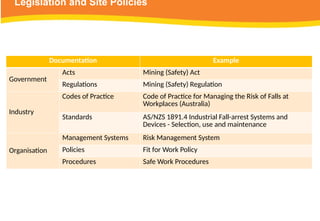
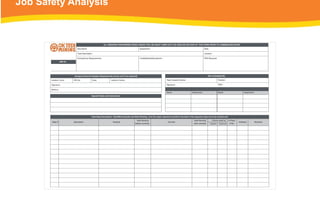
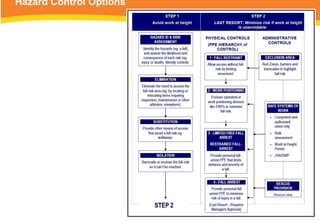
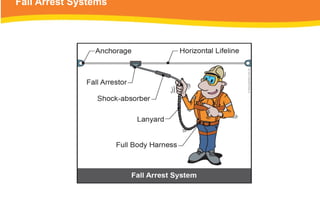
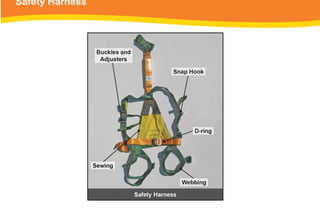
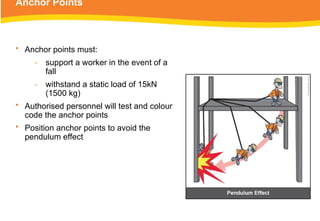
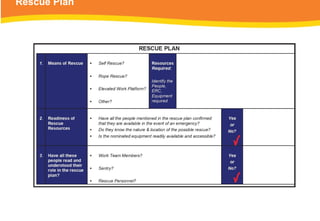
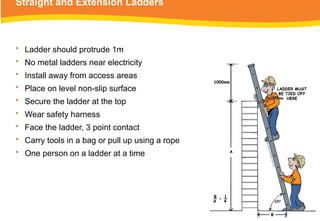
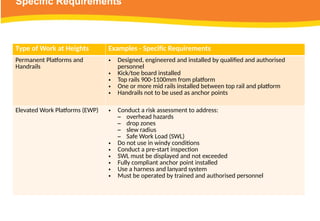
The document provides guidelines for safely working at heights, detailing planning, hazard identification, equipment selection, and safety measures. It emphasizes operator obligations, risk management, personal protective equipment, and specific procedures for various equipment types, including ladders and scaffolding. Additionally, it outlines post-operational tasks and promotes adherence to safety regulations to mitigate risks associated with working at heights.