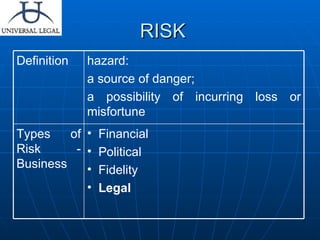
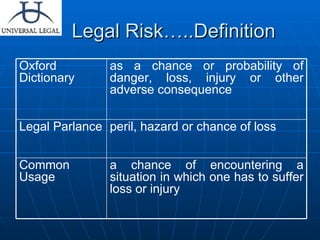
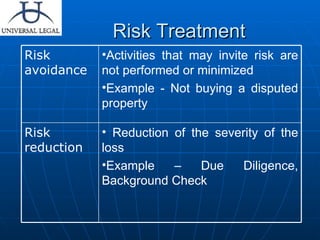
The document discusses various types of legal risks that companies may face and strategies to mitigate them. It outlines risks including contractual risks, product liability, employee liability, compliance defaults, taxes, intellectual property, and environmental issues. It emphasizes the importance of properly drafting contracts, conducting due diligence, buying insurance policies, and complying with applicable laws to minimize exposure to legal risks.


















































![THANK YOU ! Universal Legal, Advocates 5th Floor, Kimatrai Building, 77/79, Maharshi Karve Road, Mumbai – 400 002 Tel: +91 22 22034293-95 Fax: +91 22 2209845 Email: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/risk-12511815379093-phpapp01/85/Risk-54-320.jpg)