The document is a recitation session focusing on application logging and object-relational mapping using tools like Log4j and Hibernate. It covers the definitions, importance, and tips for effective logging, as well as the challenges of object-relational impedance mismatch, and how Hibernate addresses these issues. Additionally, practical examples of Hibernate configuration and coding are included, along with several relevant references for further reading.


![BLG 411E
Software
Engineering
Recitation 4
Logging
Log4j
ORM
Hibernate
References
Application Logging
Logging Levels
OFF No logging
FATAL Only errors that cause the application to abort
ERROR Critical errors that prevent the use case from
continuing
WARN Other errors and exceptions where processes
may still continue, i.e. “Current data
unavailable, using cached values”
INFO Life cycle events, completion of use cases, i.e.
“[Who] booked ticket from [Where] to [Where]”
DEBUG All other (sub) events
TRACE All method invocations with parameter and
return values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rs4-141128072702-conversion-gate02/75/Software-Engineering-RS4-4-2048.jpg)
![BLG 411E
Software
Engineering
Recitation 4
Logging
Log4j
ORM
Hibernate
References
Application Logging
Tips
Apply logging levels appropriately
Avoid side effects (no impact on the application’s
behavior)
Log for easy reading and easy parsing
Include both data and description, no magic numbers
or characters (i.e. &&&)
Use a logging pattern (i.e. %d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}
%-5level [%thread][%logger{0}] %m%n)
Maximize logging for external systems
Maximize logging when in trouble, not otherwise
Avoid excessive string concatenation, use parametrized
logging methods
Do not log sensitive information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rs4-141128072702-conversion-gate02/75/Software-Engineering-RS4-5-2048.jpg)
![BLG 411E
Software
Engineering
Recitation 4
Logging
Log4j
ORM
Hibernate
References
Log4j
Introduction
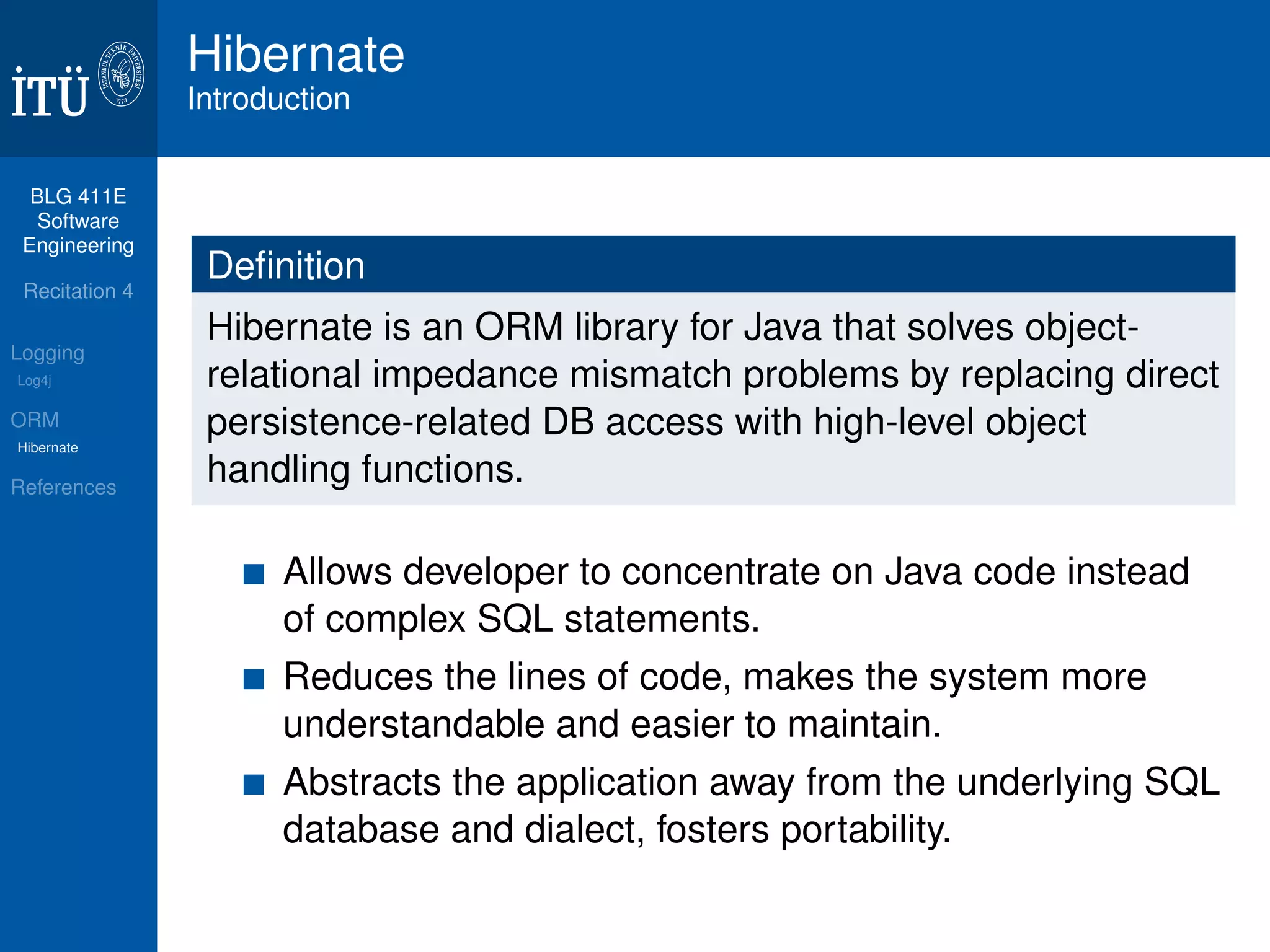
Definition
A Java-based logging utility which provides performance
improvements and advanced filtering.
import org . apache . logging . l o g 4 j . LogManager ;
import org . apache . logging . l o g 4 j . Logger ;
public class HelloWorld {
pr ivate s t a t i c f i n a l Logger l
= LogManager . getLogger ( " HelloWorld " ) ;
public s t a t i c void main ( St r i n g [ ] args ) {
l . i n f o ( " Hello , World ! " ) ;
l . e r r o r ( " Mission f a i l e d ! " ) ;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rs4-141128072702-conversion-gate02/75/Software-Engineering-RS4-6-2048.jpg)


![BLG 411E
Software
Engineering
Recitation 4
Logging
Log4j
ORM
Hibernate
References
Hibernate
Sample program code
import org . hibernate . ;
import org . hibernate . cfg . ;
public class Cl ientForSave {
public s t a t i c void main ( St r i n g [ ] args ) {
Conf igurat ion cfg = new Conf igurat ion ( ) ;
cfg . conf igure ( hibernate . cfg . xml ) ;
SessionFactory f a c t o r y = cfg . bui ldSessionFactory ( ) ;
Session session = f a c t o r y . openSession ( ) ;
Product p = new Product ( ) ;
p . setProduct Id ( 1 0 1 ) ;
p . setProName ( iPhone ) ;
p . setPr i ce (25000) ;
p . setDate (new Date ( ) ) ;
session . beginTransact ion ( ) ;
session . save ( p ) ;
session . getTransact ion ( ) . commit ( ) ;
session . close ( ) ;
f a c t o r y . close ( ) ;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rs4-141128072702-conversion-gate02/75/Software-Engineering-RS4-13-2048.jpg)

