Embed presentation
Download to read offline


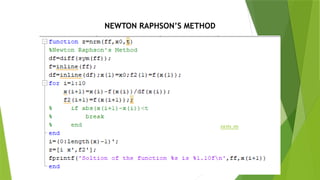
![clear;clc;
%ff='x^3-2*x-5';
%ff='cos(x)-x*exp(x)'
%ff='x*log10(x)-1.2'
ff='x^4-32'
a=2;b=3;
% Method of False Position or Regula False Method
f=inline(ff);k=1;i=1;x=[];
while i<10
c=a-(b-a)*f(a)/(f(b)-f(a));d=c;a1=a;b1=b;
if f(a)*f(c)<0
b=c;
else
a=c;
end
x=[x;i a1 f(a1) b1 f(b1) d f(d)];
i=i+1;
end
fprintf('%gt %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ftn',x')
fprintf('Approximate solution of %s = 0 is %1.5fn',ff,d)
FALSE POSITION METHOD
False Position Method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15-241116201025-8bf1671b/85/Root-Finding-Methods-in-Numerical-Analysis-3-320.jpg)






The document outlines numerical methods for finding roots of functions, specifically focusing on the method of false position and Newton-Raphson method. It includes MATLAB code snippets for implementing these algorithms and provides parameters for execution. The document concludes by referring to an attached function for the Newton-Raphson method.


![clear;clc;
%ff='x^3-2*x-5';
%ff='cos(x)-x*exp(x)'
%ff='x*log10(x)-1.2'
ff='x^4-32'
a=2;b=3;
% Method of False Position or Regula False Method
f=inline(ff);k=1;i=1;x=[];
while i<10
c=a-(b-a)*f(a)/(f(b)-f(a));d=c;a1=a;b1=b;
if f(a)*f(c)<0
b=c;
else
a=c;
end
x=[x;i a1 f(a1) b1 f(b1) d f(d)];
i=i+1;
end
fprintf('%gt %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ft %1.5ftn',x')
fprintf('Approximate solution of %s = 0 is %1.5fn',ff,d)
FALSE POSITION METHOD
False Position Method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15-241116201025-8bf1671b/85/Root-Finding-Methods-in-Numerical-Analysis-3-320.jpg)






