This document provides an overview and introduction to the Internet of Things (IoT). It discusses how IoT is transforming business through improved customer experiences, growth, safety, and more sophisticated applications. Key points include:
- IoT connects physical assets through sensors and analytics to extract valuable data and insights.
- Adoption is growing rapidly across sectors like transportation, manufacturing, energy, and public.
- IoT provides benefits like optimized operations, new revenue streams, improved safety and risk management, and regulatory compliance.
- As technologies mature and costs decline, the potential for IoT to impact organizations and society is vast. The document urges organizations to develop an IoT strategy to harness these opportunities.



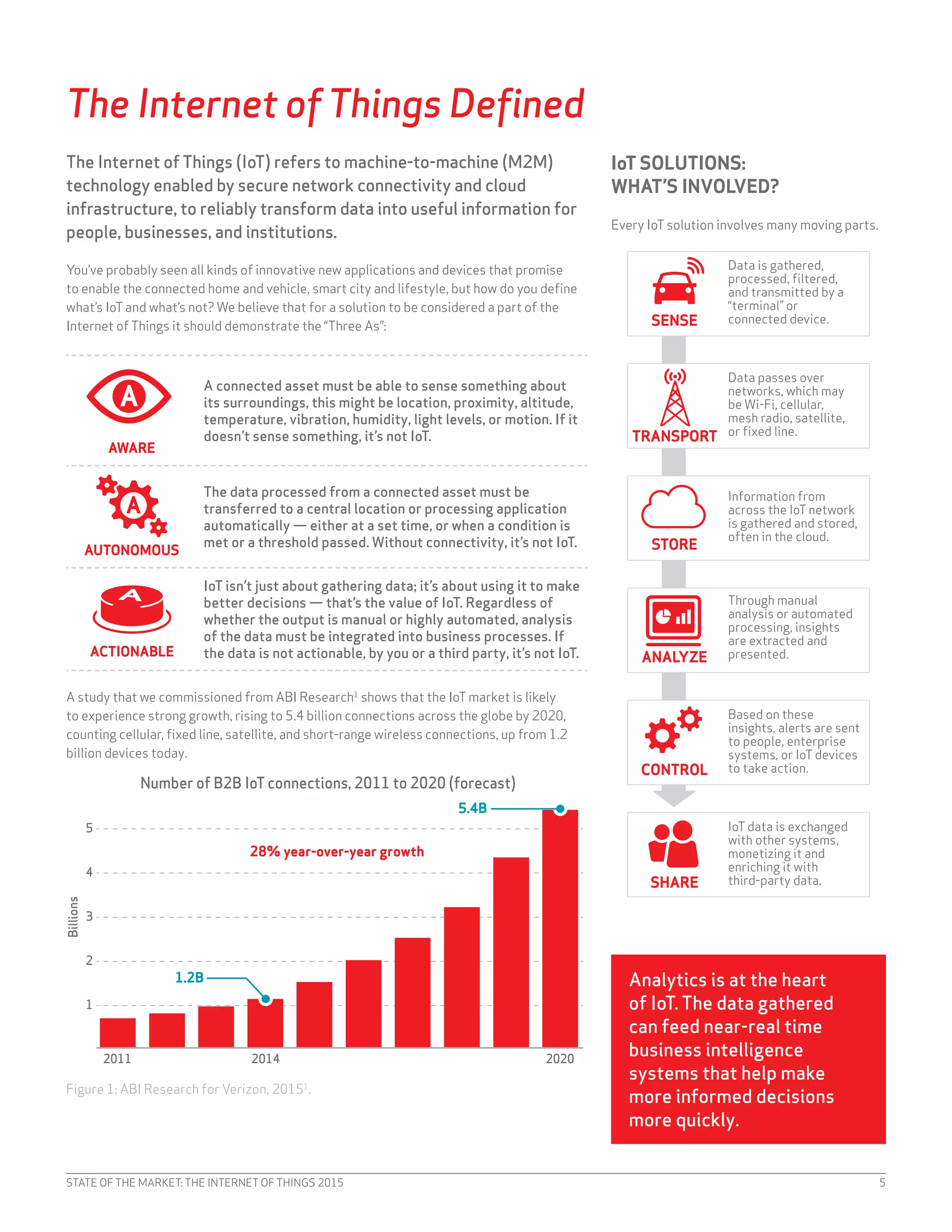















![STATE OF THE MARKET: THE INTERNET OF THINGS 2015 23
References
1. ABI Research, 2015
2. Verizon usage data, 2013–2014
3. CDC/National Center for Health Statistics, Accidents of Unintentional injuries, July 2014
4. ABI research, Corporate Wellness is a 13 Million Unit Wearable Wireless Device Opportunity, 2013
[https://www.abiresearch.com/press/corporate-wellness-is-a-13-million-unit-wearable-w]
5. Verizon pilot involving nearly 2,500 volunteers made up of Verizon employees and
their partners, 2014.
6. Navigant Research, Smart Electric Meters, Advanced Metering Infrastructure, and Meter
Communications: Global Market Analysis and Forecasts, November 2013
7. Navigant Research, The Installed Base of Smart Meters Will Surpass 1 Billion by
2022, November 2013
8. Accenture, Achieving high performance with theft analytics, 2011
9. US DoT, Pipeline Basics
10. Navigant Research, Shipments of Smart Thermostats Are Expected to Reach Nearly 20 Million by
2023, October 2014
11. Canalys, Wearable band shipments set to exceed 43.2 million units in 2015, 2014
12. Oxford Economics, Manufacturing Transformation: Achieving competitive advantage in a changing
global marketplace, 2014
13. Harvard Business Review Analytics Services, The Digital Dividend: First-Mover Advantage, 2014
14. Schindler, Schindler & Verizon are Redefining Reliability with Connected
Monitoring Solution, 2014
15. Illuminating Concepts/Intellistreets case study
16. WHO, Global Health Observatory, Urban Population Growth
17. United Nations, World urbanization prospects, 2014
18. University of California Transportation Center, Free Parking or Free Markets, 2011
19. M2M world news, Opportunities and challenges for the connected city, April 2014
20. Navigant Research Blog, Smart Street Lights Face Financial Hurdles, November 2012
21. UN Commission on Sustainable Development, May 2007
22. Texas A&M Transportation Institute, 2012 Urban Mobility Report, David Schrank et al, December
2012 [http://mobility.tamu.edu/ums/media-information/press-release]
23. Verizon, Envision Charlotte and Verizon
24. GE, Industrial Internet: Pushing the Boundaries of Minds and Machines, Peter C Evans and Marco
Annunziata, November 2012
25. Frost & Sullivan, Customer research from LCVTelematics Market, 2013
26. McKinsey, The road to 2020 and beyond: What’s driving the global automotive industry?, 2013
27. Internet of Things in Banking” Study, American Banker and SourceMedia Research for
Verizon, August 2014.
28. HP, Internet of Things Research Study, September 2014
29. Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Managed Machine-to-Machine Services, Eric Goodness et al,
October 2014, G00263526
30. Verizon connected car survey, 2014
Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications,
and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings
or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s
research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims
all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of
merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ae690f88-76a0-46b4-96d2-8b015ed0185a-150304144536-conversion-gate01/75/rp_state-of-market-the-market-the-internet-of-things-2015_en_xg-23-2048.jpg)
