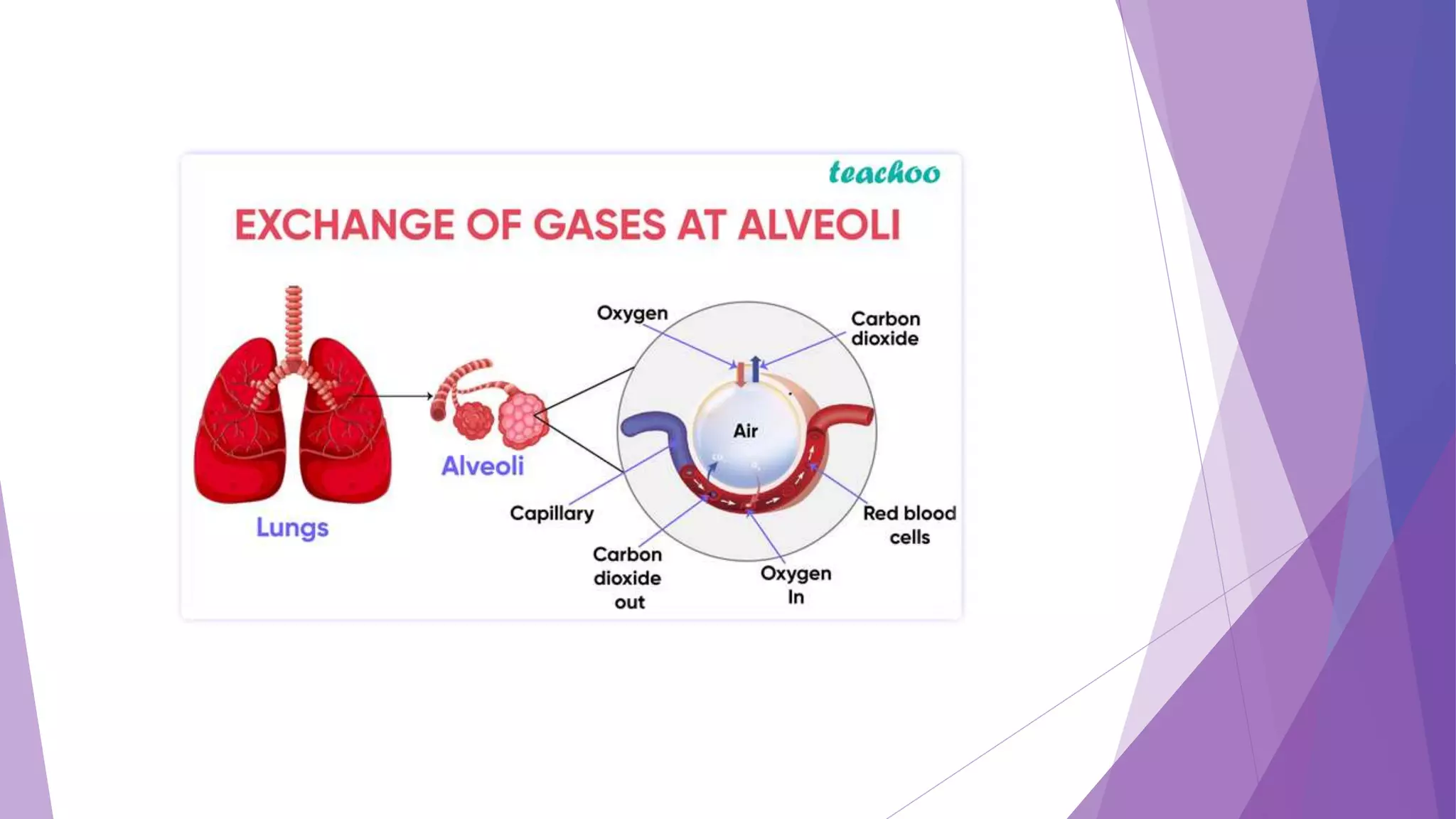
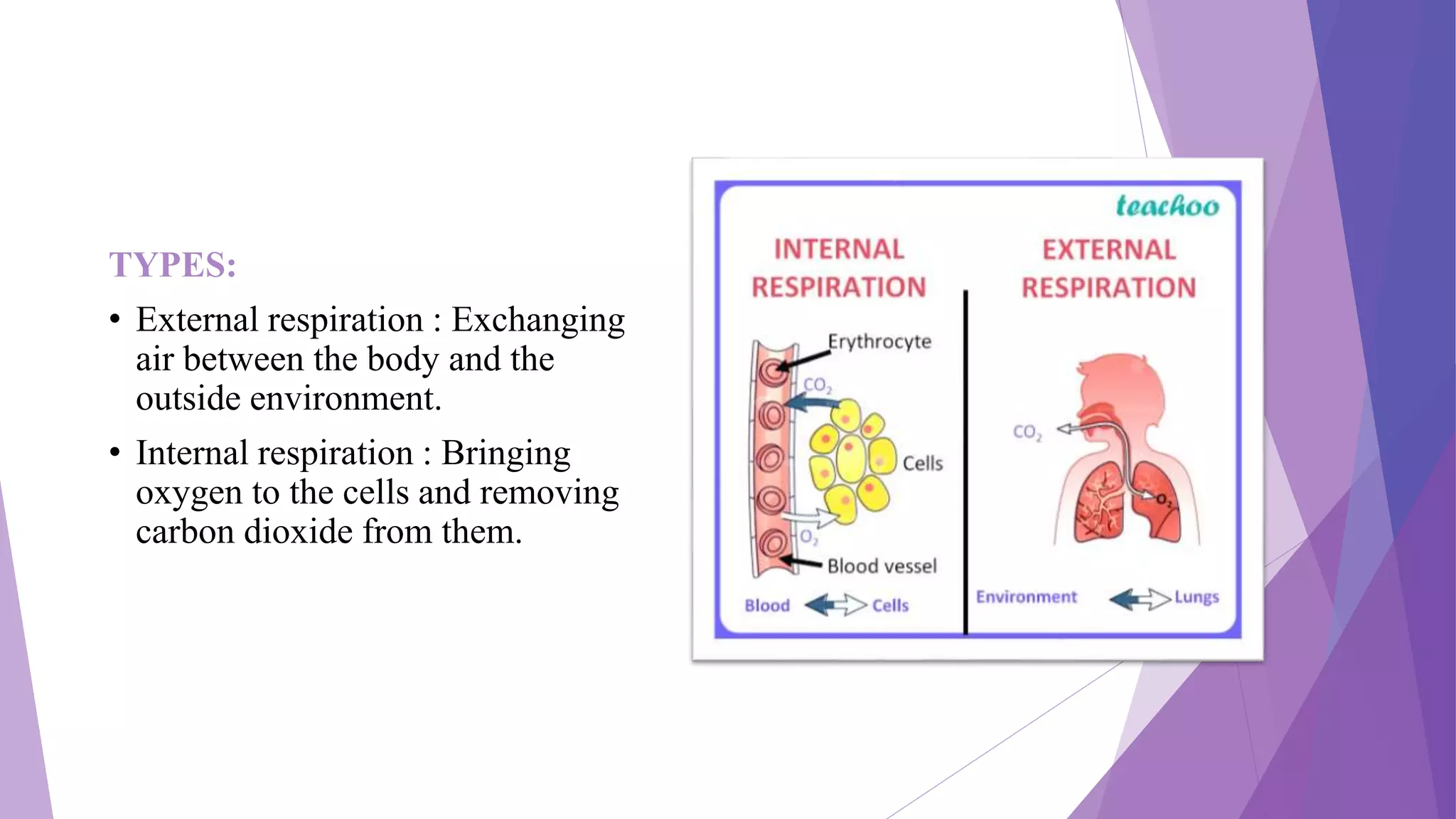
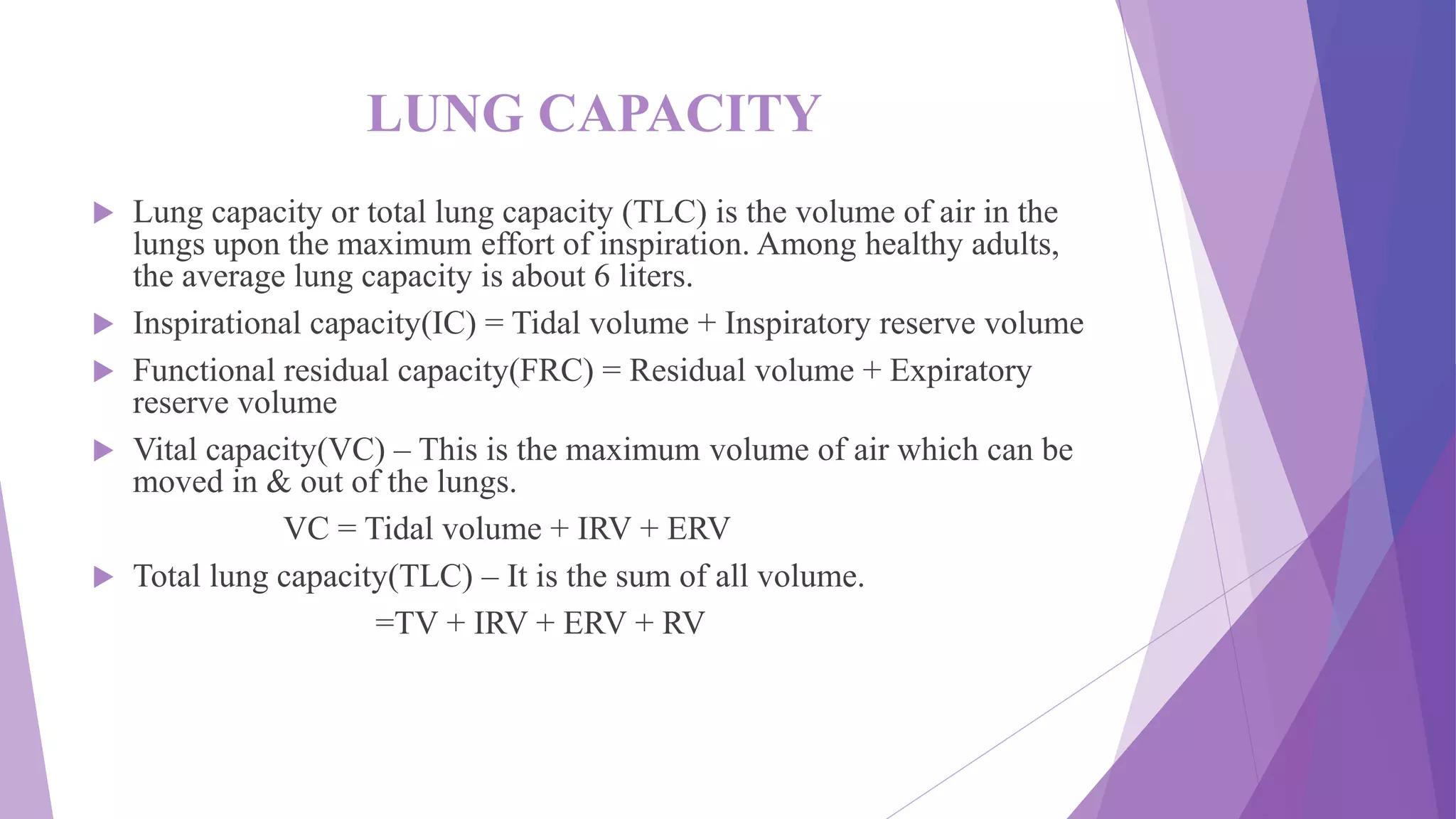
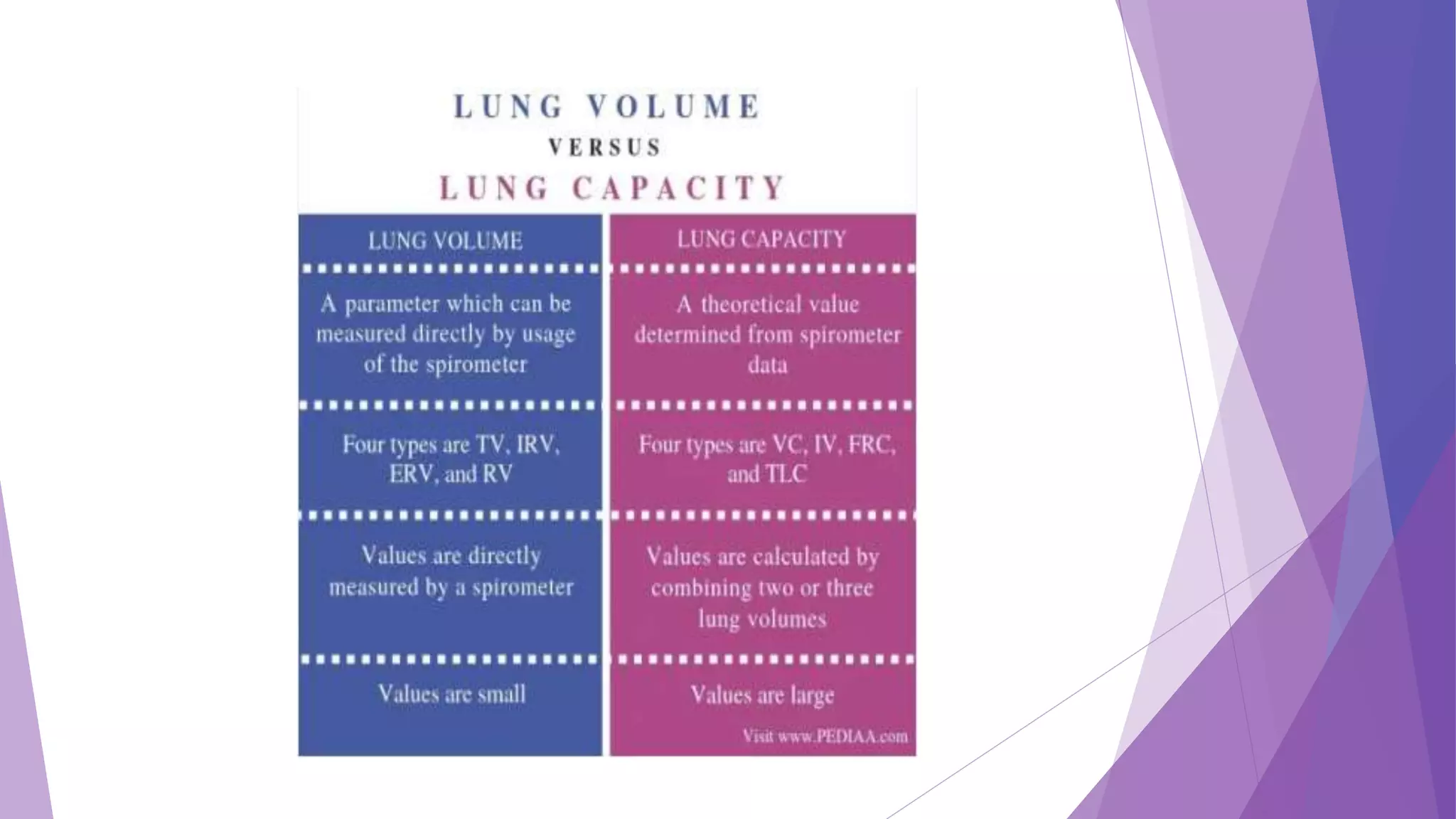
This document discusses the process of respiration and gas exchange in the human body. It describes how oxygen passes from the lungs into the bloodstream in the alveoli, and carbon dioxide passes out of the bloodstream and into the lungs to be exhaled. It defines external respiration as the exchange of gases between the lungs and environment, and internal respiration as the transport of oxygen to cells and removal of carbon dioxide. Key lung volumes and capacities such as tidal volume, vital capacity, and total lung capacity are also outlined.