The document discusses object-oriented design principles, particularly the SOLID principles, which are essential for building maintainable and scalable software. It provides examples of violations and refactorings for each principle, including Single Responsibility, Open/Closed, Liskov Substitution, Interface Segregation, and Dependency Inversion. The content emphasizes the importance of clean, understandable code and best practices in software development.







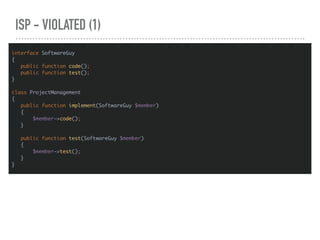
![SRP EXAMPLE - VIOLATED (1)
class SalesReport
{
private string $title;
private array $conditions;
private array $connectionParams;
public function __construct(string $title, array $conditions, array $connectionParams)
{
$this->title = $title;
$this->conditions = $conditions;
$this->connectionParams = $connectionParams;
}
public function getData()
{
return [
'title' => $this->getTitle(),
'generatedOn' => new DateTime(),
'date' => $this->loadReportData($this->conditions, $this->connectionParams),
];
}
// Cont…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-10-320.jpg)
![SRP EXAMPLE - VIOLATED (2)
public function getData()
{
return [
'title' => $this->getTitle(),
'generatedOn' => new DateTime(),
'date' => $this->loadReportData($this->conditions, $this->connectionParams),
];
}
public function getJsonData()
{
return json_encode($this->getData());
}
private function loadReportData(array $conditions, array $connectionParams) : array
{
// Create PDO Connection
// Query for Report Data based on conditions
// return Array result
}
// Getter/Setter and other functions
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-11-320.jpg)


![SRP EXAMPLE - REFACTORED (3)
class SalesReport implements Exportable
{
private string $title;
private array $conditions;
private DataRepository $repository;
public function __construct(string $title, array $conditions, DataRepository $repository)
{
$this->title = $title;
$this->conditions = $conditions;
$this->repository = $repository;
}
public function getData()
{
return [
'title' => $this->getTitle(),
'generatedOn' => new DateTime(),
'data' => $this->repository->findByCondition($this->conditions),
];
}
// Removed getJsonData() and loadReportData()
// Other relevant methods
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-14-320.jpg)
![SRP EXAMPLE - REFACTORED (4)
$dataSource = new SalesDataRepository($connectionParams);
$conditions = [
'from' => $startDate,
'to' => $endDate,
];
$salesReport = new SalesReport("Summary of January 2020", $conditions, $dataRepository);
$formatter = new JSONReportExporter();
$formatter->export($salesReport);
➤ Cleaner Code
➤ Easier to understand
➤ Easier to change code
➤ Code becomes reusable
➤ Easier to write test codes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-15-320.jpg)
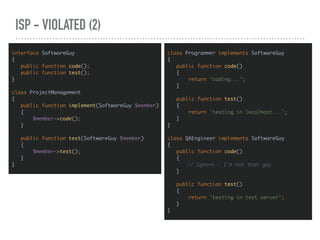
![SRP EXAMPLE - REFACTORED (4)
$dataSource = new SalesDataRepository($connectionParams);
$conditions = [
'from' => $startDate,
'to' => $endDate,
];
$salesReport = new SalesReport("Summary of January 2020", $conditions, $dataRepository);
$formatter = new JSONReportExporter();
$formatter->export($salesReport);
➤ Cleaner Code
➤ Easier to understand
➤ Easier to change code
➤ Code becomes reusable
➤ Easier to write test codes
➤ New features are easy to implement
class JSONReportExporter {
public function export(Exportable $report)
{
return json_encode($report->getData());
}
}
class CSVReportExporter {} { /** collapsed **/}
class XMLReportExporter {} { /** collapsed **/}
class PDFReportExporter {} { /** collapsed **/}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-16-320.jpg)


![OCP EXAMPLE - VIOLATED (1)
class AreaCalculator {
protected $shapes;
public function __construct($shapes = array())
{
$this->shapes = $shapes;
}
public function sum()
{
foreach($this->shapes as $shape) {
if($shape instanceof Square) {
$area[] = pow($shape->length, 2);
} else if($shape instanceof Rectangle) {
$area[] = $shape->width * $shape->height;
}
}
return array_sum($area);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-19-320.jpg)
![OCP EXAMPLE - VIOLATED (1)
class AreaCalculator {
protected $shapes;
public function __construct($shapes = array())
{
$this->shapes = $shapes;
}
public function sum()
{
foreach($this->shapes as $shape) {
if($shape instanceof Square) {
$area[] = pow($shape->length, 2);
} else if($shape instanceof Rectangle) {
$area[] = $shape->width * $shape->height;
}
}
return array_sum($area);
}
}
$shapes = array(
new Square(5),
new Square(2),
new Rectangle(6, 5)
);
$calc = new AreaCalculator($shapes);
echo $calc->sum();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-20-320.jpg)
![OCP EXAMPLE - REFACTORED (1)
interface Shape {
public function area();
}
class AreaCalculator {
protected $shapes;
public function __construct($shapes = array())
{
$this->shapes = $shapes;
}
public function sum()
{
foreach($this->shapes as $shape) {
$area[] = $shape->area();
}
return array_sum($area);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-21-320.jpg)


![OCP EXAMPLE - REFACTORED (1)
interface Shape {
public function area();
}
class AreaCalculator {
protected $shapes;
public function __construct($shapes = array()) {
$this->shapes = $shapes;
}
public function sum() {
foreach($this->shapes as $shape) {
$area[] = $shape->area();
}
return array_sum($area);
}
}
$shapes = array(
new Square(5),
new Square(2),
new Rectangle(6, 5),
new Circle(7),
);
$calc = new AreaCalculator($shapes);
echo $calc->sum();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-24-320.jpg)


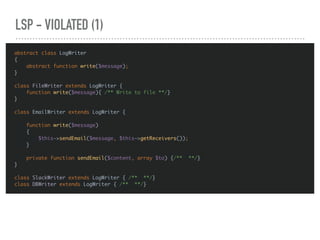
![LSP - VIOLATED (2)
class Logger {
private $writers;
public function addWriter(LogWriter $writer)
{
$this->writers[] = $writer;
}
public function log($message)
{
foreach ($this->writers as $logWriter) {
$logWriter->write($message);
}
}
}
$logger = new Logger();
$logger->addWriter(new FileWriter());
$logger->addWriter(new DBWriter());
$logger->addWriter(new EmailWriter());
$logger->log("We are at Eskimi Tech Adda!");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/solid-210807074603/85/Revisiting-SOLID-Principles-28-320.jpg)