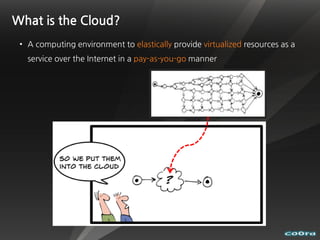
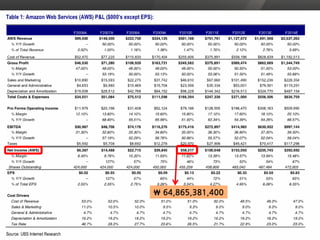
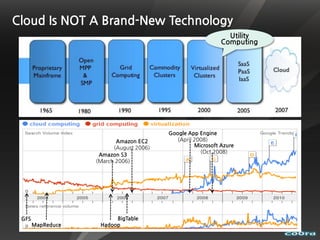
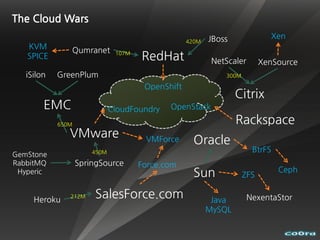
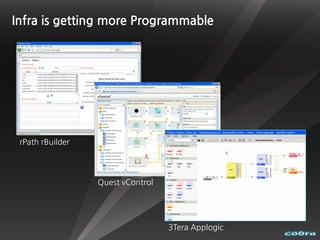
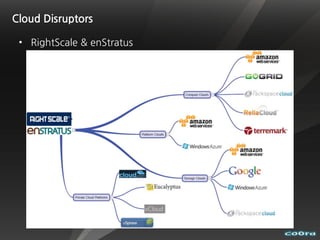
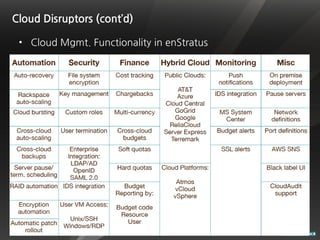
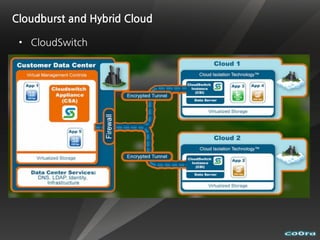
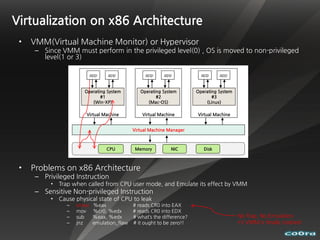
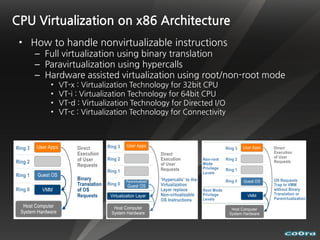
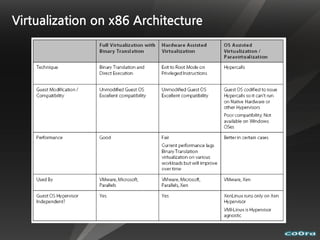
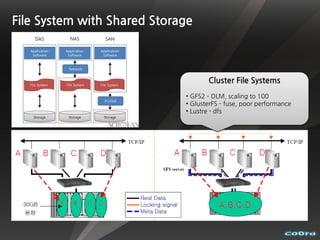
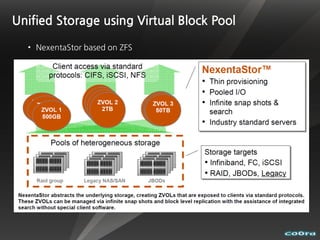
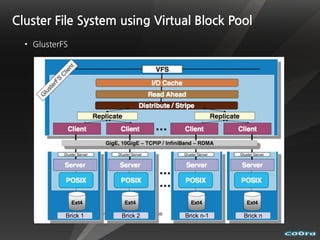
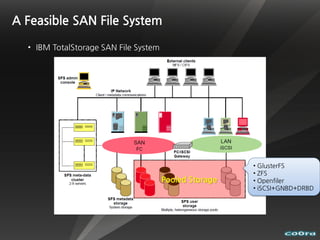
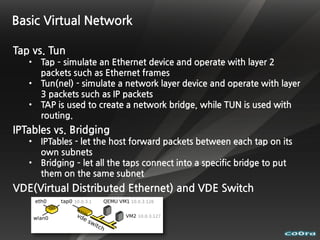
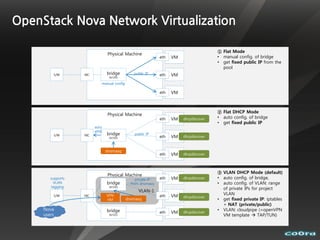
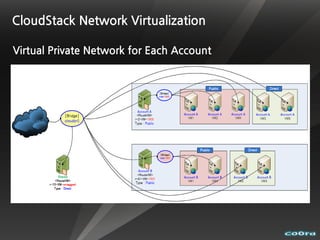
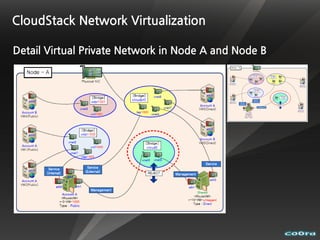
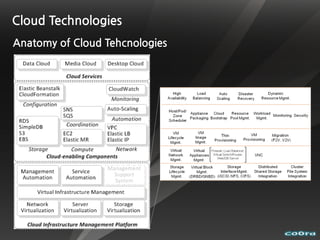
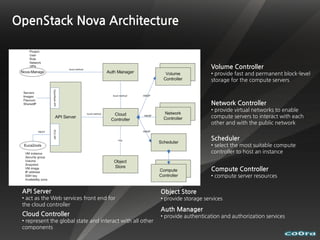
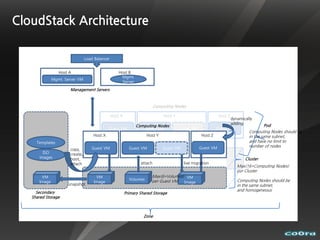
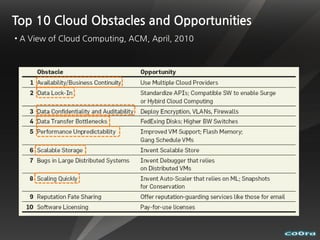
The document discusses cloud computing and virtualization technologies. It provides examples of how companies have used Amazon Web Services to save costs and scale efficiently. It also outlines challenges with cloud computing including outages and the need for high service level agreements from providers. The cloud is described as building on older technologies like grid computing and utility computing. Virtualization, storage, networking, and platform technologies that enable the cloud are also summarized.