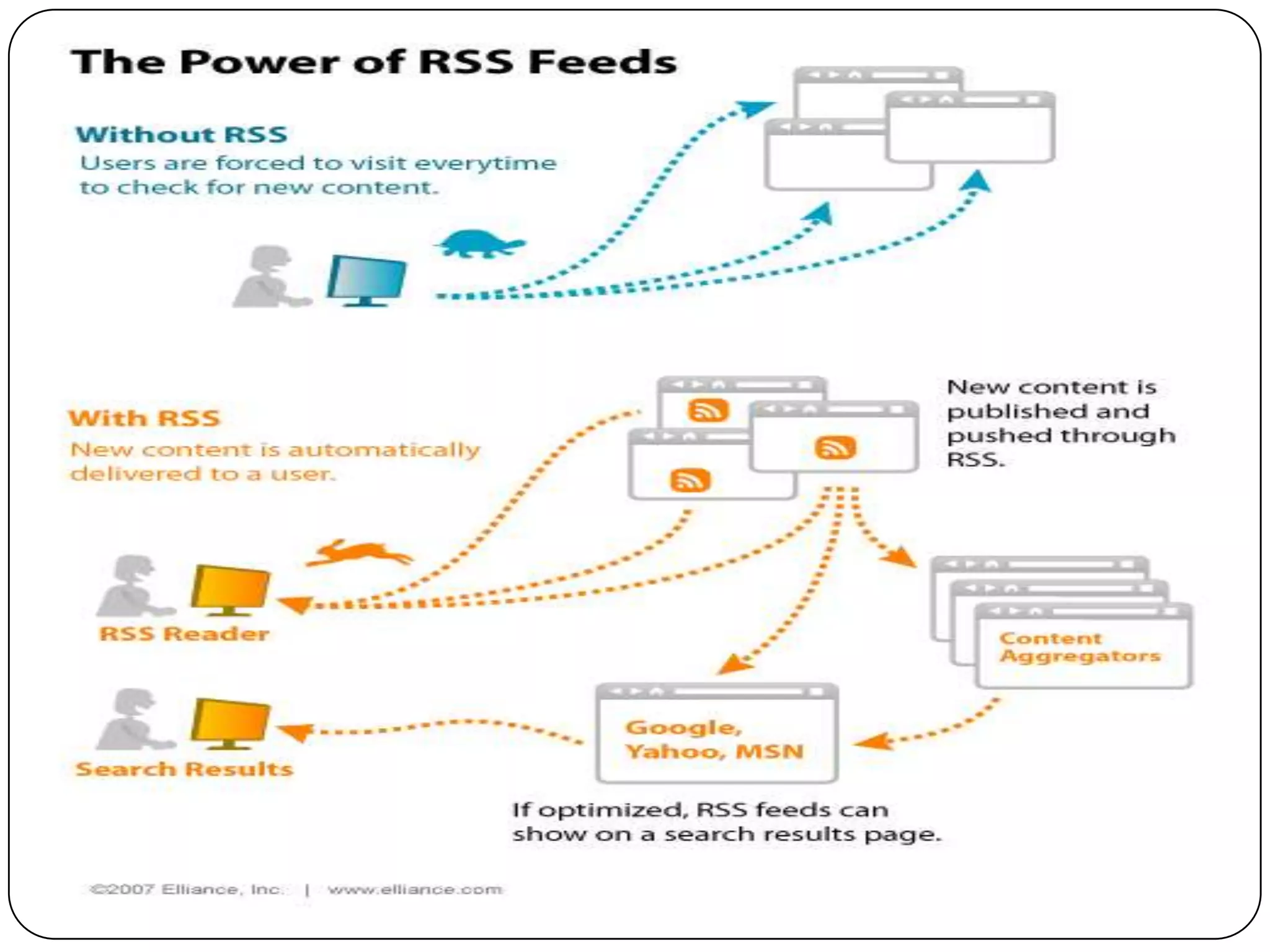
RSS (Really Simple Syndication) is an XML format that allows users to subscribe to frequently updated content such as blog posts or news headlines from websites. RSS feeds can be read using an RSS reader, which aggregates feeds from multiple sources into a single interface. Common uses of RSS include blogs, newsletters, calendars, and industry-specific content syndication.