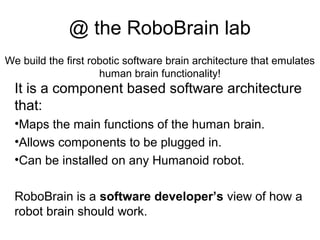
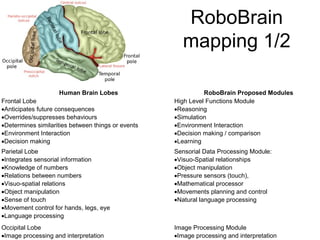
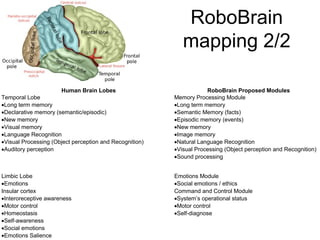
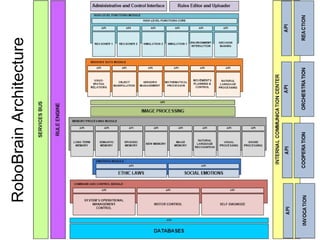
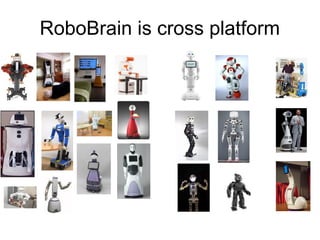
The document discusses Robobrain, a software architecture that mimics human brain functionalities to enable robots to operate autonomously in various environments. It outlines the proposed modules based on different brain lobes, focusing on components for decision making, memory processing, and sensory integration. The project aims to establish an open-source community for collaboration and is seeking funding and partners for further development.