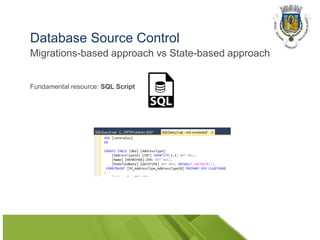
This document discusses database source control and automation. It introduces Flyway, an open source tool for database migrations. Flyway uses SQL scripts to represent database changes and tracks their execution in a metadata table. It scans script directories and applies migrations in order of their version numbers. The document demonstrates Flyway and discusses challenges like managing branches, script expiration, dependencies, and developer sandboxes when using a version control system for database scripts and Flyway.