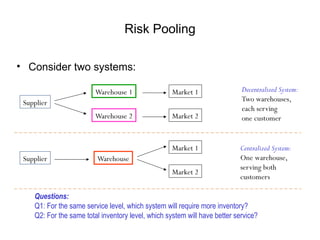
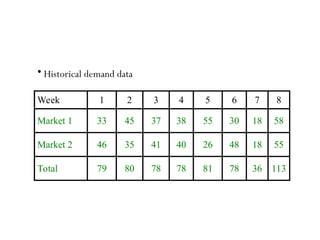
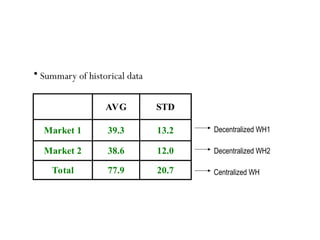
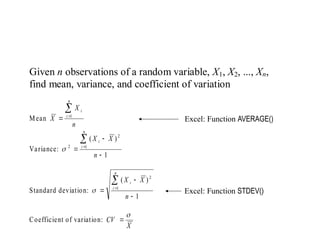
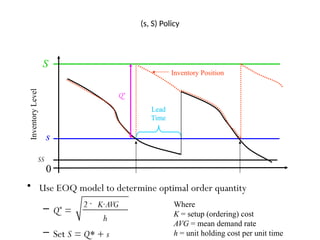
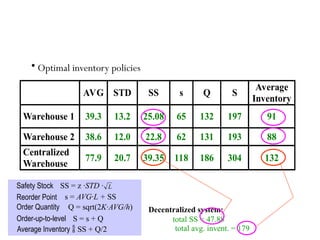
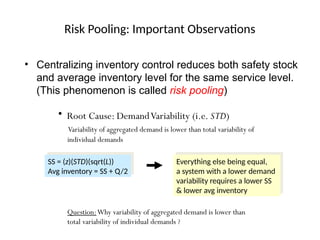
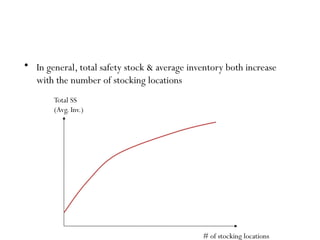
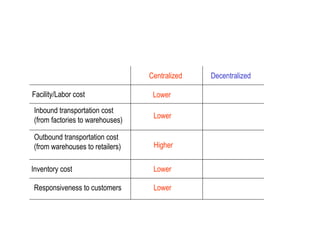
The document discusses risk pooling in inventory management, comparing decentralized and centralized systems in terms of service levels and inventory requirements. It highlights that centralizing inventory can reduce both safety stock and average inventory levels due to decreased demand variability. Key observations include that higher demand correlations between markets reduce the benefits of risk pooling, while a higher coefficient of variation increases these benefits.